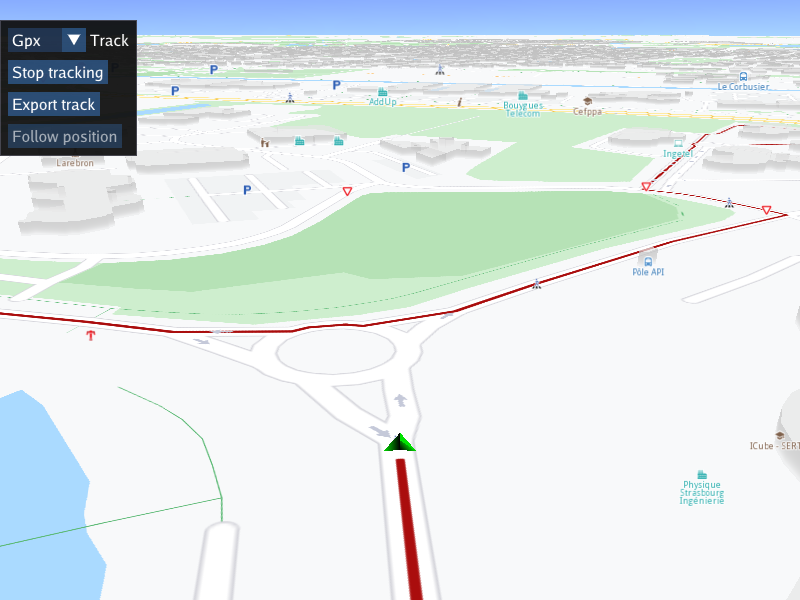
Export Track¶
|
Setup¶
Prerequisites¶
Setting your API key token¶
To set your API key token, define it like this:
#define API_TOKEN "YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN"
replacing YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN with your actual API key token text, within the quotes.
This can be done in the main() function, before the following line:
#if defined(API_TOKEN)
or outside the main() function, further up, or in a header file.
Although it is also possible to define your API key token as the text value of the GEM_TOKEN
environment variable, this is not recommended, as it is not secure.
Build and run¶
In Visual Studio, right-click on the ExportTrack project, and select
Set as Startup Project then press F5 to run.
How it works¶
1int main( int argc, char** argv )
2{
3 std::string projectApiToken = "";
4#define API_TOKEN "YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN"
5#if defined(API_TOKEN)
6 projectApiToken = std::string( API_TOKEN );
7#endif
8 // Sdk objects can be created & used below this line
9 Environment::SdkSession session(projectApiToken, { argc > 1 ? argv[1] : "" });
10
11 // Create an interactive map view
12 CTouchEventListener pTouchEventListener;
13 gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView = gem::MapView::produce(session.produceOpenGLContext(
14 Environment::WindowFrameworks::ImGUI, "ExportTrack", &pTouchEventListener, getUiRender()));
15 if ( !mapView )
16 {
17 GEM_LOGE( "Error creating gem::MapView: %d", GEM_GET_API_ERROR() );
18 }
19 WAIT_UNTIL_WINDOW_CLOSE();
20 return 0;
21}
First, the API key token is set.
Environment::SdkSession session(projectApiToken, { argc > 1 ? argv[1] : "" });CTouchEventListener pTouchEventListener;MapView interactive map instance is created, using an OpenGL context for rendering,
and selecting ImGui for the graphic control interface.gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView = gem::MapView::produce(session.produceOpenGLContext(Environment::WindowFrameworks::ImGUI,"ExportTrack", &pTouchEventListener, getUiRender()));Finally, the getUiRender() function is passed in, which uses ImGui to render GUI elements,
capture user control input, and call the appropriate SDK functions.
A function is defined to create a filename for the track output file using the current date and time plus given extension, specific to the selected output format:
1std::string generateFilename(const std::string& extension)
2{
3 auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
4 std::time_t now_c = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(now);
5 std::tm local_tm = *std::localtime(&now_c);
6 std::ostringstream filenameStream;
7 filenameStream << "track_"
8 << std::put_time(&local_tm, "%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S")
9 << "." << extension;
10 return filenameStream.str();
11}
The UI render function:
1auto getUiRender()
2{
3 auto sdkExamplesPath = Environment::GetInstance().GetSDKExamplesPath();
4 auto sdkCachePath = Environment::GetInstance().GetCachePath();
5
6 auto dstCacheResPath = gem::FileSystem().makePath(sdkCachePath.c_str(), u"Data", u"Res/");
7 gem::FileSystem().createFolder(dstCacheResPath, true);
8
9 auto srcNMEAPath = gem::FileSystem().makePath(sdkExamplesPath.c_str(), u"Examples", u"Interactive", u"ExportTrack", u"strasbourg_parc.nmea");
10 int ret;
11 if ((ret = gem::FileSystem().copyFile(srcNMEAPath, dstCacheResPath)) != gem::KNoError)
12 {
13 GEM_LOGE("Error copy NMEA resource (%d)", GEM_GET_API_ERROR());
14 }
15 srcNMEAPath = gem::FileSystem().makePath(dstCacheResPath, "strasbourg_parc.nmea");
16
17 auto dstGPXTracksPath = gem::FileSystem().makePath(sdkCachePath, u"Data", u"Tracks/");
18 gem::FileSystem().createFolder(dstGPXTracksPath, true);
19
20 auto dstLogsPath = gem::FileSystem().makePath(dstGPXTracksPath, "GPSLogs/");
21 gem::FileSystem().createFolder(dstLogsPath, true);
22
23 auto dataSourceNMEA = gem::sense::GMDataSourceFactory::produceLog(srcNMEAPath);
24 gem::PositionService().setDataSource(dataSourceNMEA);
The custom GUI function creates the SDK/Data/Tracks/ and SDK/Data/Tracks/GPSLogs/ directories, where SDK is the SDK install directory itself;
the final output track files, in the selected format, such as .gpx or .kml or .nmea or .geojson are saved in the Tracks directory.
An NMEA data source is created from a pre-recorded navigation, included with this example,
using gem::sense::GMDataSourceFactory::produceLog(srcNMEAPath);
after the .nmea input file is copied to the Data/Res/ directory within the SDK install directory.
The lambda function within the UI render function:
1return std::bind([dataSourceNMEA, dstGPXTracksPath](gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView)
2{
3 ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
4 const ImGuiViewport* main_viewport = ImGui::GetMainViewport();
5 ImGui::SetNextWindowPos(ImVec2(main_viewport->WorkPos.x + 0, main_viewport->WorkPos.y + 20), ImGuiCond_FirstUseEver);
6 ImGui::Begin("panel", nullptr, ImGuiWindowFlags_NoMove
7 | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoDecoration
8 | ImGuiWindowFlags_AlwaysAutoResize
9 | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoSavedSettings);
10
11 static bool started = true;
12 int millisecondFrequency = 300;
13 if (started)
14 {
15 mapView->startFollowingPosition();
16 started = false;
17 }
18 gem::MarkerCollectionRenderSettings markerCollectionRenderSettings;
19 if (dataSourceNMEA.get()->isStopped())
20 {
21 ImGui::BeginDisabled(true);
22 ImGui::Spacing();
23 ImGui::Button("Start tracking");
24 ImGui::EndDisabled();
25 }
26 else
27 {
28 static const char* outputTrackFileExtension[]{ "Gpx","Kml","Nmea","GeoJson","LatLonTxt","LonLatTxt" };
29 static int selectedOutputTrackFileExtension = 0;
30 float strwidth = getStringWidth(std::string("LatLonTxt"));
31 ImGui::SetNextItemWidth(strwidth + ImGui::GetStyle().FramePadding.x * 2);
32 std::string filename = generateFilename(outputTrackFileExtension[selectedOutputTrackFileExtension]);
33 if (ImGui::Combo("Track", &selectedOutputTrackFileExtension, outputTrackFileExtension, IM_ARRAYSIZE(outputTrackFileExtension)))
34 {
35 filename = generateFilename(outputTrackFileExtension[selectedOutputTrackFileExtension]);
36 }
37 if (mapView->extensions().isTrackedPositions())
38 {
39 ImGui::Spacing();
40 if (ImGui::Button("Stop tracking"))
41 {
42 mapView->extensions().stopTrackPositions();
43 }
44 ImGui::Spacing();
45 if (ImGui::Button("Export track"))
46 {
47 auto path = mapView->extensions().getTrackedPositions();
48 if (path.second == gem::KNoError)
49 {
50 auto buff = gem::Path(path.first).exportAs(gem::EPathFileFormat(selectedOutputTrackFileExtension));
51 if (GEM_GET_API_ERROR() == gem::KNoError)
52 {
53 auto dstTrackFileName = gem::FileSystem().makePath(dstGPXTracksPath.toStdString(), filename);
54 // Open the output file in binary mode
55 std::ofstream outputFile(dstTrackFileName.toStdString(), std::ios::binary);
56 if (outputFile)
57 {
58 outputFile.write((const char*)buff.getBytes(), buff.size());
59 outputFile.close();
60 }
61 }
62 }
63 }
64 }
65 else
66 {
67 ImGui::Spacing();
68 if (ImGui::Button("Start tracking"))
69 {
70 mapView->extensions().startTrackPositions(millisecondFrequency, markerCollectionRenderSettings);
71 }
72 ImGui::BeginDisabled(true);
73 ImGui::Spacing();
74 ImGui::Button("Export track");
75 ImGui::EndDisabled();
76 }
77 }
78 if (mapView->isFollowingPosition())
79 {
80 ImGui::BeginDisabled(true);
81 ImGui::Spacing();
82 ImGui::Button("Follow position");
83 ImGui::EndDisabled();
84 }
85 else
86 {
87 if (gem::PositionService().getDataSource().get()->isStopped())
88 {
89 ImGui::BeginDisabled(true);
90 ImGui::Spacing();
91 ImGui::Button("Follow position");
92 ImGui::EndDisabled();
93 }
94 else
95 {
96 ImGui::Spacing();
97 if (ImGui::Button("Follow position"))
98 {
99 mapView->startFollowingPosition();
100 }
101 }
102 }
103 ImGui::End();
104} , std::placeholders::_1); }
Outside the lambda function, the paths are defined, and the NMEA input file is read. Inside the lambda function:
First, the main ImGui viewport is obtained, and the x,y position of the ImGui window, with the identifier “panel”, in pixels, is set within the SDK OpenGL viewport.
ImGui::Begin() function,
and the ImGui elements are defined each cycle to build the UI in the block
ending with the ImGui::End() function call.There is a drop-down combo ImGui::Combo() to select the output file track format to be written,
such as .gpx or .nmea or .kml or .geojson etc.
The width of the drop-down combo is adjusted by measuring the width of the widest element using
ImVec2 itemSize = ImGui::CalcTextSize(str.c_str()); and then adjusting the combo element using
ImGui::SetNextItemWidth()
There is a button to start tracking, that is, tracing the traveled path on the interactive map, using
mapView->extensions().startTrackPositions(millisecondFrequency, markerCollectionRenderSettings);
and a button to export (save to a file) the track rendered so far, in the format specified in the
drop-down combo, using
auto path = mapView->extensions().getTrackedPositions();
to get the tracked/traced positions so far, and
auto buff = gem::Path(path.first).exportAs(gem::EPathFileFormat(selectedOutputTrackFileExtension));
to convert them to a data buffer in the specified format, to be written out to a file.
There is also a button to resume following position, using mapView->startFollowingPosition()
in case the map was panned, thus causing the camera to no longer follow the position indicator arrow.