Range Finder
In this guide you will learn how to render all possible paths on the map, to see the furthest you can travel in any direction, in a specific amount of time which you specify in seconds.
Setup
- Get your Magic Lane API key token: if you do not have a token, see the Getting Started guide
- Download the Maps & Navigation SDK for Android archive file
- Download the RangeFinder project archive file or clone the project with Git
- See the Configure Android Example guide
Run the example
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the android device.
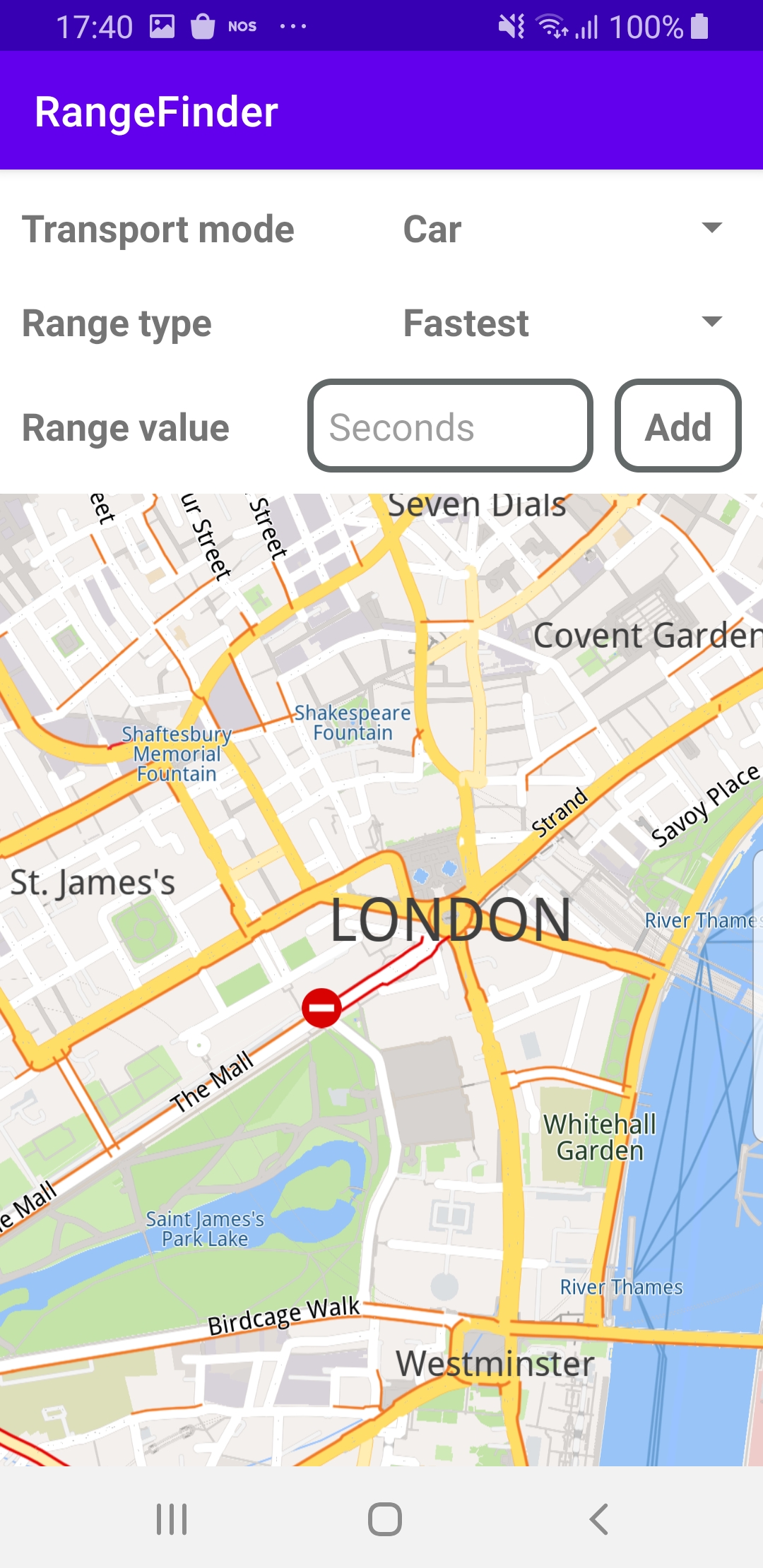
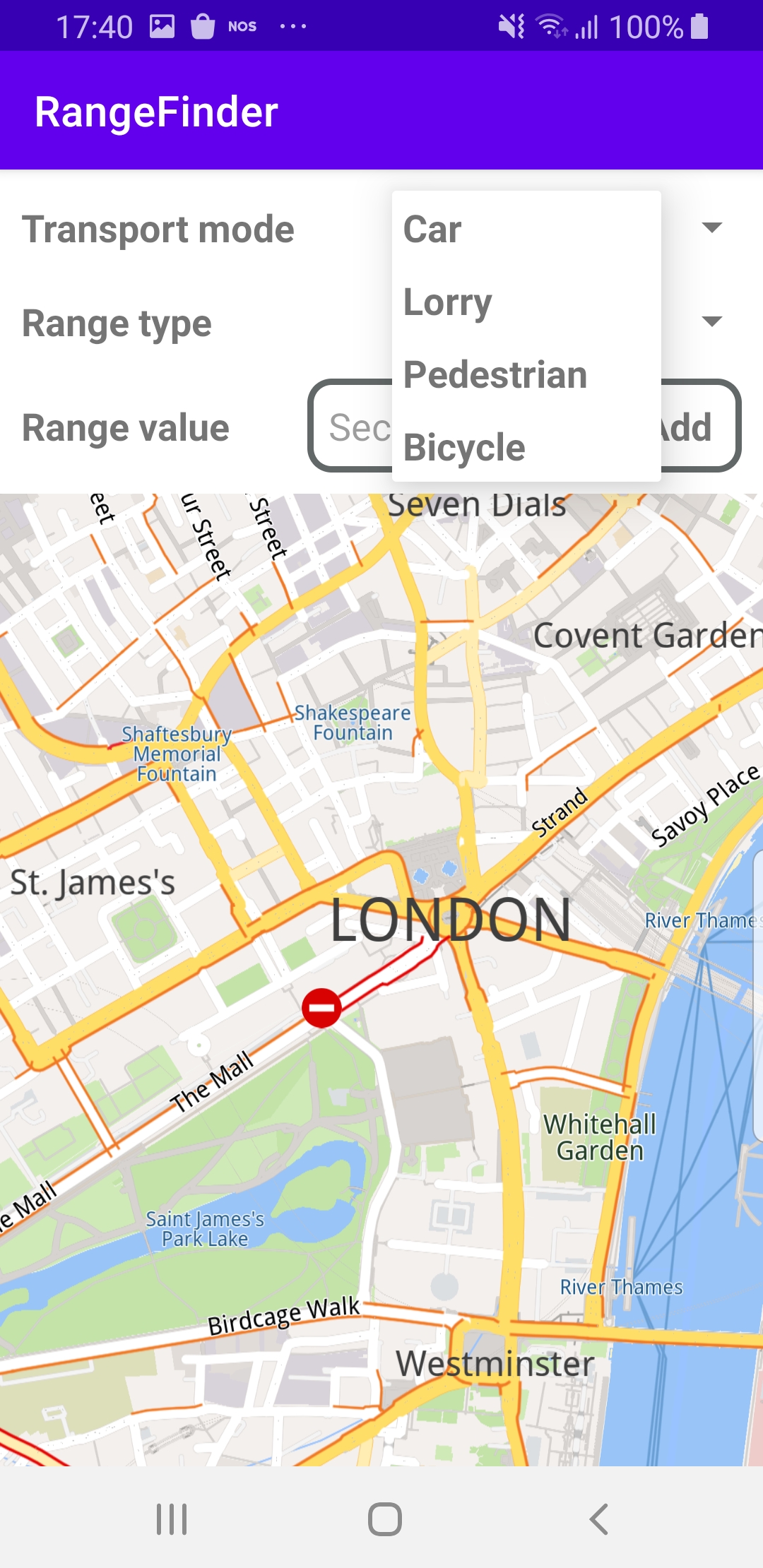
The center screenshot shows the possible transport modes to select from: car, lorry(truck), pedestrian, bicycle.
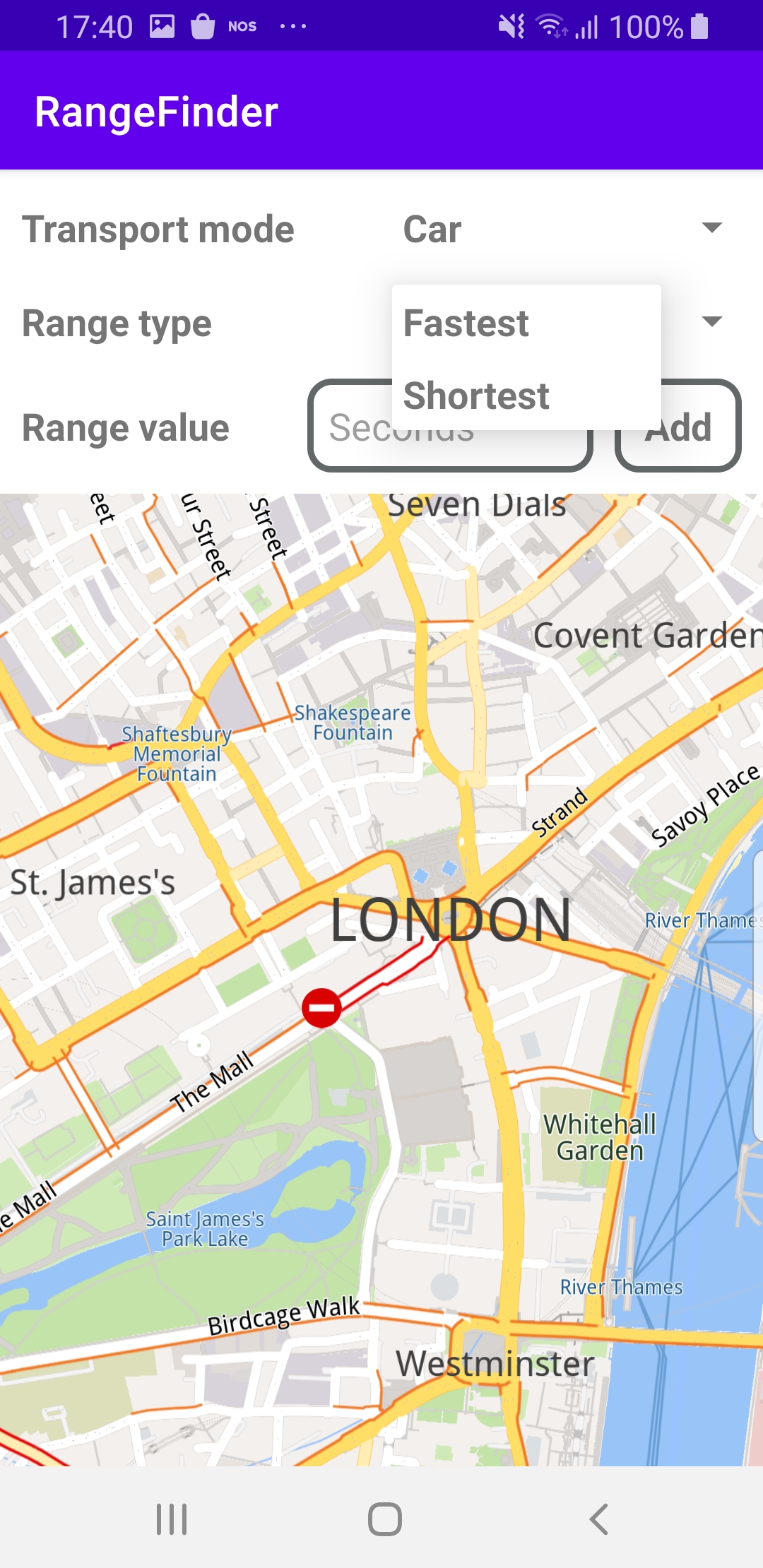
The screenshot on the right shows the possible range types to select from: fastest or shortest.
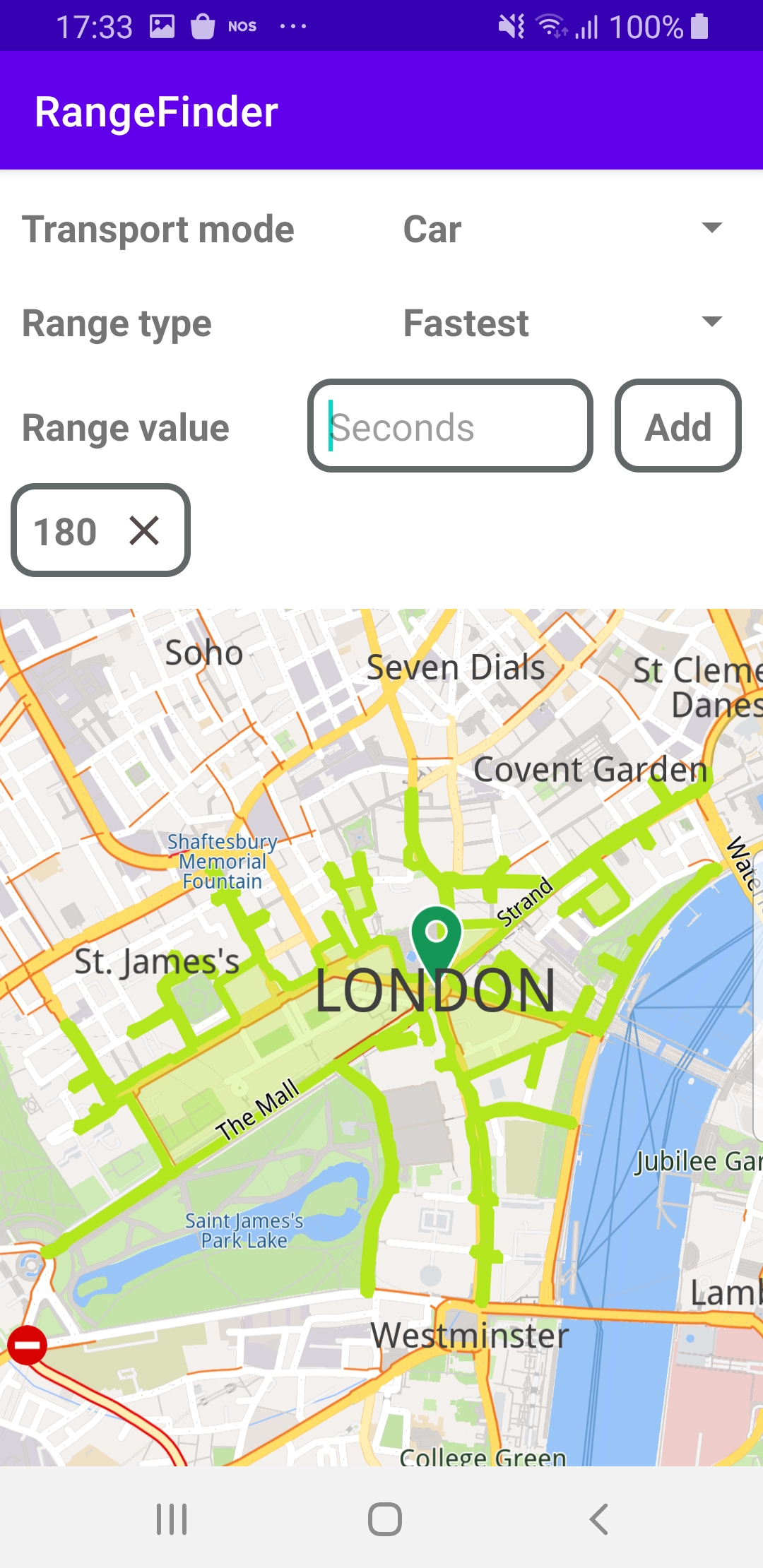
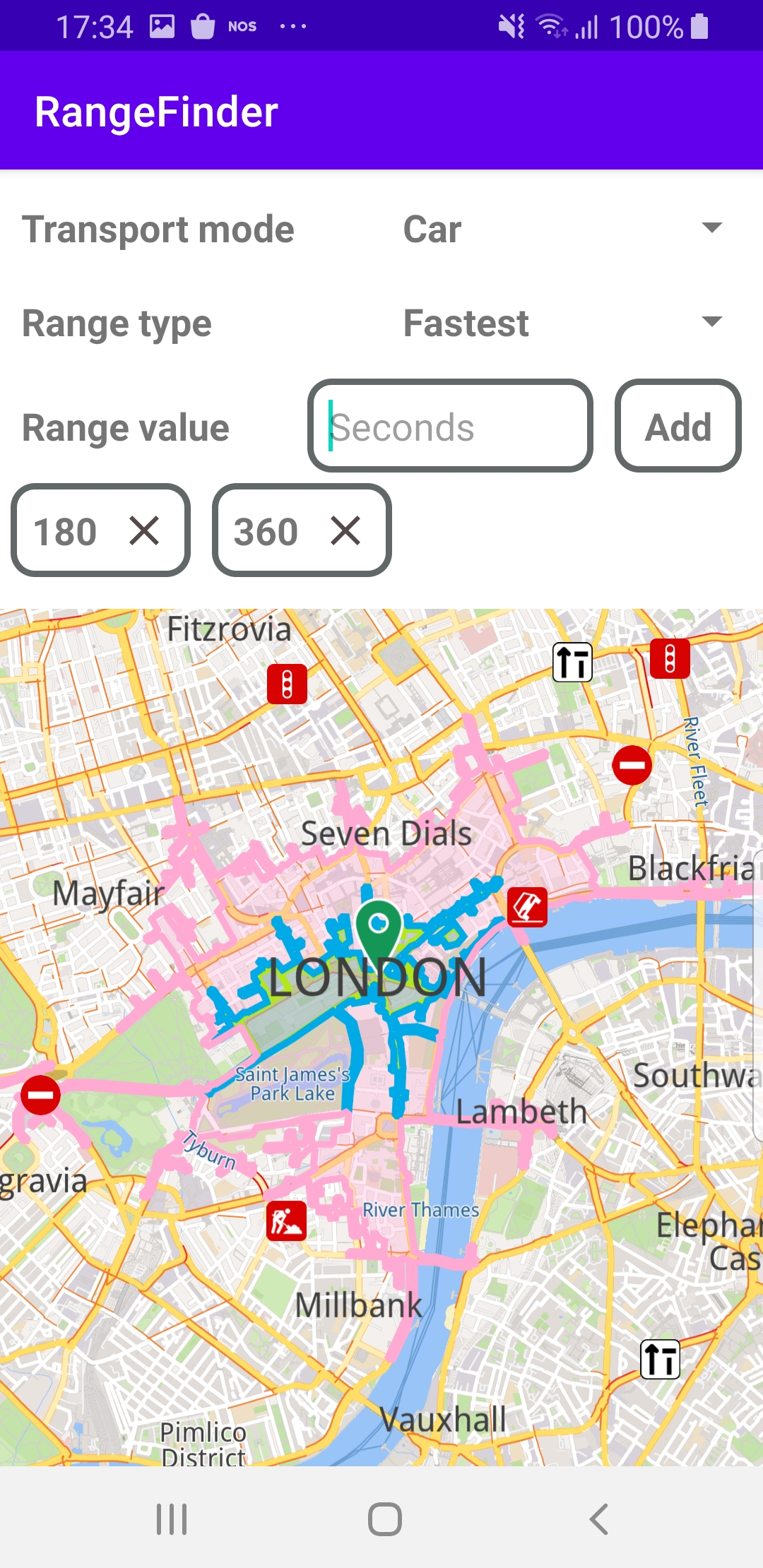
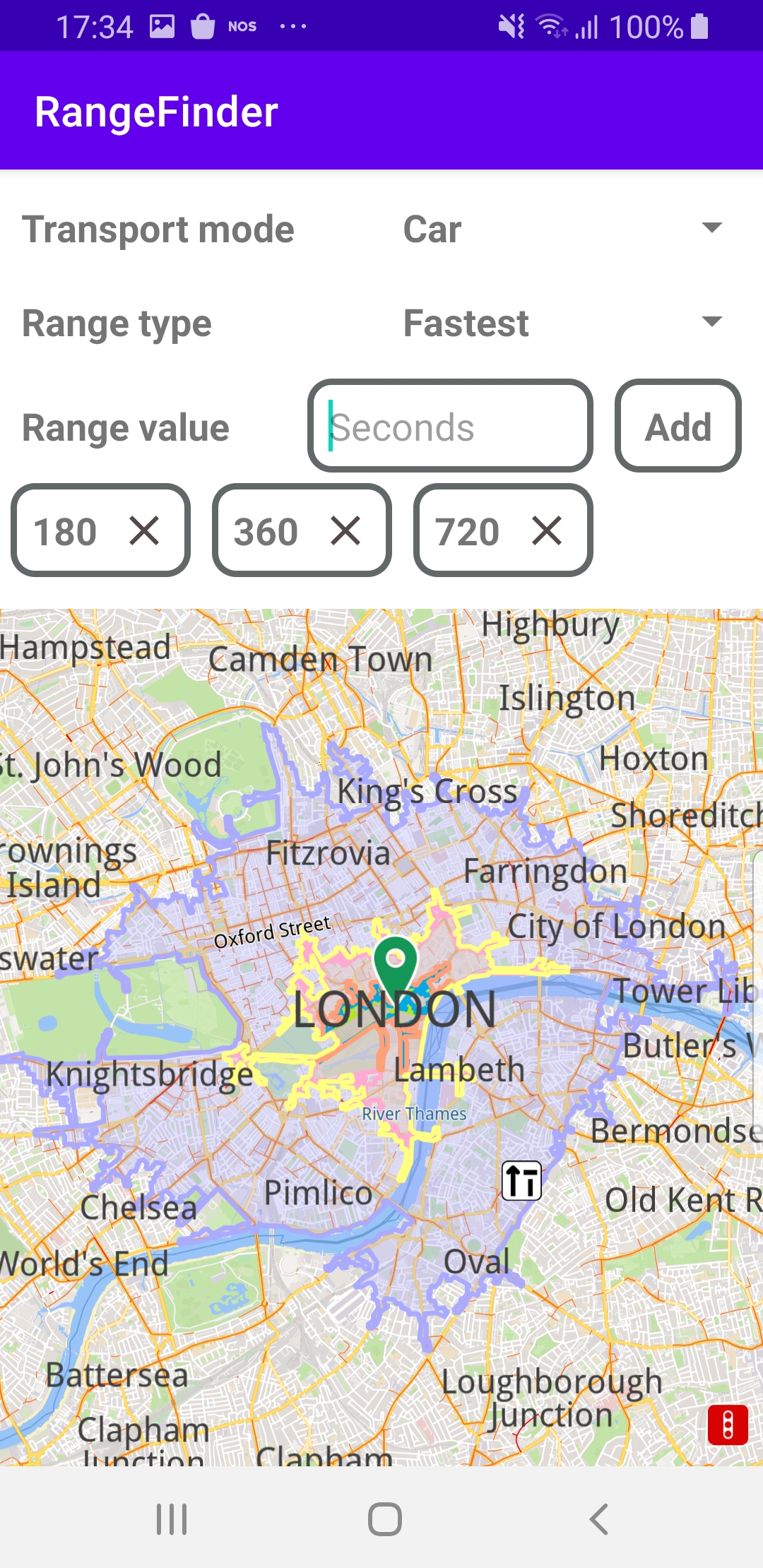
The left screenshot shows the maximum range, in green, for driving a car for 180 seconds in any direction from a location in London.
The center screenshot shows the maximum range, in pink, for driving a car for 360 seconds in any direction from a location in London.
The right screenshot shows the maximum range, in blue, for driving a car for 720 seconds in any direction from a location in London.
How it works
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how the range is rendered on the map based on the transportation mode and time input by the user.
private fun calculateRange(transportMode: ERouteTransportMode,
routeType: ERouteType,
ranges: ArrayList<Int>)
{
SdkCall.execute {
routingService.preferences.transportMode = transportMode
routingService.preferences.routeType = routeType
routingService.preferences.setRouteRanges(ranges, 100)
routingService.calculateRoute(arrayListOf(Landmark("London", 51.5073204, -0.1276475)))
}
}
The calculateRange() function first sets the user-selected transportMode, routeType and ranges in the routingService, then calculates all possible routes from a specified (latitude, longitude) position using calculateRoute().
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
rootView = findViewById(R.id.root_view)
progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progressBar)
gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface)
transportModeSpinner = findViewById(R.id.transport_mode_spinner)
rangeTypeSpinner = findViewById(R.id.range_type_spinner)
rangeValueEditText = findViewById(R.id.range_value_edit_text)
addButton = findViewById(R.id.add_button)
currentRangesScrollContainer = findViewById(R.id.current_ranges_scroll_container)
currentRangesContainer = findViewById(R.id.current_ranges_buttons_container)
rangeViewsContainer = findViewById(R.id.range_container)
setConstraints(resources.configuration.orientation)
SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = { isReady ->
if (isReady)
{
// Defines an action that should be done when
// the world map is ready (Updated/ loaded).
progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
rangeViewsContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE
prepareViews()
}
}
SdkSettings.onApiTokenRejected = {
showDialog("TOKEN REJECTED")
}
if (!Util.isInternetConnected(this))
{
showDialog("You must be connected to internet!")
}
}
The MainActivity overrides the onCreate function, which checks that internet access is available, and calls the prepareViews function which defines a button to trigger the route calculation and the rendering of the highlighted area on the map, showing the maximum range that can be traveled in any direction in the amount of time and travel mode specified by the user.
private fun prepareViews()
{
val transportTypesList = mutableListOf(getString(R.string.car),
getString(R.string.lorry), getString(R.string.pedestrian), getString(R.string.bicycle))
val adapter = ArrayAdapter(this, R.layout.spinner_item, R.id.spinner_text, transportTypesList)
transportModeSpinner.adapter = adapter
transportModeSpinner.onItemSelectedListener = object : AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener
{
override fun onItemSelected(parent: AdapterView<*>?, view: View?, position: Int, id: Long)
{
onTransportModeSelected(position)
}
override fun onNothingSelected(parent: AdapterView<*>?) = Unit
}
transportModeSpinner.setSelection(0)
addButton.setOnClickListener {
if (rangeValueEditText.text.isNotEmpty())
{
currentSelectedRanges.add(rangeValueEditText.text.toString().toInt())
SdkCall.execute { calculateRanges() }
rangeValueEditText.setText("")
hideKeyboard()
}
else
{
showDialog("Range value is empty!")
}
}
}
The prepareViews function sets a listener for the button to call calculateRanges(), which calls the calculateRange() function shown above, to compute the routes, if the user enters a valid range value, in seconds.
private val routingService = RoutingService(
onStarted = {
progressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE
addButton.visibility = View.GONE
},
onCompleted = { routes, errorCode, _ ->
progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
addButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
when (errorCode)
{
GemError.NoError ->
{
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.presentRoutes(routes, displayBubble = true)
}
}
GemError.Cancel ->
{ // The routing action was cancelled.
}
else ->
{
currentSelectedRanges.removeAt(currentSelectedRanges.size - 1)
showDialog("Routing service error: ${GemError.getMessage(errorCode)}")
}
}
}
)
The routingService() computes the routes and calls presentRoutes() to highlight the ranges on the map.
Android Examples
Maps SDK for Android Examples can be downloaded or cloned with Git