Define Persistent Roadblock¶
In this guide you will learn how to render
an interactively defined road block on an
interactive map, and fly to the road block.
Setup¶
First, get an API key token, see the Getting Started guide.
Download the Maps & Navigation SDK for Android archive fileDownload the DefinePersistentRoadblock project archive file or clone the project with Git
See the Configure Android Example guide.
Run the example¶
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the
android device.
|
Once the map is loaded, zoom in and tap on a road to define
a road block.
|
|
|
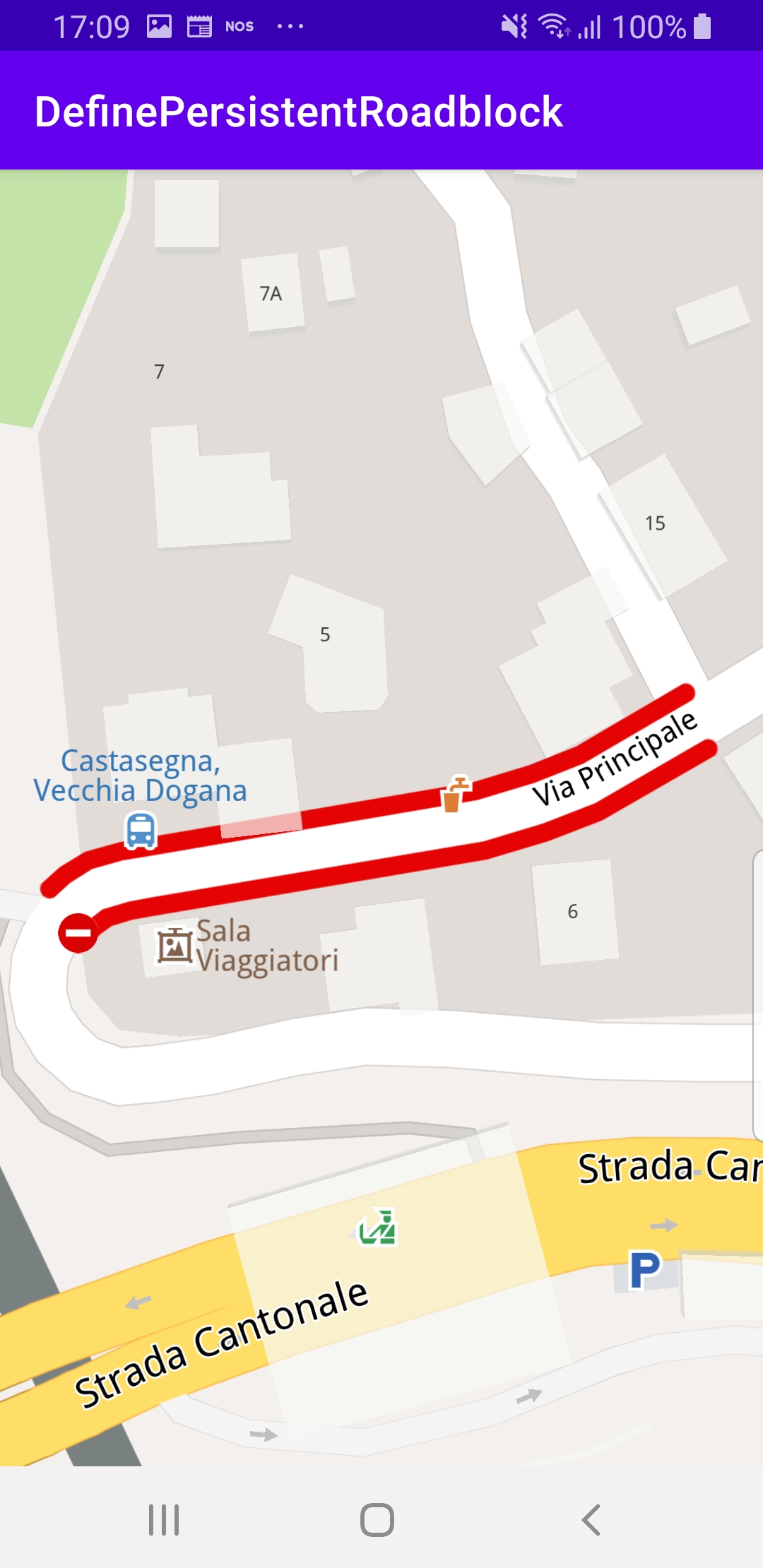
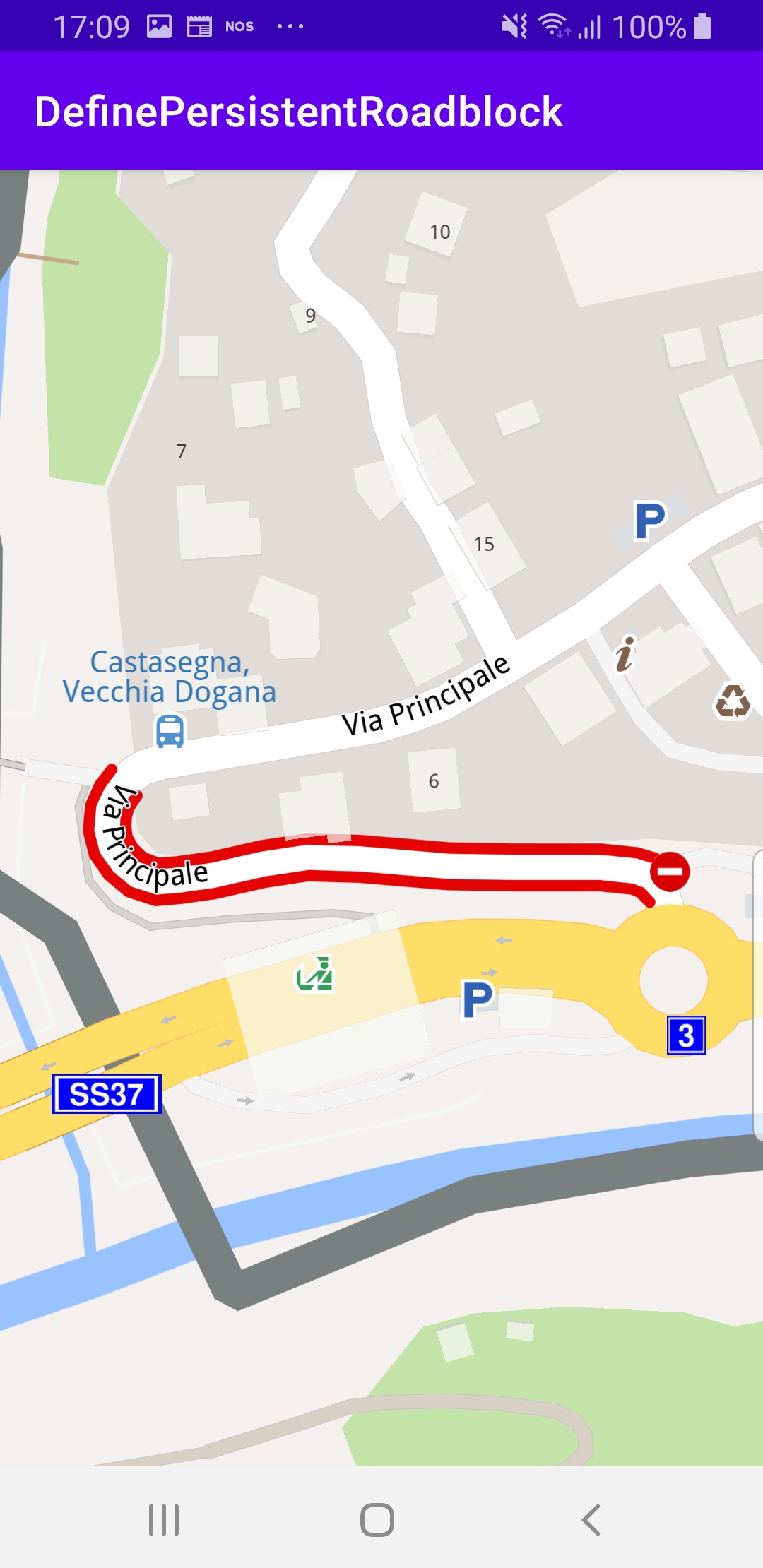
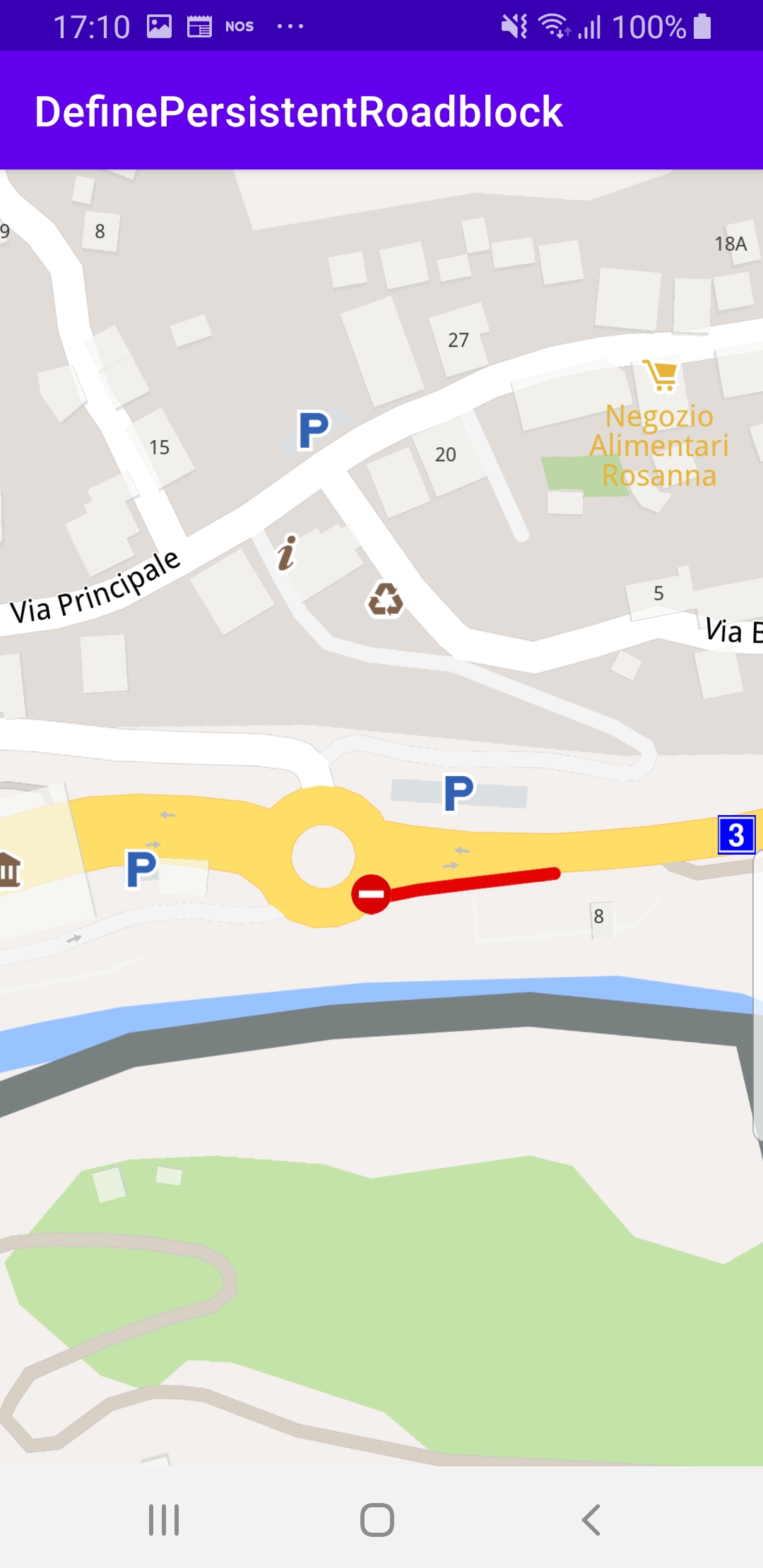
The selected road section is indicated with red roadblock polylines
which may be on one or both sides of the road, depending on the road type.
Clicking on a different road section will move the roadblock there.
The map is interactive and fully 3D,
supporting pan, pinch-zoom, rotate and tilt.
How it works¶
You can open the MainActivity.kt file and edit the search text as shown in the code block below, and run the app again to fly to a different area.
1private var roadblock: TrafficEvent? = null
The
roadblock variable is defined in the
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() class
to store the current section of road set as a roadblock
by the user. 1override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
2{
3 ...
4 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.onTouch = { xy ->
5 SdkCall.execute {
6 // tell the map view where the touch event happened
7 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorScreenPosition = xy
8 val trafficEvents = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionTrafficEvents
9 if (!trafficEvents.isNullOrEmpty())
10 {
11 val trafficEvent = trafficEvents[0]
12 if (trafficEvent.isRoadblock())
13 {
14 return@execute
15 }
16 }
17 val streets = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionStreets
18 if (!streets.isNullOrEmpty())
19 {
20 streets[0].coordinates?.let { addPersistentRoadblock(it) }
21 }
22 }
23 }
24 ...
25}
In the
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), in the onCreate()
function the x,y position of a user touch event is obtained using onTouch
and set in cursorScreenPosition so the map can be queried about
traffic events, if any, at that location.If there are 1 or more traffic events at the touch location,
if (!trafficEvents.isNullOrEmpty())then the roadblock is set on the first traffic event in the list (at index 0).
val trafficEvent = trafficEvents[0]if (trafficEvent.isRoadblock())Otherwise, if there are 1 or more road sections at the touch location,
if (!streets.isNullOrEmpty())then the roadblock is set on the first street in the list (at index 0).
streets[0].coordinates?.let { addPersistentRoadblock(it) } 1private fun addPersistentRoadblock(coordinates: Coordinates)
2{
3 val startTime = Time.getUniversalTime()
4 val endTime = Time.getUniversalTime().also { endTime -> endTime?.let { it.minute += 1 } }
5 if (startTime != null && endTime != null)
6 {
7 val traffic = Traffic()
8 roadblock?.let { roadblock ->
9 roadblock.referencePoint?.let { coordinates ->
10 traffic.removePersistentRoadblock(coordinates)
11 }
12 }
13 roadblock = traffic.addPersistentRoadblock(
14 coords = arrayListOf(coordinates),
15 startUTC = startTime,
16 expireUTC = endTime,
17 transportMode = ERouteTransportMode.Car.value
18 )
19 if (roadblock?.referencePoint?.valid() == true)
20 {
21 roadblock?.boundingBox?.let {
22 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnArea(
23 area = it,
24 zoomLevel = -1,
25 xy = null,
26 animation = Animation(EAnimation.Linear)
27 )
28 }
29 Util.postOnMain { hint.visibility = View.GONE }
30 }
31 }
32}
The
addPersistentRoadblock() function gets the current time
and sets the roadblock end time 1 minute into the future.The roadblock class member variable is initially set to null,
as we have seen above. Here it is checked and if it is not null,
roadblock?.let { roadblock ->that means the user already set a previous roadblock.
In that case, the previous roadblock is removed first:
roadblock.referencePoint?.let { coordinates ->traffic.removePersistentRoadblock(coordinates) }Then the new roadblock is added, and saved in the class member
variable:
roadblock = traffic.addPersistentRoadblock(coords = arrayListOf(coordinates),startUTC = startTime,expireUTC = endTime,transportMode = ERouteTransportMode.Car.value)Finally, the camera flies to the bounding box enclosing the
roadblock section to center it in the viewing area such that
it fills the viewport:
roadblock?.boundingBox?.let {gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnArea(area = it,zoomLevel = -1,xy = null,animation = Animation(EAnimation.Linear))}