Reverse Geocoding¶
In this guide you will learn how to use SearchService
to perform a reverse geocoding search to find the positions of
points of interest (POIs) near a programmatically or interactively/visually
specified position on the map.
See the Search Example guide on how to perform an assisted address search.
See the Text Search guide on how to search for anything on the map with a free-form text query.
Get the Coordinates of a Point¶
First, get an API key token, see the Getting Started guide.
Qt should be installed to continue.The Maps SDK for Qt should be installed, see the Setup Maps SDK for Qt guide.
Overview¶
ReverseGeocoding demonstrates how to use SearchService
to perform reverse geocoding. This example presents an application window
displaying a list on the left and a map on the right.
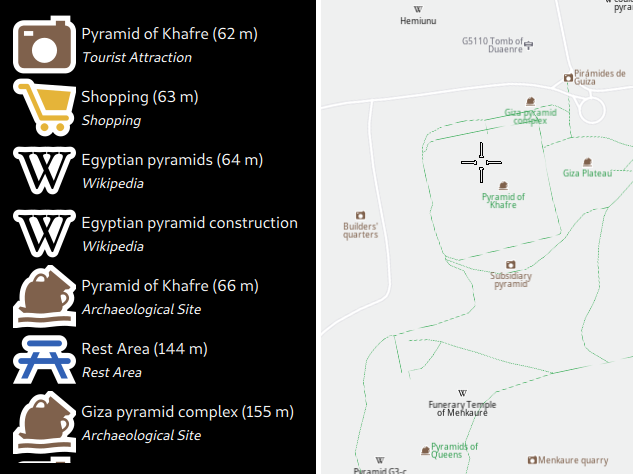
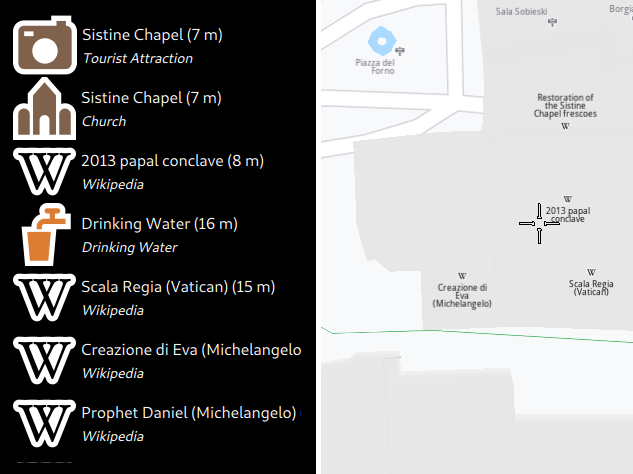
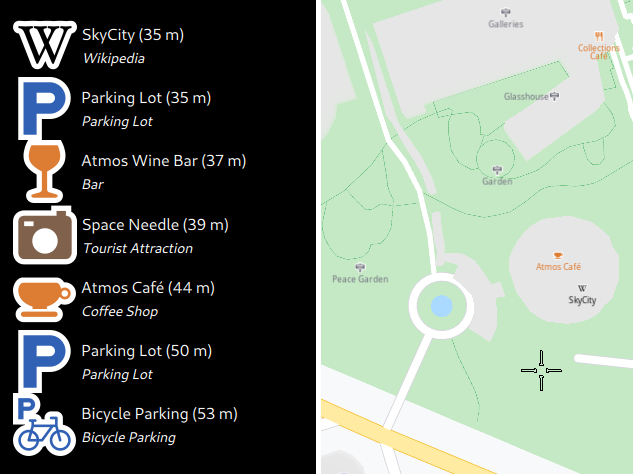
Clicking on the map will trigger a reverse geocoding search on that spot and the results will be displayed in the list on the left.
How it works
In Qt, go to the File menu and select Open File or Project…
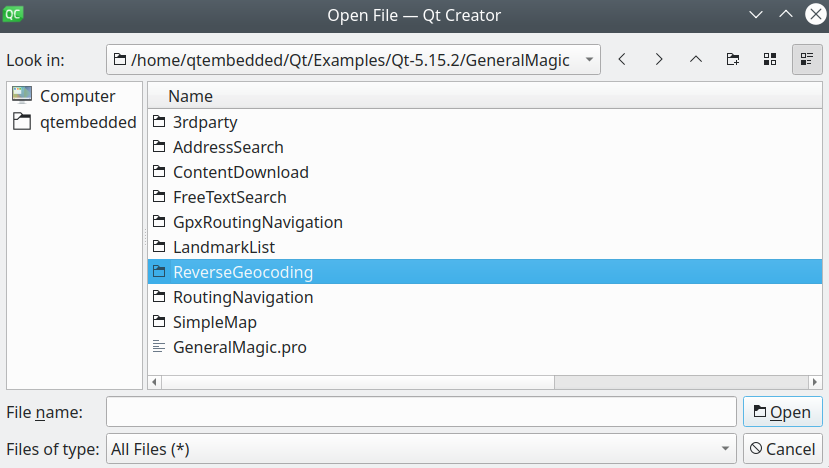
then browse to the ReverseGeocoding example folder and open ReverseGeocoding.pro
You may want to have a look at Setting your API Key to see how to open and configure a project and set your API Key.
In main.qml, we import the GeneralMagic QML plugin. Next, we need to make sure we allow online access, and that we are using the latest data.
1import QtQuick.Window 2.12
2import GeneralMagic 2.0
3
4Window
5{
6 visible: true
7 width: 640
8 height: 480
9 title: qsTr("Reverse Geocoding Example")
10 Component.onCompleted:
11 {
12 ServicesManager.settings.token = __my_secret_token;
13
14 ServicesManager.settings.allowInternetConnection = true;
15
16 var updater = ServicesManager.contentUpdater(ContentItem.Type.RoadMap);
17 updater.autoApplyWhenReady = true;
18 updater.update();
19 }
The __my_secret_token property in the above QML code is set in C++ like this.
1// C++ code
2QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
3//...
4//! [Set API Key token safely]
5// go to https://developer.magiclane.com to get your token
6engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("__my_secret_token", "YOUR_TOKEN");
7//! [Set API Key token safely]
8
9engine.load(url);
In this example, in main.cpp, replace YOUR_TOKEN with your actual Magic Lane Maps API Key.
We need to declare a SearchService model to perform
the reverse geocoding search.
1SearchService
2{
3 id: reverseGeocoding
4 preferences
5 {
6 searchMapPOIs: true
7 searchAddresses: true
8 limit: 10
9 thresholdDistance: 500
10 }
11}
On the left we have a ListView where we show
the results of the reverse geocoding search.
1ListView
2{
3 id: searchList
4 anchors.fill: parent
5 anchors.margins: 15
6 clip: true
7 model: reverseGeocoding
8 function distance(meters)
9 {
10 return meters >= 1000 ? (meters / 1000.).toFixed(3)
11 + " Km" : meters.toFixed(0) + " m";
12 }
13 delegate: Item
14 {
15 height: row.height
16 RowLayout
17 {
18 id: row
19 IconView
20 {
21 iconSource: landmark.icon
22 Layout.maximumHeight: row.height
23 Layout.maximumWidth: row.height
24 width: height
25 height: row.height
26 }
27 ColumnLayout
28 {
29 Layout.fillHeight: true
30 Layout.fillWidth: true
31 Text
32 {
33 Layout.fillWidth: true
34 text: landmark.name + " (" + searchList.distance(
35 landmark.coordinates.distance(reverseGeocoding.coordinates)) + ")"
36 color: "white"
37 font.pixelSize: 16
38 wrapMode: Text.WrapAnywhere
39 }
40 Text
41 {
42 Layout.fillWidth: true
43 text: landmark.description
44 color: "white"
45 font.pixelSize: 14
46 font.italic: true
47 wrapMode: Text.WrapAnywhere
48 }
49 }
50 }
51 }
52}
On the right we have a simple map, and when we click on it
we are using SearchService::reverseGeocode
1MapView
2{
3 id: mapView
4 Layout.fillWidth: true
5 Layout.fillHeight: true
6 gesturesEnabled: true
7 onCursorPositionChanged: reverseGeocoding.reverseGeocode(
8 mapView.cursorWgsPosition());
9}

