Route Alarms¶
In this guide you will learn how to simulate navigation
along a computed route rendered on an interactive map,
from a departure position to a desired destination.
The map is fully 3D, supporting pan, pinch-zoom,
rotate and tilt.
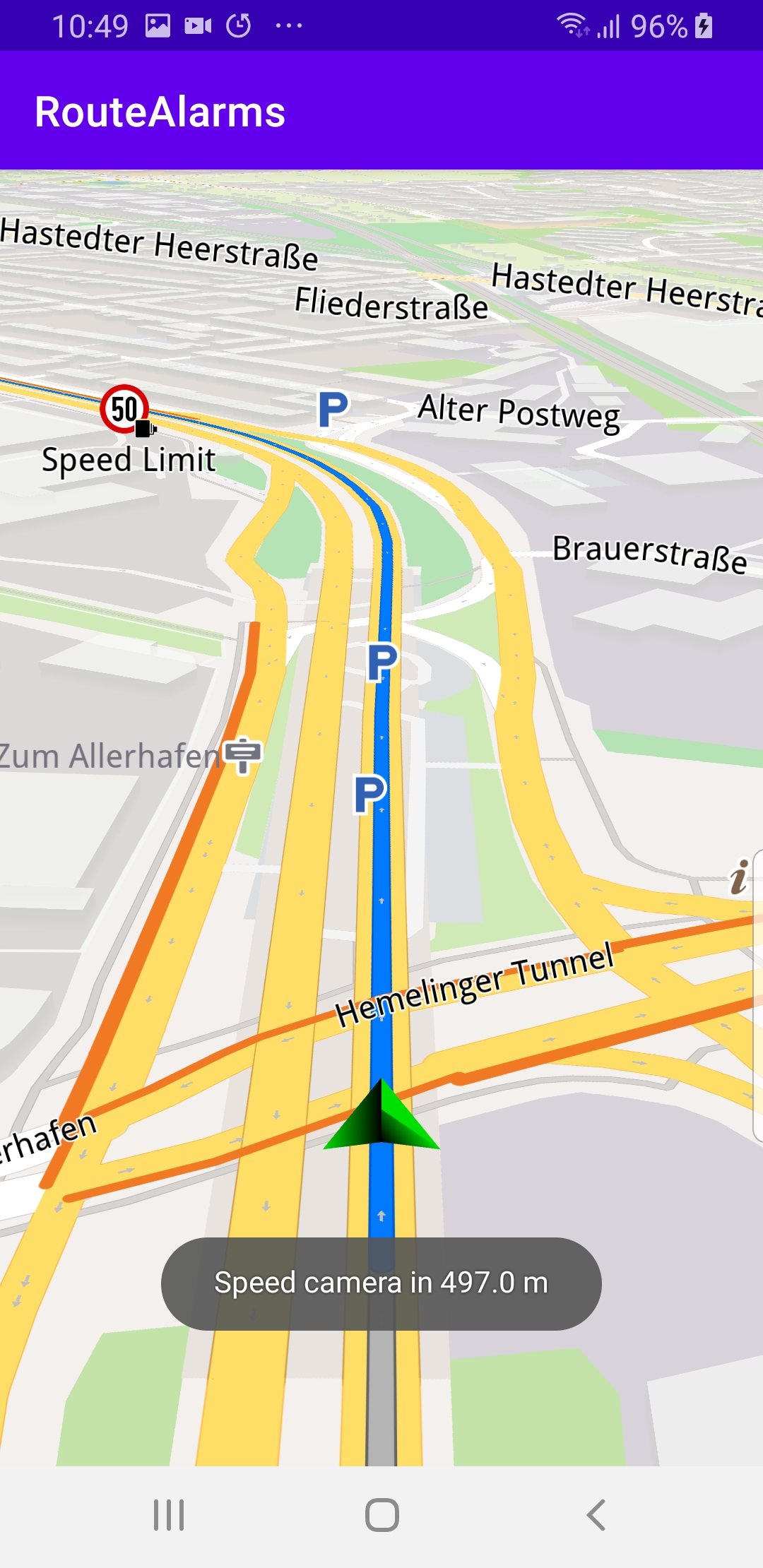
The navigation includes pop-up speed camera warnings.
Setup¶
First, get an API key token, see the
Getting Started guide.
Download the RouteAlarms project archive file or clone the project with Git
See the Configure Android Example guide.
Run the example¶
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
|
|||
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the
android device.
How it works¶
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how simulated navigation along a computed route with speed camera warning alarms works.
1private val navigationService = NavigationService()
A NavigationService() is instantiated, which carries out
both simulated navigation and real navigation.
1private val navigationListener = NavigationListener.create(
2 onNavigationStarted = {
3 SdkCall.execute {
4 // Set the overlay for which to be notified.
5 setAlarmOverlay(ECommonOverlayId.Safety)
6 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.let { mapView ->
7 mapView.preferences?.enableCursor = false
8 navRoute?.let { route ->
9 mapView.presentRoute(route)
10 }
11 enableGPSButton()
12 mapView.followPosition()
13 }
14 }
15 }
16)
The
NavigationListener receives event updates (notifications) from
the navigation service, during navigation or simulation on a route, such as
when the destination is reached, or when the route to the desired destination
has been recomputed, because a detour away from the original route was taken.Only the
onNavigationStarted listener is instantiated in this case. 1private val alarmListener = AlarmListener.create(
2 onOverlayItemAlarmsUpdated = {
3 SdkCall.execute execute@{
4 // Get the maximum distance until an alarm is reached.
5 val maxDistance = alarmService?.alarmDistance ?: 0.0
6 // Get the overlay items that are present and relevant.
7 val markerList = alarmService?.overlayItemAlarms
8 if (markerList == null || markerList.size == 0) return@execute
9 // Get the distance to the closest alarm marker.
10 val distance = markerList.getDistance(0)
11 if (distance <= maxDistance) {
12 // If you are close enough to the alarm item, notify the user.
13 Toast.makeText(
14 this@MainActivity,
15 "Speed camera in $distance m",
16 Toast.LENGTH_LONG
17 ).show()
18 // Remove the alarm listener if you want to notify only once.
19 alarmService?.setAlarmListener(null)
20 }
21 }
22 }
23)
Also instantiated a
onOverlayItemAlarmsUpdated alarm listener to get
speed camera notifications from the navigation service, including
the distance to the next speed camera. 1@Suppress("SameParameterValue")
2private fun setAlarmOverlay(overlay: ECommonOverlayId) {
3 SdkCall.execute {
4 alarmService = AlarmService.produce(alarmListener)
5 alarmService?.alarmDistance = 500.0 // meters
6 val availableOverlays = OverlayService().getAvailableOverlays(null)?.first
7 if (availableOverlays != null) {
8 for (item in availableOverlays) {
9 if (item.uid == overlay.value) {
10 alarmService?.overlays?.add(item.uid)
11 }
12 }
13 }
14 }
15}
When the
navigationListener is instantiated above, it calls
this function which sets the alarmDistance
to 500 meters in the AlarmService.That is how the
alarmListener instantiated above knows
at what distance prior to the speed camera to
display the notification it received.1private val routingProgressListener = ProgressListener.create(
2 onStarted = {
3 progressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE
4 },
5 onCompleted = { _, _ ->
6 progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
7 },
8 postOnMain = true
9)
Define a listener to indicate when the route computation is completed,
so real or simulated navigation (simulated in this case) can start.
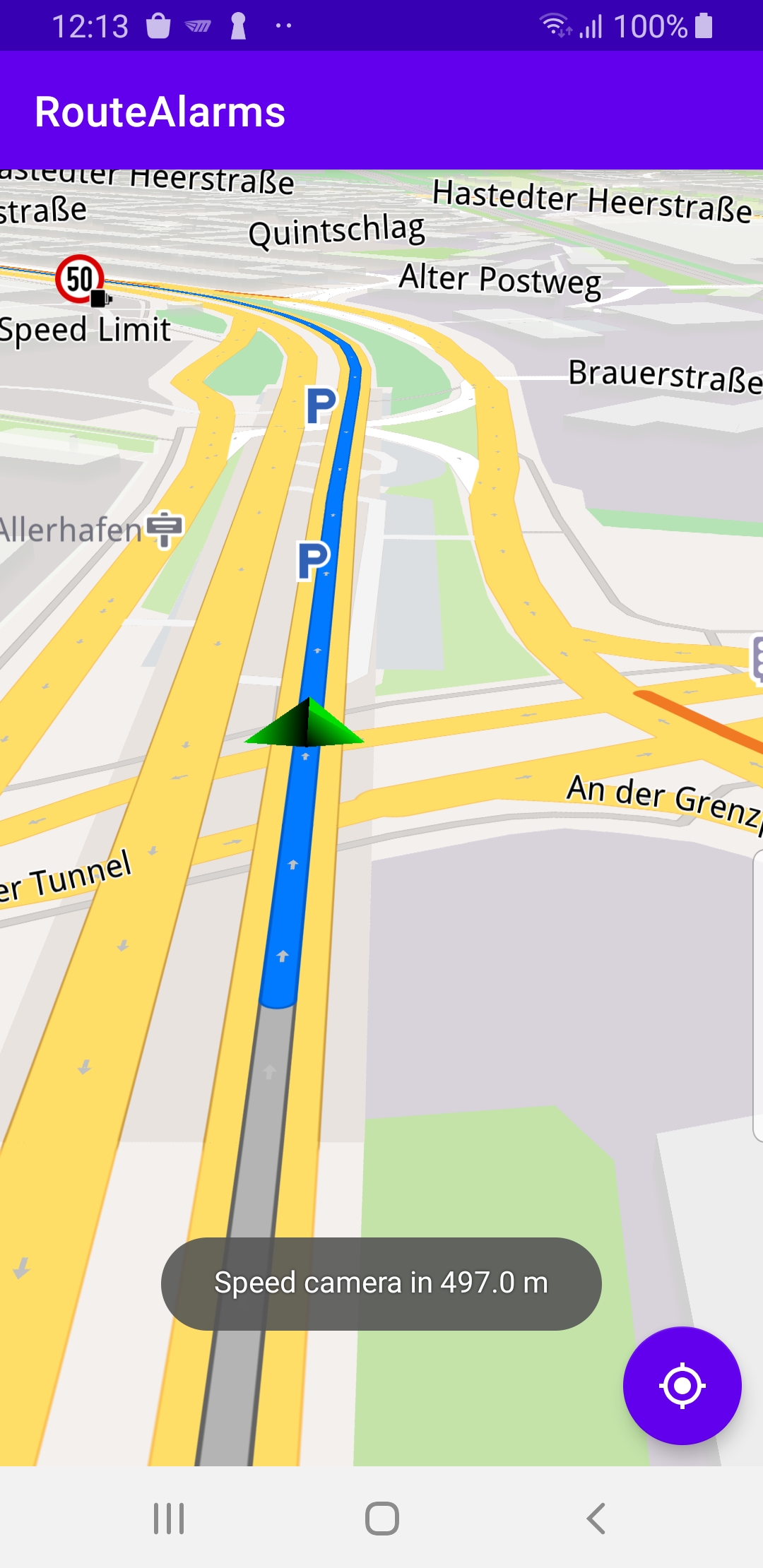
When navigation is started,
mapView.followPosition() causes
the camera to follow the green arrow.If the user pans (moves) the map to another location,
the camera no longer follows the green arrow.
|
|||
1private fun enableGPSButton() {
2 // Set actions for entering/ exiting following position mode.
3 gemSurfaceView.mapView?.apply {
4 onExitFollowingPosition = {
5 followCursorButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
6 }
7 onEnterFollowingPosition = {
8 followCursorButton.visibility = View.GONE
9 }
10 // Set on click action for the GPS button.
11 followCursorButton.setOnClickListener {
12 SdkCall.execute { followPosition() }
13 }
14 }
15}
enableGPSButton() causes a round purple button to appear in the lower
right corner of the screen, whenever the simulation is active and
the camera is not following the green arrow. If the user pushes this button,
the followPosition() function is called, and thus the camera
starts to follow the green arrow once again.1private fun startSimulation() = SdkCall.execute {
2 val waypoints = arrayListOf(
3 Landmark("A", 53.056306247688326, 8.882596560149098),
4 Landmark("B", 53.06178963549359, 8.876610724727849)
5 )
6 navigationService.startSimulation(waypoints, navigationListener, routingProgressListener)
7}
The starting, or departure point of the route is the first waypoint in a list of
2 or more Landmarks (2 in this case), each containing a name, latitude (in degrees)
and longitude (in degrees). The destination point is the last waypoint in the list.
1override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
2 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
3 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
4 progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar)
5 gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface)
6 followCursorButton = findViewById(R.id.followCursor)
7
8 SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = onMapDataReady@{ isReady ->
9 if (!isReady) return@onMapDataReady
10 // Defines an action that should be done when
11 // the world map is ready (updated / loaded).
12 startSimulation()
13 }
14 SdkSettings.onApiTokenRejected = {
15 Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "TOKEN REJECTED",
16 Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
17 }
18 if (!Util.isInternetConnected(this)) {
19 Toast.makeText(this, "You must be connected to internet!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
20 }
21}
The
MainActivity overrides the onCreate() function which checks that
internet access is available, and then, when the map is instantiated
and ready, starts the simulation: startSimulation().