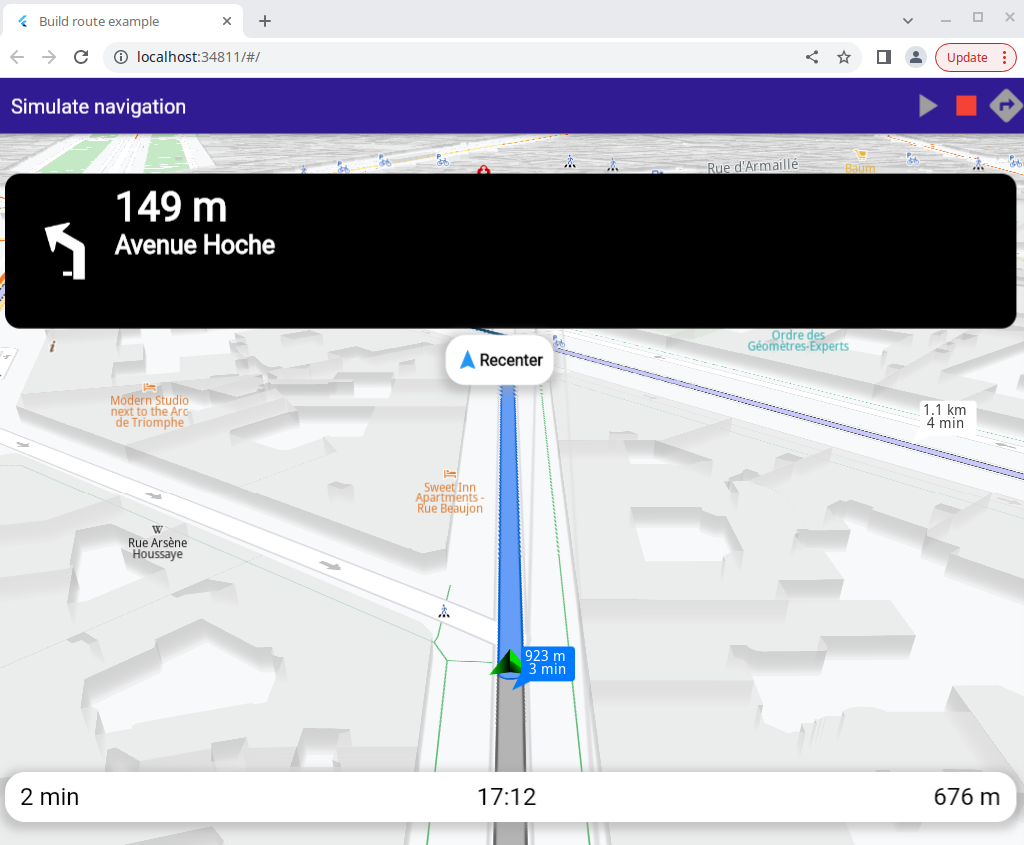
Simulate Route¶
|
|||
Setup¶
Prerequisites¶
Build and Run¶
Go to the simulate_route directory within the Flutter examples directory.
Note - the gem_kit directory containing the Maps SDK for Flutter
should be in the plugins directory of the example, e.g.
example_pathname/plugins/gem_kit - see the environment setup guide above.
Run: flutter pub get
Configure the native parts:
First, verify that the ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable
is set to the root path of your android SDK.
In android/build.gradle add the maven block as shown,
within the allprojects block, for both debug and release builds:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {
url "${rootDir}/../plugins/gem_kit/android/build"
}
}
}
in android/app/build.gradle
within the android block, in the defaultConfig block,
the android SDK version minSdk must be set as shown below.
Additionally, for release builds, in android/app/build.gradle,
within the android block, add the buildTypes block as shown:
Replace example_pathname with the actual project pathname
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.magiclane.gem_kit.examples.example_pathname"
minSdk 21
targetSdk flutter.targetSdk
versionCode flutterVersionCode.toInteger()
versionName flutterVersionName
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
shrinkResources false
// TODO: Add your own signing config for the release build.
// Signing with the debug keys for now, so `flutter run --release` works.
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
}
}
}
Then run the project:
flutter run --debugorflutter run --release
Import Necessary Packages¶
Start by importing the required packages.
import 'package:gem_kit/core.dart';
import 'package:gem_kit/map.dart';
import 'package:gem_kit/navigation.dart';
import 'package:gem_kit/routing.dart';
import 'bottom_navigation_panel.dart';
import 'top_navigation_panel.dart';
import 'utility.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart' hide Animation, Route;
App entry and initialization¶
const projectApiToken = String.fromEnvironment('GEM_TOKEN');
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
This code initializes the projectApiToken with the required authorization token and launches the app.
How It Works¶
This example demonstrates the following features:
Compute a route.
Simulate navigation on route.
This example demonstrates how to compute and simulate a route on a map.
Build the Main Application¶
Define the main application widget, MyApp.
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'Simulate Route',
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
Handle Map and Route Functionality¶
Create the stateful widget, MyHomePage, which will handle the map and routing functionality.
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
Define State Variables and Methods¶
Within _MyHomePageState, define the necessary state variables and methods to manage the map and routing.
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
late GemMapController _mapController;
late NavigationInstruction currentInstruction;
bool _areRoutesBuilt = false;
bool _isSimulationActive = false;
TaskHandler? _routingHandler;
TaskHandler? _navigationHandler;
@override
void dispose() {
GemKit.release();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("Simulate Navigation", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white)),
backgroundColor: Colors.deepPurple[900],
actions: [
if (!_isSimulationActive && _areRoutesBuilt)
IconButton(
onPressed: _startSimulation,
icon: const Icon(Icons.play_arrow, color: Colors.white),
),
if (_isSimulationActive)
IconButton(
onPressed: _stopSimulation,
icon: const Icon(Icons.stop, color: Colors.white),
),
if (!_areRoutesBuilt)
IconButton(
onPressed: () => _onBuildRouteButtonPressed(context),
icon: const Icon(Icons.route, color: Colors.white),
),
],
),
body: Stack(children: [
GemMap(
onMapCreated: _onMapCreated,
),
if (_isSimulationActive)
Positioned(
top: 10,
left: 10,
child: Column(children: [
NavigationInstructionPanel(instruction: currentInstruction),
const SizedBox(height: 10),
FollowPositionButton(
onTap: () => _mapController.startFollowingPosition(),
),
]),
),
]),
resizeToAvoidBottomInset: false,
);
}
void _onMapCreated(GemMapController controller) {
_mapController = controller;
}
void _onBuildRouteButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
// Define the departure and destination landmarks.
final departureLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 45.6517672, longitude: 25.6271132);
final destinationLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 44.4379187, longitude: 26.0122374);
// Define the route preferences.
final routePreferences = RoutePreferences();
_showSnackBar(context, message: 'The route is calculating.');
// Calling the calculateRoute SDK method.
_routingHandler = RoutingService.calculateRoute(
[departureLandmark, destinationLandmark], routePreferences,
(err, routes) async {
_routingHandler = null;
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).clearSnackBars();
if (err == GemError.success) {
final routesMap = _mapController.preferences.routes;
for (final route in routes!) {
routesMap.add(route, route == routes.first, label: route.getMapLabel());
}
_mapController.centerOnRoutes(routes);
}
setState(() {
_areRoutesBuilt = true;
});
});
}
void _startSimulation() {
final routes = _mapController.preferences.routes;
_navigationHandler = NavigationService.startSimulation(routes.mainRoute,
(type, instruction) async {
if (type == NavigationEventType.destinationReached || type == NavigationEventType.error) {
setState(() {
_isSimulationActive = false;
_cancelRoute();
});
return;
}
_isSimulationActive = true;
if (instruction != null) {
setState(() => currentInstruction = instruction);
}
});
// Set the camera to follow position.
_mapController.startFollowingPosition();
}
void _stopSimulation() {
NavigationService.cancelNavigation(_navigationHandler!);
_navigationHandler = null;
_cancelRoute();
setState(() => _isSimulationActive = false);
}
void _cancelRoute() {
_mapController.preferences.routes.clear();
if (_routingHandler != null) {
RoutingService.cancelRoute(_routingHandler!);
_routingHandler = null;
}
setState(() {
_areRoutesBuilt = false;
});
}
void _showSnackBar(BuildContext context, {required String message, Duration duration = const Duration(hours: 1)}) {
final snackBar = SnackBar(content: Text(message), duration: duration);
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(snackBar);
}
}