Display Current Street Name¶
In this guide you will learn how to display the street name for the current position on the map of the green arrow/device position indicator.
Setup¶
First, get an API key token, see the Getting Started guide.
Download the Maps & Navigation SDK for Android archive fileDownload the DisplayCurrentStreetName project archive file or clone the project with Git
See the Configure Android Example guide.
Run the example¶
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
|
|
|
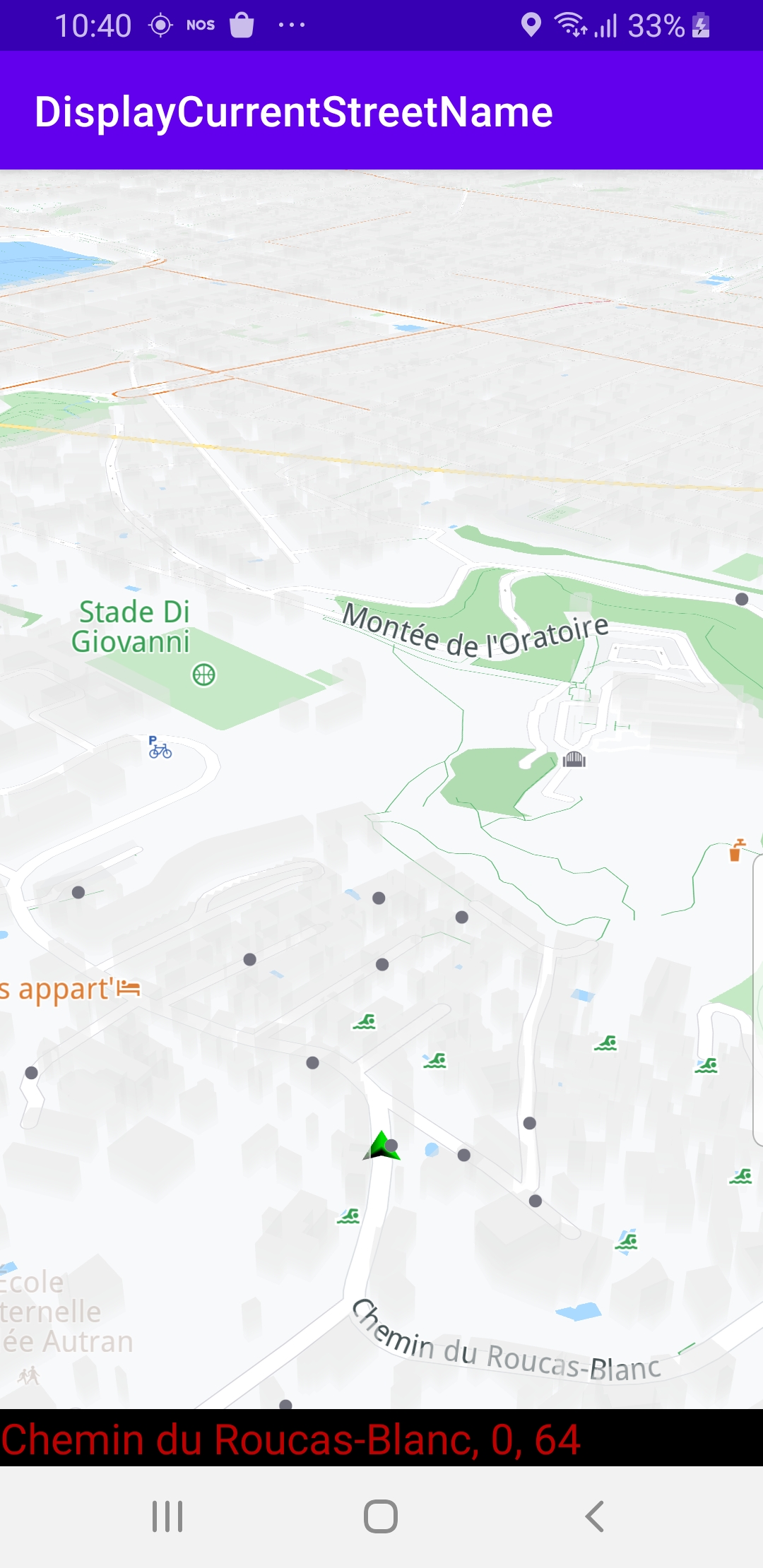
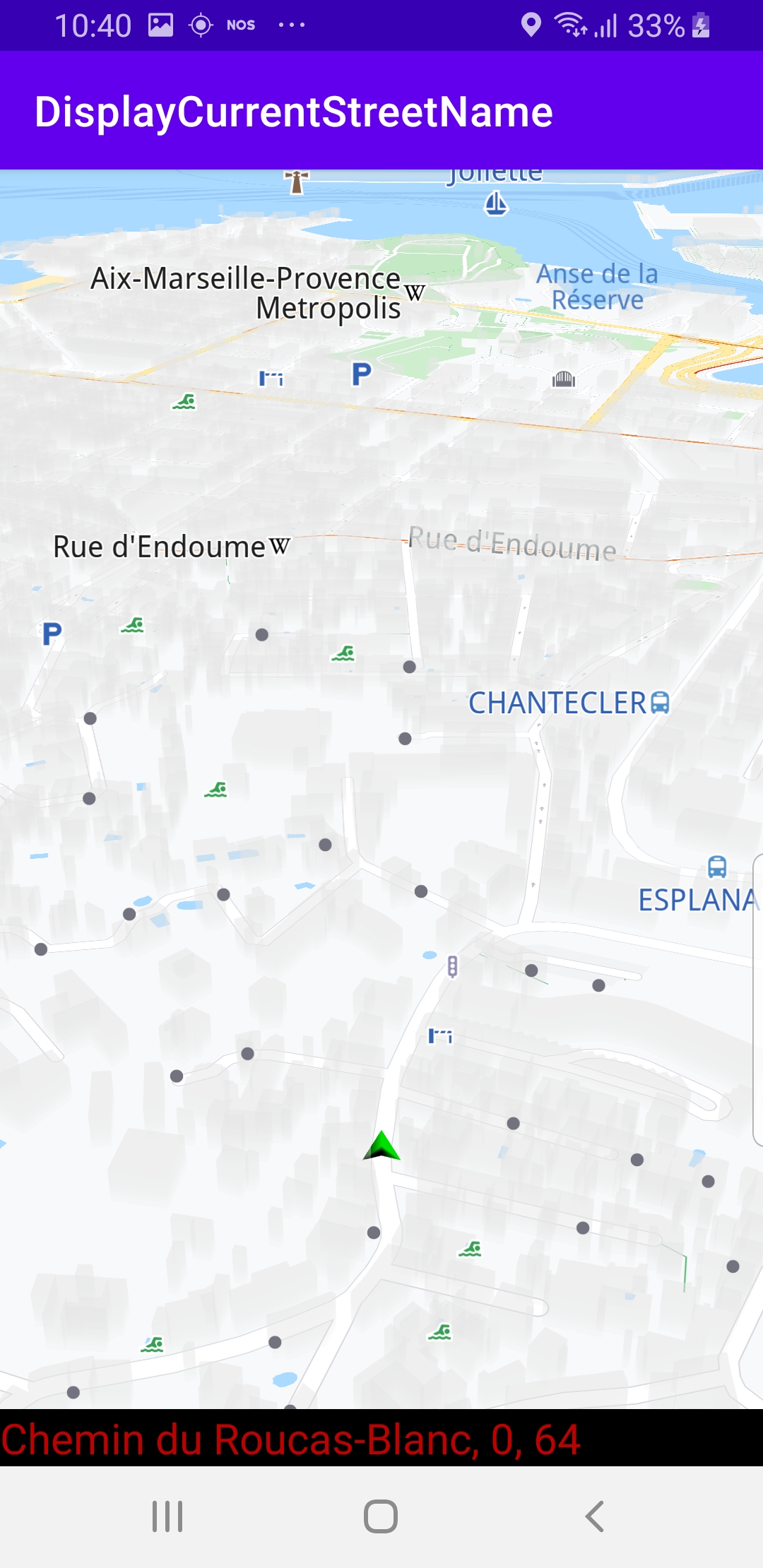
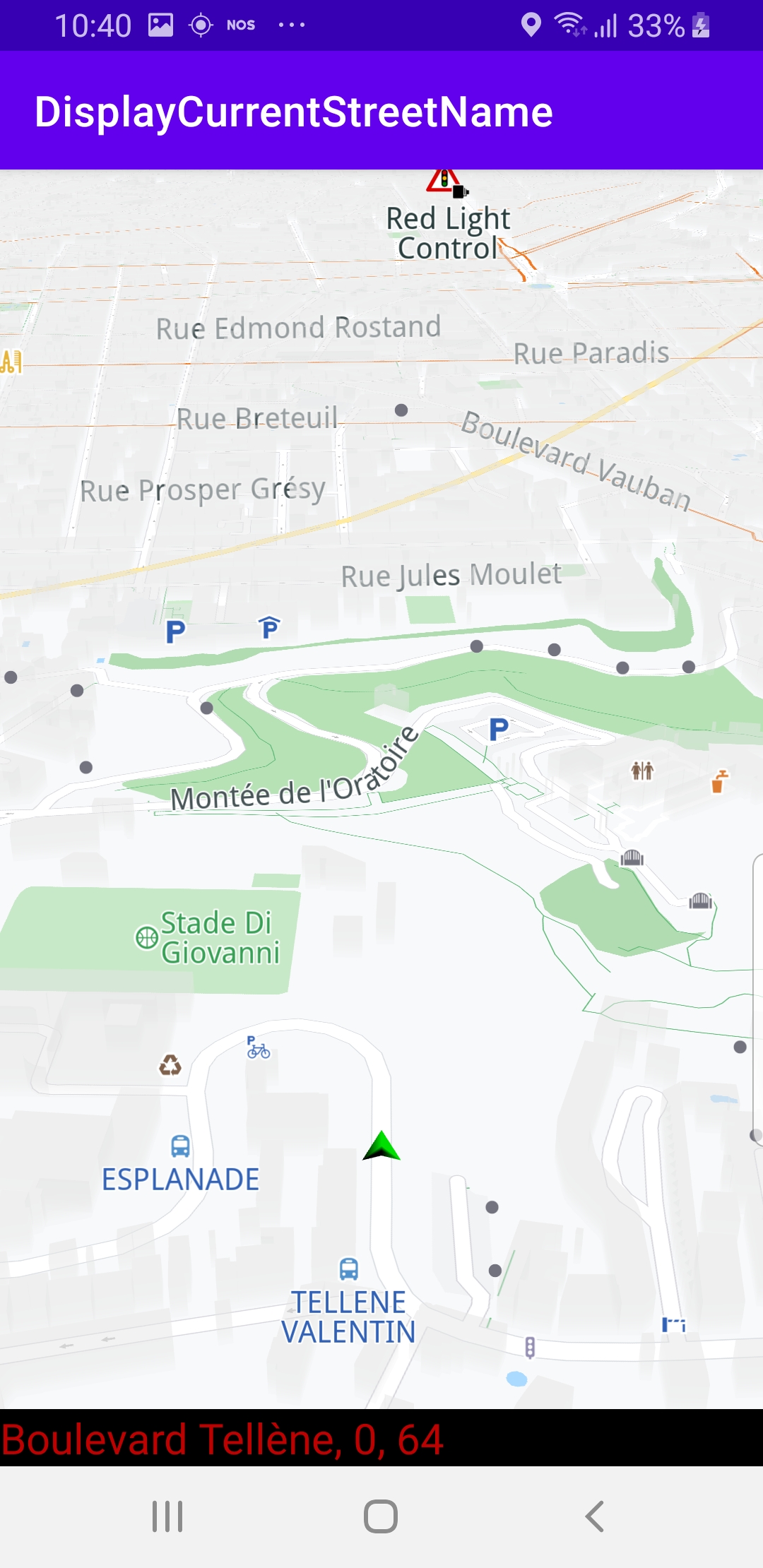
The map is loaded, showing the current position of the device using the green arrow GPS position indicator. The name of the current street is displayed in the black text box at the bottom of the screen. If the device is moving, the name of the street displayed is updated every time the device moves onto a different street.
How it works¶
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how the current street name is obtained and displayed.
1private var dataSource: DataSource? = null
2 private val dataSourceListener = object : DataSourceListener() {
3 override fun onNewData(dataType: EDataType) {
4 if (dataType != EDataType.ImprovedPosition)
5 return
6 var text = ""
7 SdkCall.execute execute@{
8 val lastData = dataSource?.getLatestData(dataType) ?: return@execute
9 val improvedPositionData = ImprovedPositionData(lastData)
10 val roadAddress = improvedPositionData.roadAddress ?: return@execute
11 roadAddress.format()?.let let@{
12 val df = DecimalFormat("#.##")
13 df.roundingMode = RoundingMode.CEILING
14 if (it.isEmpty())
15 {
16 text = "Current street name not available."
17 return@let
18 }
19 text = "Current street name: $it"
20 val speedLimit = (improvedPositionData.roadSpeedLimit * 3.6).toInt()
21 if (speedLimit != 0)
22 {
23 text += "\nRoad speed limit: $speedLimit km/h"
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 Util.postOnMain {
28 currentStreetNameView.apply {
29 if (!isVisible)
30 {
31 visibility = View.VISIBLE
32 }
33 this.text = text
34 }
35 }
36 }
37}
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(),
an instance ofprivate val dataSourceListener = object : DataSourceListener() {
is created.dataSourceListener automatically receives updates, such as
changes in the device position.override fun onNewData(dataType: EDataType) { } }onNewData() function
within the dataSourceListener.val roadAddress = improvedPositionData.roadAddress ?: return@execute
and set along with the speed limit for the current segmentimprovedPositionData.roadSpeedLimit 1override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
2{
3 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
4 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
5 gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface)
6 currentStreetNameView = findViewById(R.id.current_street_name)
7 followCursorButton = findViewById(R.id.followCursor)
8 gemSurfaceView.onDefaultMapViewCreated = {
9 enableGPSButton()
10 }
11 SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = {
12 val hasPermissions = PermissionsHelper.hasPermissions(this, permissions)
13 if (hasPermissions) {
14 SdkCall.execute {
15 startImprovedPositionListener()
16 }
17 } else {
18 requestPermissions(this)
19 }
20 }
21 if (!Util.isInternetConnected(this))
22 {
23 showDialog("You must be connected to internet!")
24 }
25}
override fun onCreate() function checks if internet access is
available, and then requests high precision position permission from the
user, if necessary. Then it calls the
startImprovedPositionListener() function after the map is loaded.1private fun startImprovedPositionListener() {
2 if (gemSurfaceView.mapView?.isFollowingPosition() != true)
3 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.followPosition()
4 if (dataSource == null)
5 dataSource = DataSourceFactory.produceLive()
6 dataSource?.addListener(dataSourceListener, EDataType.ImprovedPosition)
7}
startImprovedPositionListener() function instantiates a high
precision position listenerdataSource?.addListener(dataSourceListener, EDataType.ImprovedPosition)
which will be called automatically every time new position data
is available, such as, for example, the position (longitude, latitude)
of the device has changed.gemSurfaceView.mapView?.followPosition(), and it also instantiates
a connection to the dataSource, if not already instantiated:dataSource = DataSourceFactory.produceLive()1private fun enableGPSButton() { 2 // Set actions for entering/ exiting following position mode. 3 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.apply { 4 onExitFollowingPosition = { 5 followCursorButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE 6 } 7 onEnterFollowingPosition = { 8 followCursorButton.visibility = View.GONE 9 } 10 // Set on click action for the GPS button. 11 followCursorButton.setOnClickListener { 12 SdkCall.execute { followPosition() } 13 } 14 } 15}
enableGPSButton() causes a round purple button to appear in the lower
right corner of the screen, whenever the simulation is active and
the camera is not following the green arrow. If the user pushes this button,
the followPosition() function is called, and thus the camera
starts to follow the green arrow once again.