External Position Source Navigation¶
This example demonstrates how to create a Flutter app that utilizes external position sources for navigation on a map using ``gem_kit``package. The app allows users to navigate to a predefined destination while following the route on the map.
|
|||
Setup¶
Prerequisites¶
Build and Run¶
Navigate to the external_position_navigation directory within the Flutter examples directory. This is the project folder for this example.
Note - the gem_kit directory containing the Maps SDK for Flutter
should be in the plugins directory of the example, e.g.
example_pathname/plugins/gem_kit - see the environment setup guide above.
Run: flutter pub get
Configure the native parts:
First, verify that the ANDROID_SDK_ROOT environment variable
is set to the root path of your android SDK.
In android/build.gradle add the maven block as shown,
within the allprojects block, for both debug and release builds:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {
url "${rootDir}/../plugins/gem_kit/android/build"
}
}
}
in android/app/build.gradle
within the android block, in the defaultConfig block,
the android SDK version minSdk must be set as shown below.
Additionally, for release builds, in android/app/build.gradle,
within the android block, add the buildTypes block as shown:
Replace example_pathname with the actual project pathname
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.magiclane.gem_kit.examples.example_pathname"
minSdk 21
targetSdk flutter.targetSdk
versionCode flutterVersionCode.toInteger()
versionName flutterVersionName
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
shrinkResources false
// TODO: Add your own signing config for the release build.
// Signing with the debug keys for now, so `flutter run --release` works.
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
}
}
}
Then run the project:
flutter run --debugorflutter run --release
App entry and initialization¶
const projectApiToken = String.fromEnvironment('GEM_TOKEN');
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
This code initializes the projectApiToken with the required authorization token and launches the app.
How It Works¶
The example app demonstrates the following features:
Uses GemKit SDK to initialize the map.
Implements navigation using external position sources.
Allows route building and starts navigation with real-time position updates.
UI and Navigation Integration¶
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
title: 'External Position Source Navigation',
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
late GemMapController _mapController;
late NavigationInstruction currentInstruction;
bool _areRoutesBuilt = false;
bool _isNavigationActive = false;
bool _hasDataSource = false;
final DataSource _dataSource = DataSource([DataType.position]);
@override
void dispose() {
GemKit.release();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text("ExternalPositionNavigation",
style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white)),
backgroundColor: Colors.deepPurple[900],
actions: [
if (!_isNavigationActive && _areRoutesBuilt)
IconButton(
onPressed: () => _startNavigation(),
icon: const Icon(Icons.play_arrow, color: Colors.white),
),
if (_isNavigationActive)
IconButton(
onPressed: _stopNavigation,
icon: const Icon(
Icons.stop,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
if (!_areRoutesBuilt && _hasDataSource)
IconButton(
onPressed: () => _onBuildRouteButtonPressed(context),
icon: const Icon(
Icons.route,
color: Colors.white,
),
),
if (!_isNavigationActive)
IconButton(
onPressed: _onFollowPositionButtonPressed,
icon: const Icon(
Icons.location_searching_sharp,
color: Colors.white,
))
],
),
body: Stack(children: [
GemMap(
onMapCreated: _onMapCreated,
),
if (_isNavigationActive)
Positioned(
top: 10,
left: 10,
child: Column(children: [
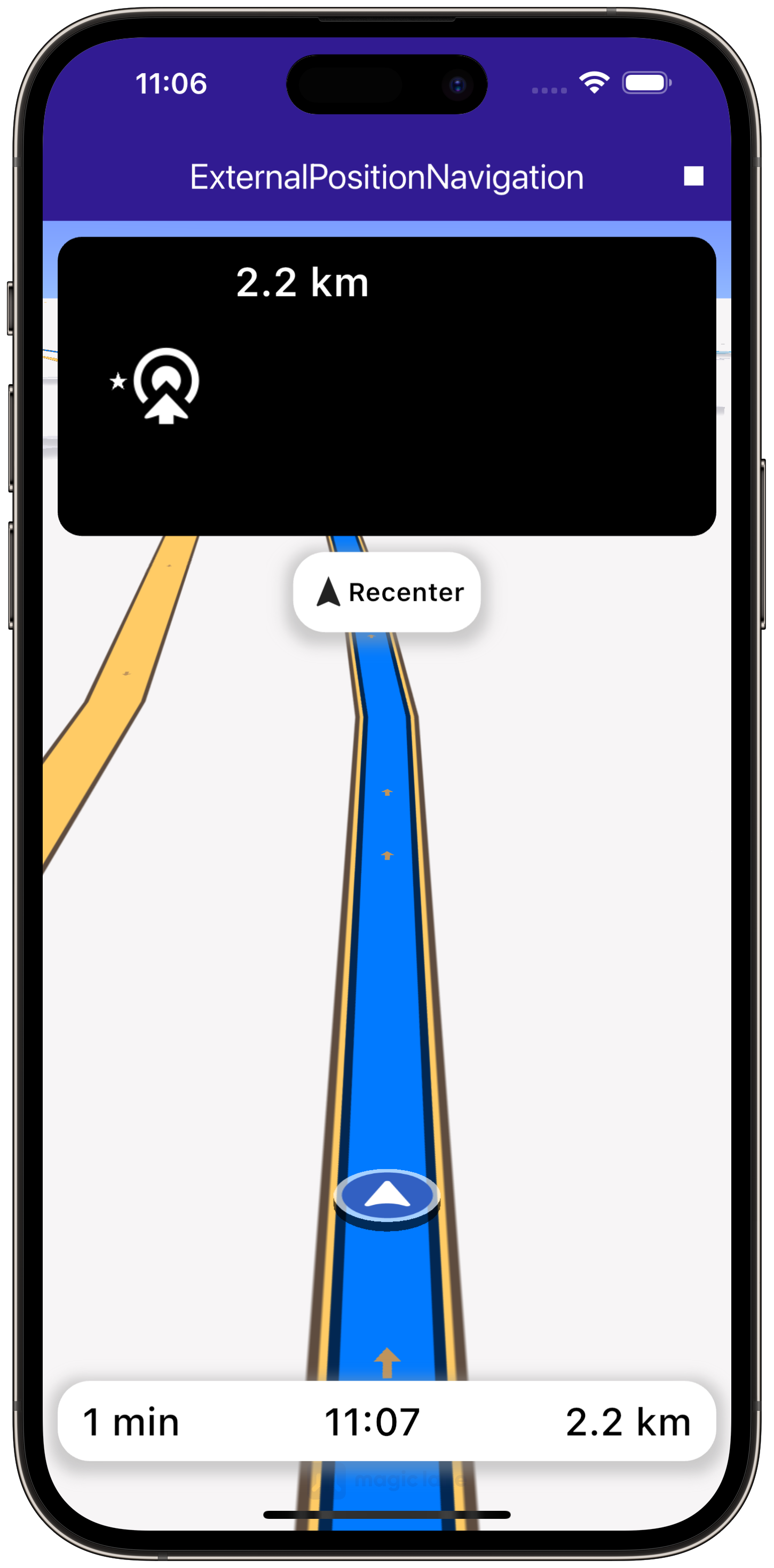
NavigationInstructionPanel(
instruction: currentInstruction,
),
const SizedBox(
height: 10,
),
FollowPositionButton(
onTap: () => _mapController.startFollowingPosition(),
),
]),
),
if (_isNavigationActive)
Positioned(
bottom: MediaQuery.of(context).padding.bottom + 10,
left: 0,
child: NavigationBottomPanel(
remainingDistance:
currentInstruction.getFormattedRemainingDistance(),
remainingDuration:
currentInstruction.getFormattedRemainingDuration(),
eta: currentInstruction.getFormattedETA(),
),
),
]),
resizeToAvoidBottomInset: false,
);
}
}
This code sets up the user interface, including a map and navigation buttons.
|
|||
Handling Navigation and External Position Data¶
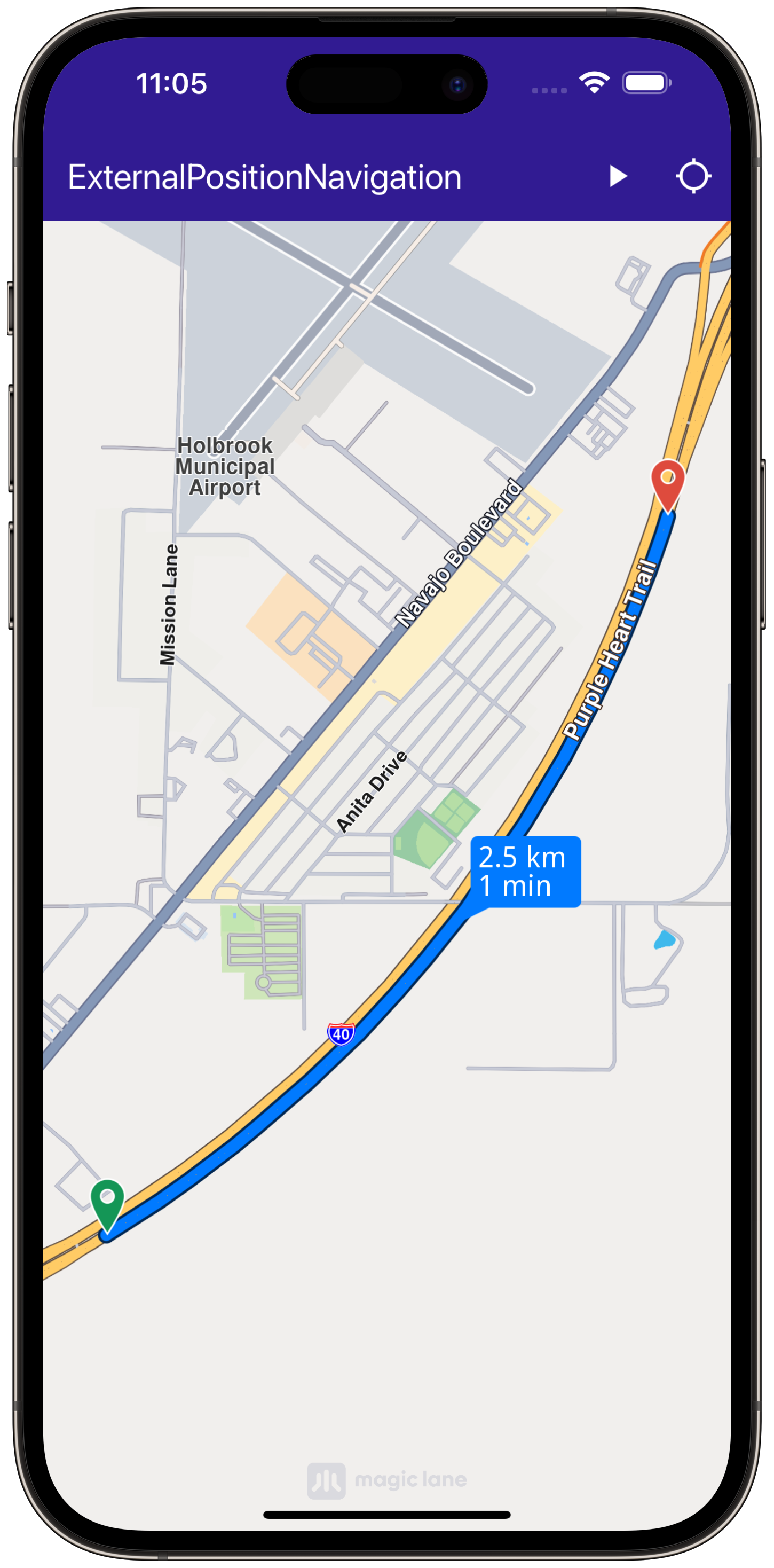
void _onBuildRouteButtonPressed(BuildContext context) {
final departureLandmark =
Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 34.915646, longitude: -110.147933);
final destinationLandmark =
Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 34.933105, longitude: -110.131363);
final routePreferences = RoutePreferences();
_showSnackBar(context, message: 'The route is calculating.');
_routingHandler = RoutingService.calculateRoute(
[departureLandmark, destinationLandmark], routePreferences,
(err, routes) {
_routingHandler = null;
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).clearSnackBars();
if (err == GemError.routeTooLong) {
print('The destination is too far from your current location. Change the coordinates of the destination.');
return;
}
if (err == GemError.success) {
final routesMap = _mapController.preferences.routes;
for (final route in routes!) {
routesMap.add(route, route == routes.first,
label: route.getMapLabel());
}
_mapController.centerOnRoutes(routes: routes);
setState(() {
_areRoutesBuilt = true;
});
}
});
}
This code handles building the route from a departure point to a destination, notifying the user when the calculation is in progress.
|
|||
Starting Navigation¶
Future<void> _startNavigation() async {
final routes = _mapController.preferences.routes;
_navigationHandler = NavigationService.startNavigation(routes.mainRoute,
(type, instruction) {
if (type == NavigationEventType.destinationReached ||
type == NavigationEventType.error) {
PositionService.instance.removeDataSource();
_dataSource.stop();
setState(() {
_isNavigationActive = false;
_cancelRoute();
});
_stopNavigation();
return;
}
_isNavigationActive = true;
if (instruction != null) {
setState(() => currentInstruction = instruction);
}
});
_mapController.startFollowingPosition();
await _pushExternalPosition();
}
This method starts the navigation and sets the map to follow the user’s position.
|
|||
Pushing External Position Data¶
Future<void> _pushExternalPosition() async {
final route = _mapController.preferences.routes.mainRoute;
final distance = route.getTimeDistance().totalDistanceM;
Coordinates prevCoordinates = route.getCoordinateOnRoute(0);
for (int currentDistance = 1;
currentDistance <= distance;
currentDistance += 1) {
if (!_hasDataSource) return;
if (currentDistance == distance) {
_stopNavigation();
return;
}
final currentCoordinates = route.getCoordinateOnRoute(currentDistance);
await Future<void>.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 25));
_dataSource.pushData(
positionData: ExternalPositionData(
timestamp: DateTime.now().toUtc().millisecondsSinceEpoch,
latitude: currentCoordinates.latitude,
longitude: currentCoordinates.longitude,
altitude: 0,
heading: _getHeading(prevCoordinates, currentCoordinates),
speed: 0));
prevCoordinates = currentCoordinates;
}
}
This code manages the position data, updating the user’s location along the route at regular intervals.