Speed Voice Warning¶
In this guide you will learn how the speed text
to speech (TTS) voice warning during navigation or
simulation along a route, or simply following
position while moving, works.
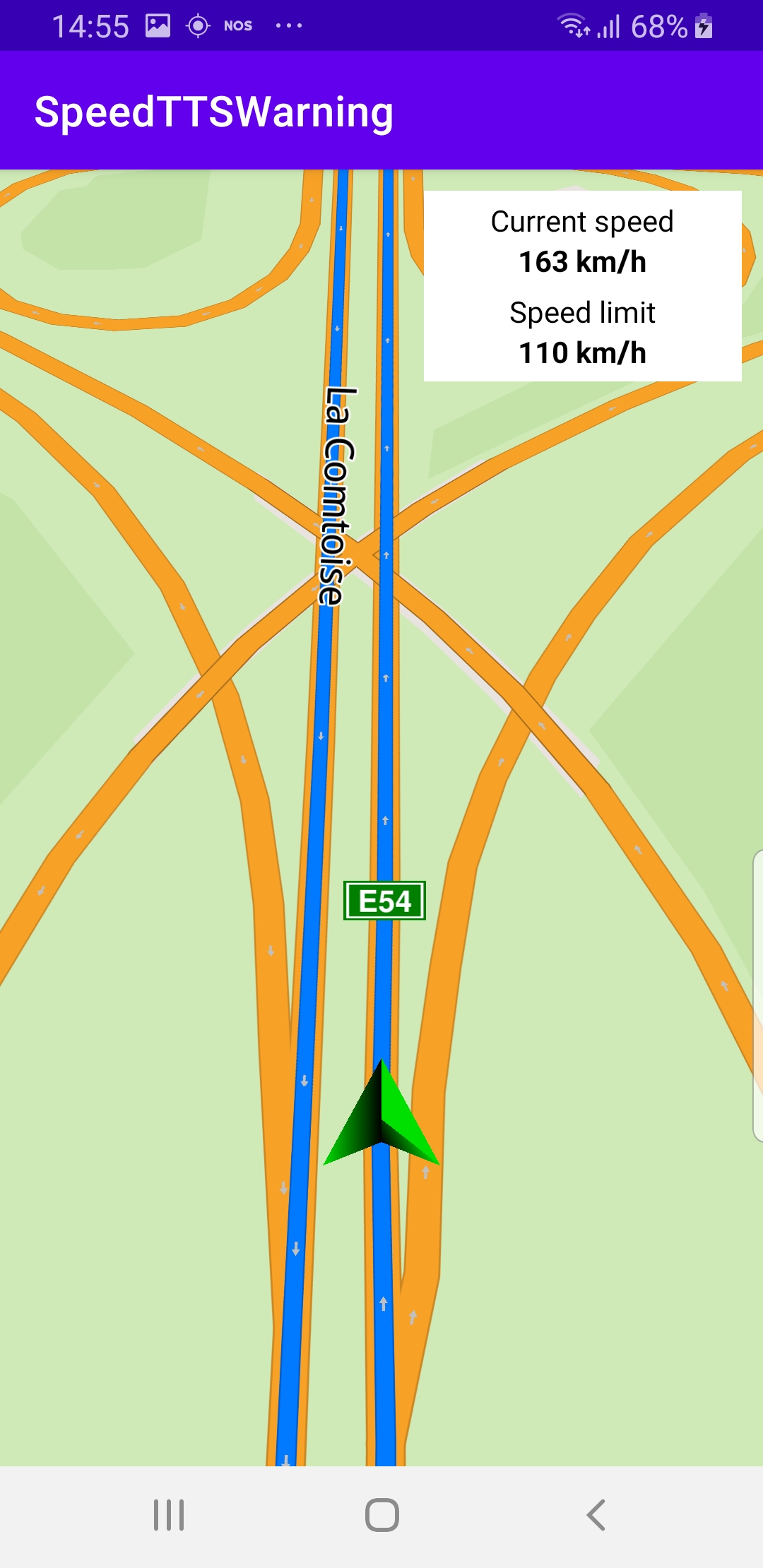
The English version of the speed warning
message played is “Mind your speed”.
Setup¶
First, get an API key token, see the
Getting Started guide.
Download the SpeedTTSWarning project archive file or clone the project with Git
See the Configure Android Example guide.
Run the example¶
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
|
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the
android device.
How it works¶
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how the speed warning
is issued during navigation/simulation along a route or following
a moving position as a result of real or simulated motion (such as
with a mock locations app).
This example demonstrates simulated navigation along a preset route.
1private val navigationService = NavigationService()
A navigation service is instantiated from which to start simulated navigation.
1override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
2{
3 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
4 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
5 gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface)
6 progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar)
7 currentSpeed = findViewById(R.id.current_speed)
8 speedLimit = findViewById(R.id.speed_limit)
9 followCursorButton = findViewById(R.id.followCursor)
10 SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = onMapDataReady@{ isReady ->
11 if (!isReady) return@onMapDataReady
12 startNavigation()
13 }
14 ...
15 requestPermissions(this)
16 if (!Util.isInternetConnected(this))
17 {
18 showDialog("You must be connected to the internet!")
19 }
20}
The
onCreate() function is overridden in the
MainActivity: AppCompatActivity() class.findViewById() is used to obtain pointers to the various
graphical user interface elements where text or graphical data
is to be displayed.The
startNavigation() function is called once the map data is loaded. 1private fun requestPermissions(activity: Activity): Boolean {
2 val permissions = arrayListOf(
3 Manifest.permission.INTERNET,
4 Manifest.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE,
5 Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
6 Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
7 )
8 return PermissionsHelper.requestPermissions(
9 REQUEST_PERMISSIONS, activity, permissions.toTypedArray()
10 )
11}
The
requestPermissions() function requests internet and
location permissions from the user, if not already available. 1override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode: Int, permissions: Array<out String>, grantResults: IntArray)
2{
3 super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults)
4 if (requestCode != REQUEST_PERMISSIONS) return
5 for (item in grantResults)
6 {
7 if (item != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
8 {
9 finish()
10 exitProcess(0)
11 }
12 }
13 SdkCall.execute {
14 // Notice permission status had changed
15 PermissionsHelper.onRequestPermissionsResult(this, requestCode, grantResults)
16 }
17 startNavigation()
18}
The
onRequestPermissionsResult() function is overridden, to receive
the results of the permission requests, and ends the program
if permissions are denied, otherwise, it calls the startNavigation() function below. 1private val navigationListener: NavigationListener = NavigationListener.create(
2 onNavigationStarted = {
3 SdkCall.execute {
4 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.let { mapView ->
5 mapView.preferences?.enableCursor = false
6 navRoute?.let { route ->
7 mapView.presentRoute(route)
8 }
9 // Start listening for new positions.
10 PositionService.addListener(positionListener, EDataType.Position)
11 enableGPSButton()
12 mapView.followPosition()
13 }
14 }
15 },
16 onNavigationInstructionUpdated = { instr ->
17 // From every new navigation instruction get the speed limit.
18 val limit = SdkCall.execute execute@{
19 val pair = GemUtil.getSpeedText(instr.currentStreetSpeedLimit, EUnitSystem.Metric)
20 speedLimitValue = pair.first.toInt()
21 return@execute pair.first + " " + pair.second
22 }
23 speedLimit.text = limit
24 },
25 onDestinationReached = {
26 // DON'T FORGET to remove the position listener after the navigation is done.
27 PositionService.removeListener(positionListener)
28 }
29)
A navigation listener is defined to receive notifications from the
navigation service, such as
onNavigationStarted or
onDestinationReached, which are the usual ones. In this case,
the onNavigationInstructionUpdated notification is also implemented,
because the current speed limit is included with the navigation
instructions, which are used for turns, for example.See the documentation for other available notifications from the
navigation service.
1private val positionListener = object : PositionListener()
2{
3 override fun onNewPosition(value: PositionData)
4 {
5 // Get the current speed for every new position received
6 val speed = GemUtil.getSpeedText(value.speed, EUnitSystem.Metric).let { speedPair ->
7 currentSpeedValue = speedPair.first.toInt()
8 speedPair.first + " " + speedPair.second
9 }
10 if (currentSpeedValue > speedLimitValue)
11 {
12 if (!wasSpeedWarningPlayed)
13 {
14 SoundPlayingService.playText(GemUtil.getTTSString(EStringIds.eStrMindYourSpeed),
15 SoundPlayingListener(), SoundPlayingPreferences())
16 wasSpeedWarningPlayed = true
17 }
18 }
19 else
20 {
21 wasSpeedWarningPlayed = false
22 }
23 Util.postOnMain {
24 currentSpeed.text = speed
25 }
26 }
27}
A position listener is defined to receive notifications from the
navigation service when the position of the devices is changed.
At every position change, the current speed is obtained, and
compared to the speed limit at that location, which is obtained
along with the instructions in the navigation listener above,
and stored in the class variable
speedLimitValue.If the current speed is greater than the speed limit value,
the “mind your speed” warning voice message is played using
SoundPlayingService.playText(GemUtil.getTTSString(EStringIds.eStrMindYourSpeed), ...1private val routingProgressListener = ProgressListener.create(
2 onStarted = {
3 progressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE
4 },
5 onCompleted = { _, _ ->
6 progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
7 },
8 postOnMain = true
9)
A ProgressListener is defined to act as a routing progress listener,
that is, receive notifications from the navigation service when the
route computation is started and when it is completed. This is to
display a progress bar during the computation. On most
devices, the route computation is quick, however, this progress
listener is a required parameter for the navigation service to start
navigation.
1private fun startNavigation()
2{
3 val startNavigationTask = {
4 val hasPermissions = PermissionsHelper.hasPermission(this,
5 Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
6 if (hasPermissions)
7 {
8 val destination = Landmark("Paris", 48.8566932, 2.3514616)
9 navigationService.cancelNavigation(navigationListener)
10 val error = navigationService.startNavigation(
11 destination,
12 navigationListener,
13 routingProgressListener,
14 )
15 Log.i(TAG, "MainActivity.startNavigation: after = $error")
16 }
17 }
18 SdkCall.execute {
19 lateinit var positionListener: PositionListener
20 if (PositionService.position?.isValid() == true)
21 {
22 startNavigationTask()
23 }
24 else
25 {
26 positionListener = PositionListener {
27 if (!it.isValid()) return@PositionListener
28 PositionService.removeListener(positionListener)
29 startNavigationTask()
30 }
31 PositionService.addListener(positionListener)
32 }
33 }
34}
The
startNavigation() function queries the PermissionsHelper to
check if location permission has been obtained in order to start navigation.If location access is available, a hardcoded destination in Paris is set
with latitude, longitude coordinates in degrees.
Next, the existing navigation, if any, is stopped:
navigationService.cancelNavigation(navigationListener)Then the destination is passed to the navigation service, along with
the listeners for navigation and routing progress.
The navigation service computes the route, selects the default route
and starts simulated navigation along the route automatically:
navigationService.startNavigation()If location access is not available, then the function waits for the
first valid position using a
PositionListener added to the
PositionService. Once the first valid location is received,
the listener is removed and navigation starts.The point of this example is to play the speed voice warning,
so a single position is sufficient, provided it is on a road with
speed limit data, to get the speed limit, and potentially play
the voice warning.
|
1private fun enableGPSButton() { 2 // Set actions for entering/ exiting following position mode. 3 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.apply { 4 onExitFollowingPosition = { 5 followCursorButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE 6 } 7 onEnterFollowingPosition = { 8 followCursorButton.visibility = View.GONE 9 } 10 // Set on click action for the GPS button. 11 followCursorButton.setOnClickListener { 12 SdkCall.execute { followPosition() } 13 } 14 } 15}
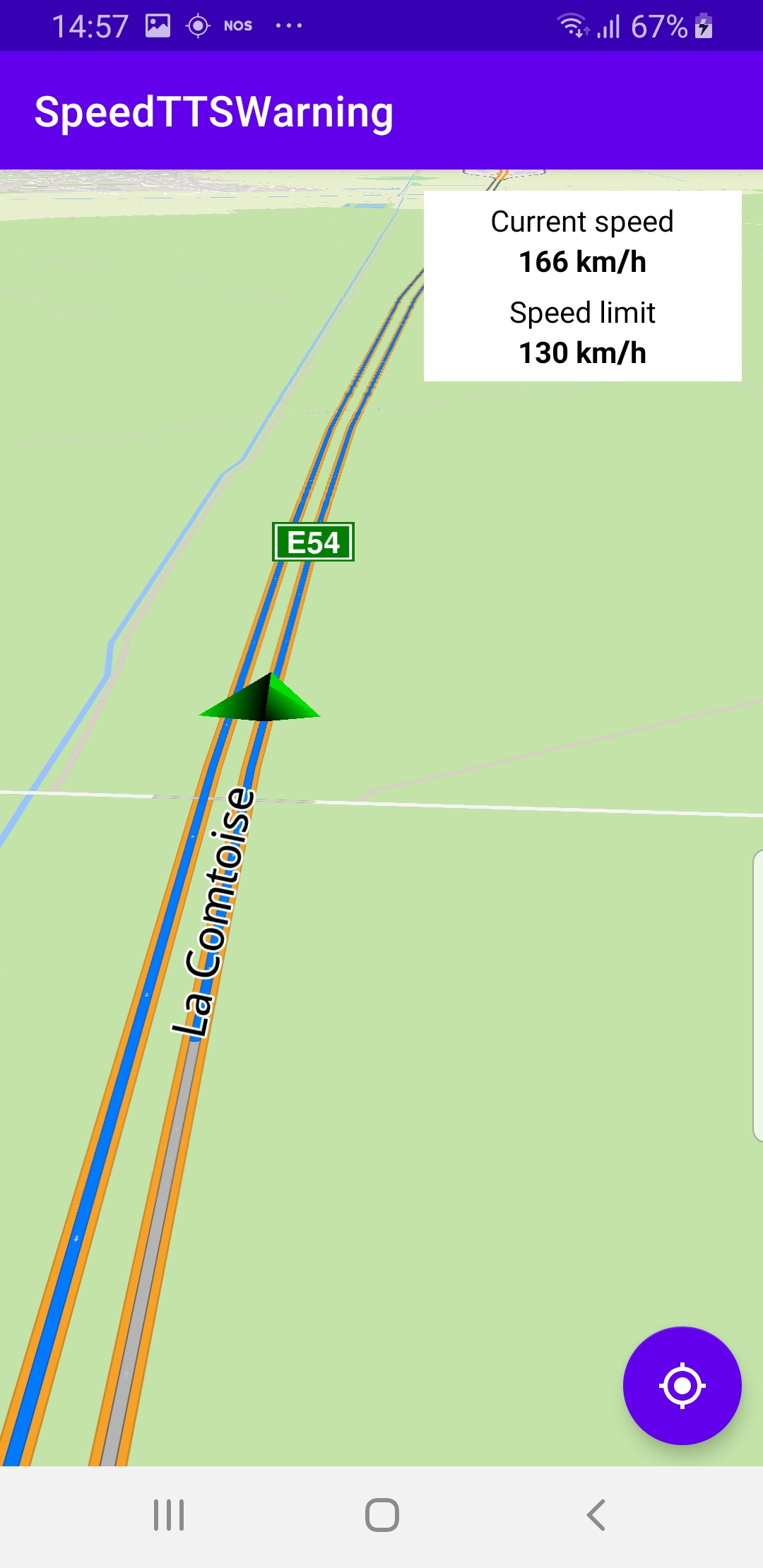
enableGPSButton() causes a round purple button to appear in the lower
right corner of the screen, whenever the simulation is active and
the camera is not following the green arrow. This can happen if the user
does a pan away from the route during the simulation.If the user pushes this button, the
followPosition() function is called,
and thus the camera starts to follow the green arrow once again.