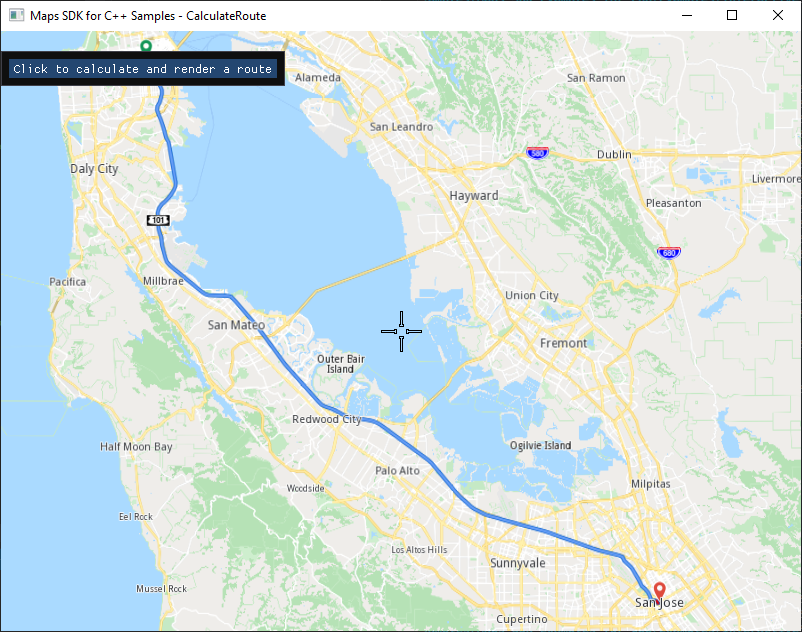
Calculate Route¶
|
Setup¶
Prerequisites¶
Setting your API key token¶
To set your API key token, define it like this:
#define API_TOKEN "YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN"
replacing YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN with your actual API key token text, within the quotes.
This can be done in the main() function, before the following line:
#if defined(API_TOKEN)
or outside the main() function, further up, or in a header file.
Although it is also possible to define your API key token as the text value of the GEM_TOKEN
environment variable, this is not recommended, as it is not secure.
Build and run¶
In Visual Studio, right-click on the CalculateRoute project, and select
Set as Startup Project then press F5 to run.
How it works¶
1int main( int argc, char** argv )
2{
3 std::string projectApiToken = "";
4#define API_TOKEN "YOUR_API_KEY_TOKEN"
5#if defined(API_TOKEN)
6 projectApiToken = std::string( API_TOKEN );
7#endif
8 // Sdk objects can be created & used below this line
9 Environment::SdkSession session(projectApiToken, { argc > 1 ? argv[1] : "" });
10
11 // Create an interactive map view
12 CTouchEventListener pTouchEventListener;
13 gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView = gem::MapView::produce(session.produceOpenGLContext(
14 Environment::WindowFrameworks::ImGUI, "CalculateRoute", &pTouchEventListener, getUiRender()));
15 if (mapView)
16 {
17 WAIT_UNTIL_WINDOW_CLOSE();
18 }
19 else
20 {
21 GEM_LOGE("Error creating gem::MapView: %d", GEM_GET_API_ERROR());
22 }
23 return 0;
24}
First, the API key token is set.
Environment::SdkSession session(projectApiToken, { argc > 1 ? argv[1] : "" });CTouchEventListener pTouchEventListener;MapView interactive map instance is created, using an OpenGL context for rendering,
and selecting ImGui for the graphic control interface.gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView = gem::MapView::produce(session.produceOpenGLContext(Environment::WindowFrameworks::ImGUI,"CalculateRoute", &pTouchEventListener, getUiRender()));Finally, the getUiRender() function is passed in, which uses ImGui to render GUI elements,
capture user control input, and call the appropriate SDK functions.
1auto getUiRender()
2{
3 return std::bind([](gem::StrongPointer<gem::MapView> mapView)
4 {
5 ImGuiIO& io = ImGui::GetIO();
6 const ImGuiViewport* main_viewport = ImGui::GetMainViewport();
7 ImGui::SetNextWindowPos(ImVec2(main_viewport->WorkPos.x + 0, main_viewport->WorkPos.y + 20), ImGuiCond_FirstUseEver);
8 ImGui::Begin("panel", nullptr, ImGuiWindowFlags_NoMove
9 | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoDecoration
10 | ImGuiWindowFlags_AlwaysAutoResize
11 | ImGuiWindowFlags_NoSavedSettings);
12 if (ImGui::Button("Click to calculate and render a route"))
13 {
14 gem::LandmarkList waypoints({
15 { "San Francisco", { 37.77903, -122.41991 } },
16 { "San Jose", { 37.33619, -121.89058 } }
17 });
18 gem::RouteList routes;
19 ProgressListener routeListener;
20 // Calculate route - car / fastest / without alternatives in result
21 gem::RoutingService().calculateRoute(routes, waypoints,
22 gem::RoutePreferences().setTransportMode(gem::RTM_Car).setRouteType(gem::RT_Fastest).setAlternativesSchema(gem::AS_Never),
23 &routeListener);
24 if (WAIT_UNTIL(std::bind(&ProgressListener::IsFinished, &routeListener), 30000) && routeListener.GetError() == gem::KNoError && !routes.empty())
25 {
26 mapView->preferences().routes().add(routes[0]);
27 mapView->centerOnRoute(routes[0], gem::Rect(), gem::Animation(gem::AnimationLinear, gem::ProgressListener(), 2000));
28 }
29 }
30 ImGui::End();
31 }
32 , std::placeholders::_1);
33}
First, the main ImGui viewport is obtained, and the x,y position of the ImGui window, with the identifier “panel”, in pixels, is set within the SDK OpenGL viewport.
ImGui::Begin() function.ImGui::Button()
which the user can click to calculate and render a predefined route.A route must have at least 2 waypoints, one for the departure, and one for the destination. Optionally, 0 or more intermediate waypoints may be specified, through which the route will pass, in order from departure to destination.
Landmark and has an optional text description, and
mandatory latitude and longitude coordinates, in degrees.gem::RoutingService().calculateRoute() is used to calculate a set of routes
between the departure and destination positions, and the resulting route(s) are
stored in the routes parameter which is a gem::RouteList;
routing preferences are also set to a car route, selecting fastest (as opposed to shortest).
The WAIT_UNTIL macro is used to wait for the route calculation to complete and
check the success/error status, and whether the resulting route list has at least one route.
mapView->preferences().routes().add(routes[0]);mapView->centerOnRoute(routes[0], gem::Rect(), gem::Animation(gem::AnimationLinear, gem::ProgressListener(), 2000));