Range Finder¶
In this guide, you will learn how to implement route range calculation from a Point of Interest (POI) using the gem_kit package. This example demonstrates how to display a map, tap on a landmark, and calculate route ranges based on different transport modes and preferences.
|
|||
Setup¶
Prerequisites¶
Build and Run¶
Start a terminal/command prompt and navigate to the route_ranges directory within the Flutter examples directory. This is the name of the example project.
Note - the gem_kit directory containing the Maps SDK for Flutter
should be in the plugins directory of the example, e.g.
example_pathname/plugins/gem_kit - see the environment setup guide above.
Run: flutter pub get
Configure the native parts:
First, verify that the ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable
is set to the root path of your android SDK.
In android/build.gradle add the maven block as shown,
within the allprojects block, for both debug and release builds:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {
url "${rootDir}/../plugins/gem_kit/android/build"
}
}
}
in android/app/build.gradle
within the android block, in the defaultConfig block,
the android SDK version minSdk must be set as shown below.
Additionally, for release builds, in android/app/build.gradle,
within the android block, add the buildTypes block as shown:
Replace example_pathname with the actual project pathname
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.magiclane.gem_kit.examples.example_pathname"
minSdk 21
targetSdk flutter.targetSdk
versionCode flutterVersionCode.toInteger()
versionName flutterVersionName
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
shrinkResources false
// TODO: Add your own signing config for the release build.
// Signing with the debug keys for now, so `flutter run --release` works.
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
}
}
}
Then run the project:
flutter run --debugorflutter run --release
Import Necessary Packages¶
First, import the required packages in your Dart code.
import 'package:gem_kit/core.dart';
import 'package:gem_kit/map.dart';
import 'ranges_panel.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
App entry and initialization¶
const projectApiToken = String.fromEnvironment('GEM_TOKEN');
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
This code initializes the projectApiToken with the required authorization token and launches the app.
How it Works¶
This example demonstrates the following features:
Allow users to interact with a map by tapping landmarks to focus on specific Points of Interest (POIs).
Perform route range calculations from selected POIs using preferences such as transport mode.
|
|||
Build the Main Application¶
Define the main application widget, MyApp.
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Range Finder',
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
Handle Maps and Routes in the Stateful Widget¶
|
|
Create the stateful widget, MyHomePage, which will handle the map and routing functionality.
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
Define State Variables and Methods¶
Within _MyHomePageState, define the necessary state variables and methods to interact with the map and manage routes.
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
late GemMapController _mapController;
Landmark? _focusedLandmark;
@override
void dispose() {
GemKit.release();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
toolbarHeight: 50,
backgroundColor: Colors.deepPurple[900],
title: const Text('Range Finder', style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white)),
),
body: Stack(
children: [
GemMap(
onMapCreated: _onMapCreated,
),
if (_focusedLandmark != null)
Align(
alignment: Alignment.bottomCenter,
child: RangesPanel(
onCancelTap: _onCancelLandmarkPanelTap,
landmark: _focusedLandmark!,
mapController: _mapController,
))
],
),
);
}
void _onMapCreated(GemMapController controller) {
_mapController = controller;
_registerLandmarkTapCallback();
}
void _registerLandmarkTapCallback() {
_mapController.registerTouchCallback((pos) async {
_mapController.setCursorScreenPosition(pos);
final landmarks = _mapController.cursorSelectionLandmarks();
if (landmarks.isEmpty) {
return;
}
_mapController.activateHighlight(landmarks);
final lmk = landmarks[0];
setState(() {
_focusedLandmark = lmk;
});
_mapController.centerOnCoordinates(lmk.coordinates);
});
}
void _onCancelLandmarkPanelTap() {
_mapController.deactivateAllHighlights();
_mapController.preferences.routes.clear();
setState(() {
_focusedLandmark = null;
});
}
}
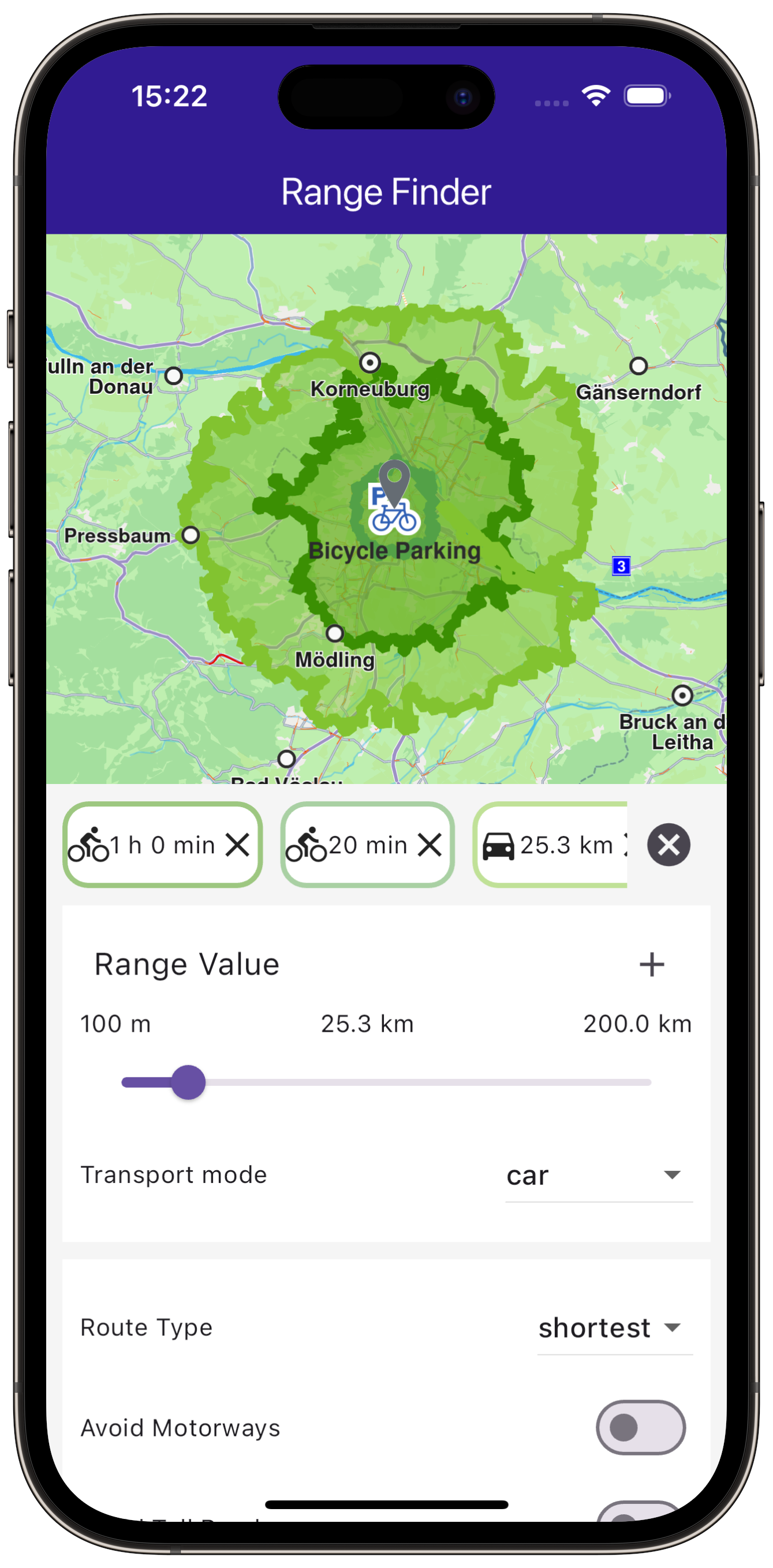
Range Calculation and Preferences¶
The RangesPanel widget handles the UI and logic for calculating and displaying route ranges. Here are the critical parts:
Define State Variables¶
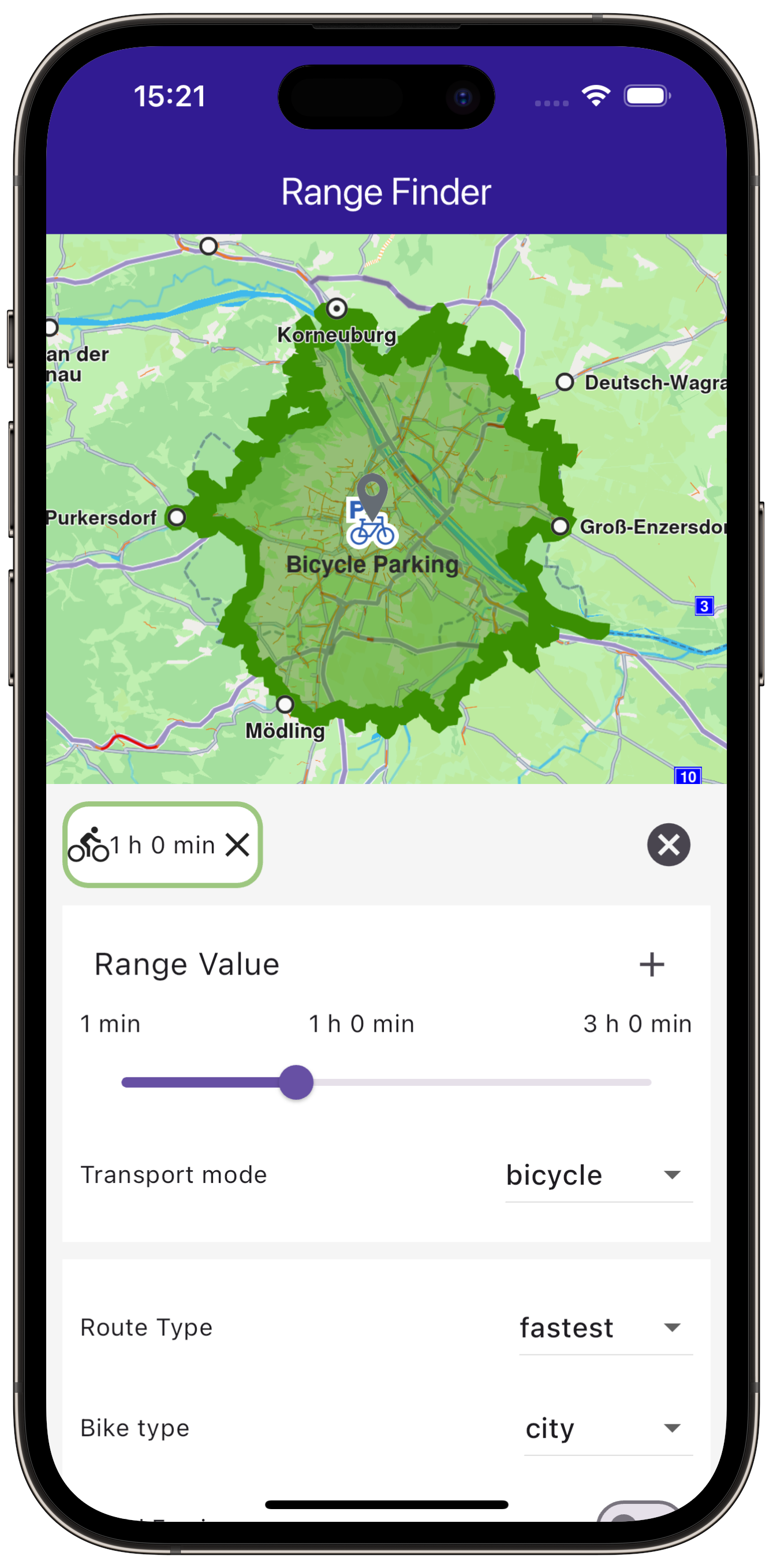
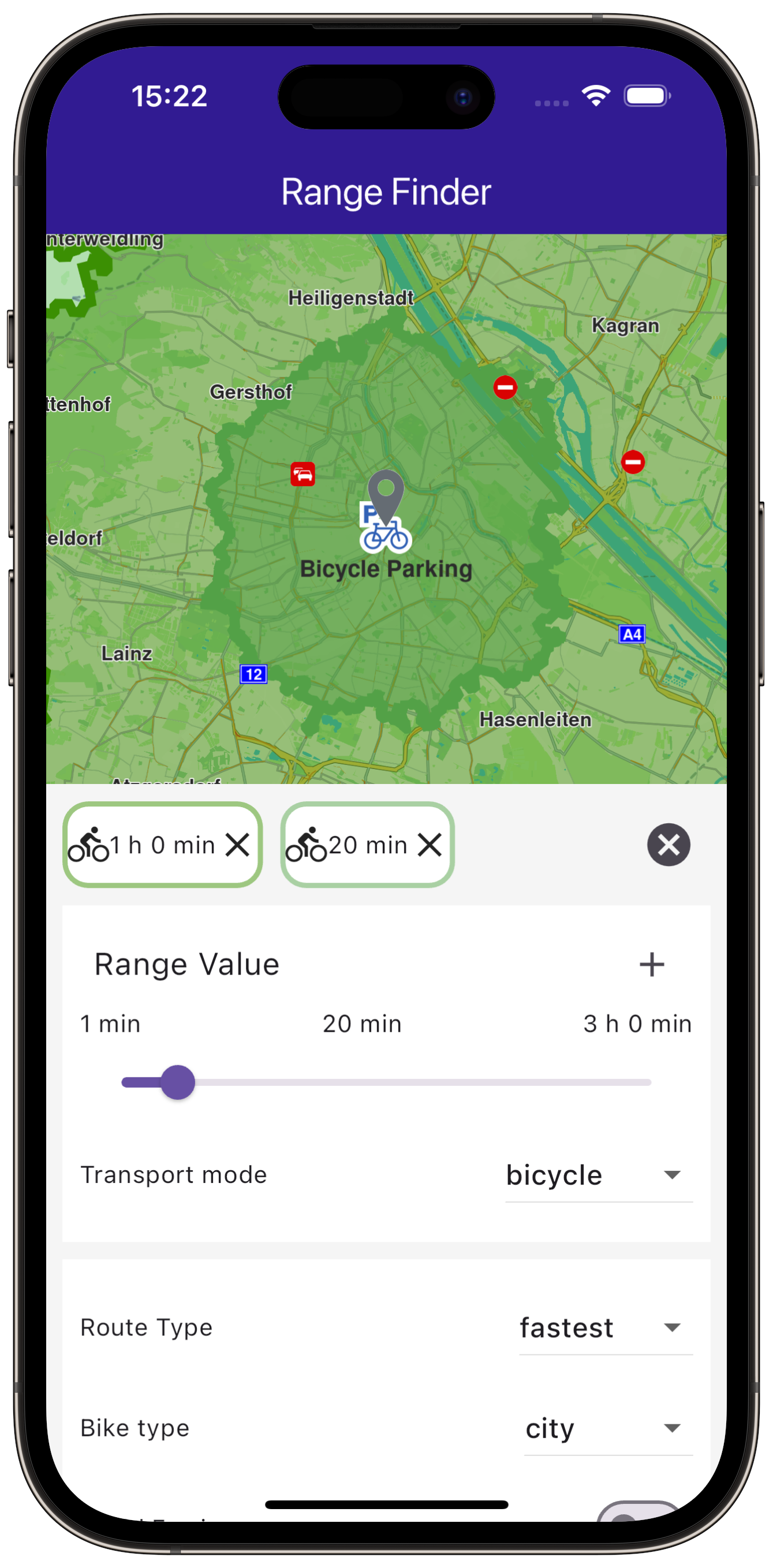
Define state variables to hold user preferences and the calculated route ranges.
class _RangesPanelState extends State<RangesPanel> {
int _rangeValue = 3600;
RouteTransportMode _transportMode = RouteTransportMode.car;
RouteType _routeType = RouteType.fastest;
bool _avoidMotorways = false;
bool _avoidTollRoads = false;
bool _avoidFerries = false;
bool _avoidUnpavedRoads = false;
BikeProfile _bikeProfile = BikeProfile.city;
double _hillsValue = 0;
TrafficAvoidance _trafficAvoidance = TrafficAvoidance.roadblocks;
List<Range> routeRanges = [];
Calculate Route Ranges¶
Use the RoutingService to calculate route ranges based on user preferences.
void _onAddRouteRangeButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
if (!_doesRouteRangeExist()) {
_showSnackBar(context, message: "The route is being calculated.");
RoutingService.calculateRoute([widget.landmark], _getRoutePreferences(),
(err, routes) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).clearSnackBars();
if (err == GemError.success) {
final routesMap = widget.mapController.preferences.routes;
final randomColor = Color.fromARGB(128, Random().nextInt(200),
Random().nextInt(200), Random().nextInt(200));
RouteRenderSettings settings =
RouteRenderSettings(fillColor: randomColor);
routesMap.add(routes!.first, true, routeRenderSettings: settings);
_centerOnRouteRange(routes.first);
setState(() {
_addNewRouteRange(routes.first, randomColor);
});
}
});
setState(() {});
}
}
Define Route Preferences¶
Create a method to build route preferences based on user inputs.
RoutePreferences _getRoutePreferences() {
switch (_transportMode) {
case RouteTransportMode.car:
return RoutePreferences(
avoidMotorways: _avoidMotorways,
avoidTollRoads: _avoidTollRoads,
avoidFerries: _avoidFerries,
avoidUnpavedRoads: _avoidUnpavedRoads,
transportMode: _transportMode,
routeType: _routeType,
routeRanges: [_rangeValue],
);
case RouteTransportMode.lorry:
return RoutePreferences(
avoidMotorways: _avoidMotorways,
avoidTollRoads: _avoidTollRoads,
avoidFerries: _avoidFerries,
avoidUnpavedRoads: _avoidUnpavedRoads,
transportMode: _transportMode,
routeType: _routeType,
routeRanges: [_rangeValue],
avoidTraffic: _trafficAvoidance,
);
case RouteTransportMode.pedestrian:
return RoutePreferences(
avoidFerries: _avoidFerries,
avoidUnpavedRoads: _avoidUnpavedRoads,
transportMode: _transportMode,
routeRanges: [_rangeValue],
);
case RouteTransportMode.bicycle:
return RoutePreferences(
avoidFerries: _avoidFerries,
avoidUnpavedRoads: _avoidUnpavedRoads,
transportMode: _transportMode,
routeType: _routeType,
routeRanges: [_rangeValue],
avoidBikingHillFactor: _hillsValue,
bikeProfile: BikeProfileElectricBikeProfile(
profile: _bikeProfile, eProfile: ElectricBikeProfile()),
);
default:
return RoutePreferences();
}
}
Handle User Interactions¶
Methods to manage user interactions, such as deleting, toggling, and centering on route ranges.
void _deleteRouteRange(int index) {
widget.mapController.preferences.routes.remove(routeRanges[index].route);
setState(() {
routeRanges.removeAt(index);
});
}
void _toggleRouteRange(int index) {
if (routeRanges[index].isEnabled) {
widget.mapController.preferences.routes.remove(routeRanges[index].route);
return;
} else {
RouteRenderSettings settings =
RouteRenderSettings(fillColor: routeRanges[index].color);
widget.mapController.preferences.routes
.add(routeRanges[index].route, true, routeRenderSettings: settings);
_centerOnRouteRange(routeRanges[index].route);
}
}
void _centerOnRouteRange(Route route) {
const appbarHeight = 50;
const padding = 20;
widget.mapController.centerOnRoute(route,
screenRect: RectType(
x: 0,
y: (appbarHeight + padding * MediaQuery.of(context).devicePixelRatio)
.toInt(),
width: (MediaQuery.of(context).size.width *
MediaQuery.of(context).devicePixelRatio)
.toInt(),
height: ((MediaQuery.of(context).size.height / 2 -
appbarHeight -
2 * padding * MediaQuery.of(context).devicePixelRatio) *
MediaQuery.of(context).devicePixelRatio)
.toInt(),
));
}
void _showSnackBar(BuildContext context,
{required String message, Duration duration = const Duration(hours: 1)}) {
final snackBar = SnackBar(
content: Text(message),
duration: duration,
);
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(snackBar);
}
You can start calculating a range by tapping the + button after adjusting your specifications
for the routes.