GPX Route Simulation
In this guide you will learn how to load a GPX route, render it on the map, and then simulate navigation along that route.
Setup
- Get your Magic Lane API key token: if you do not have a token, see the Getting Started guide
- Download the Maps & Navigation SDK for Android archive file
- Download the GPXRouteSimulation project archive file or clone the project with Git
- See the Configure Android Example guide
Run the example
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the android device.
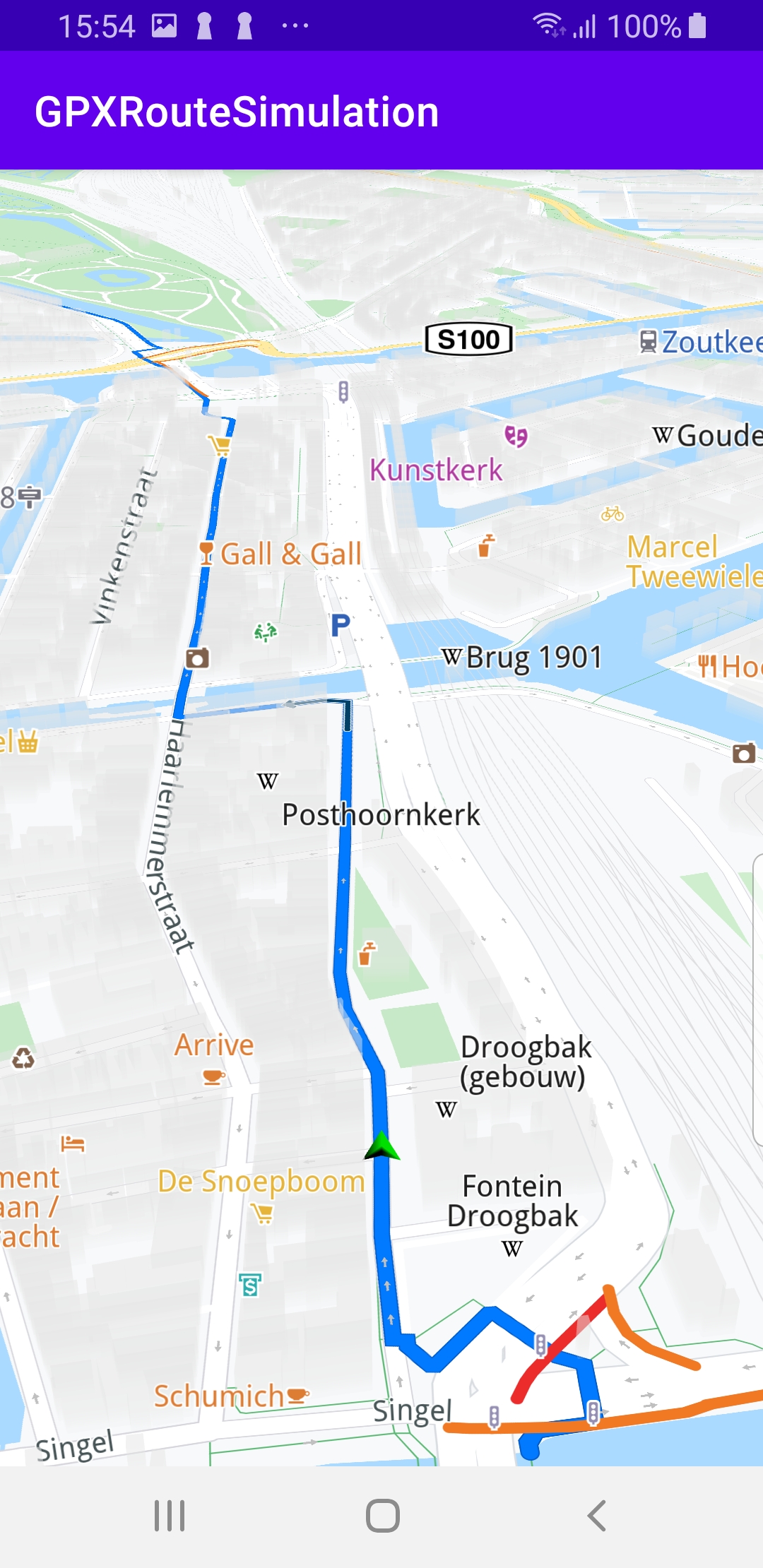
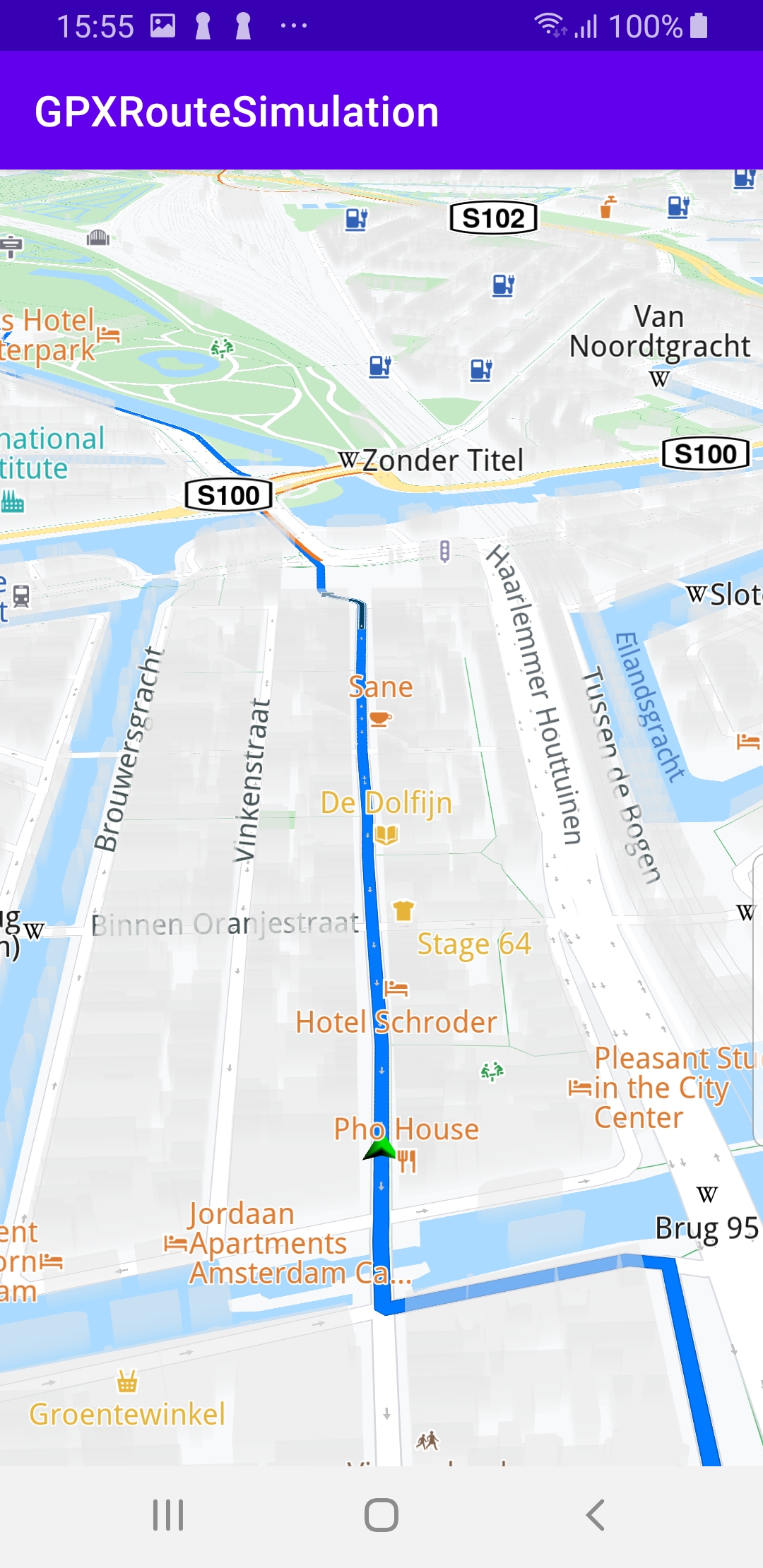
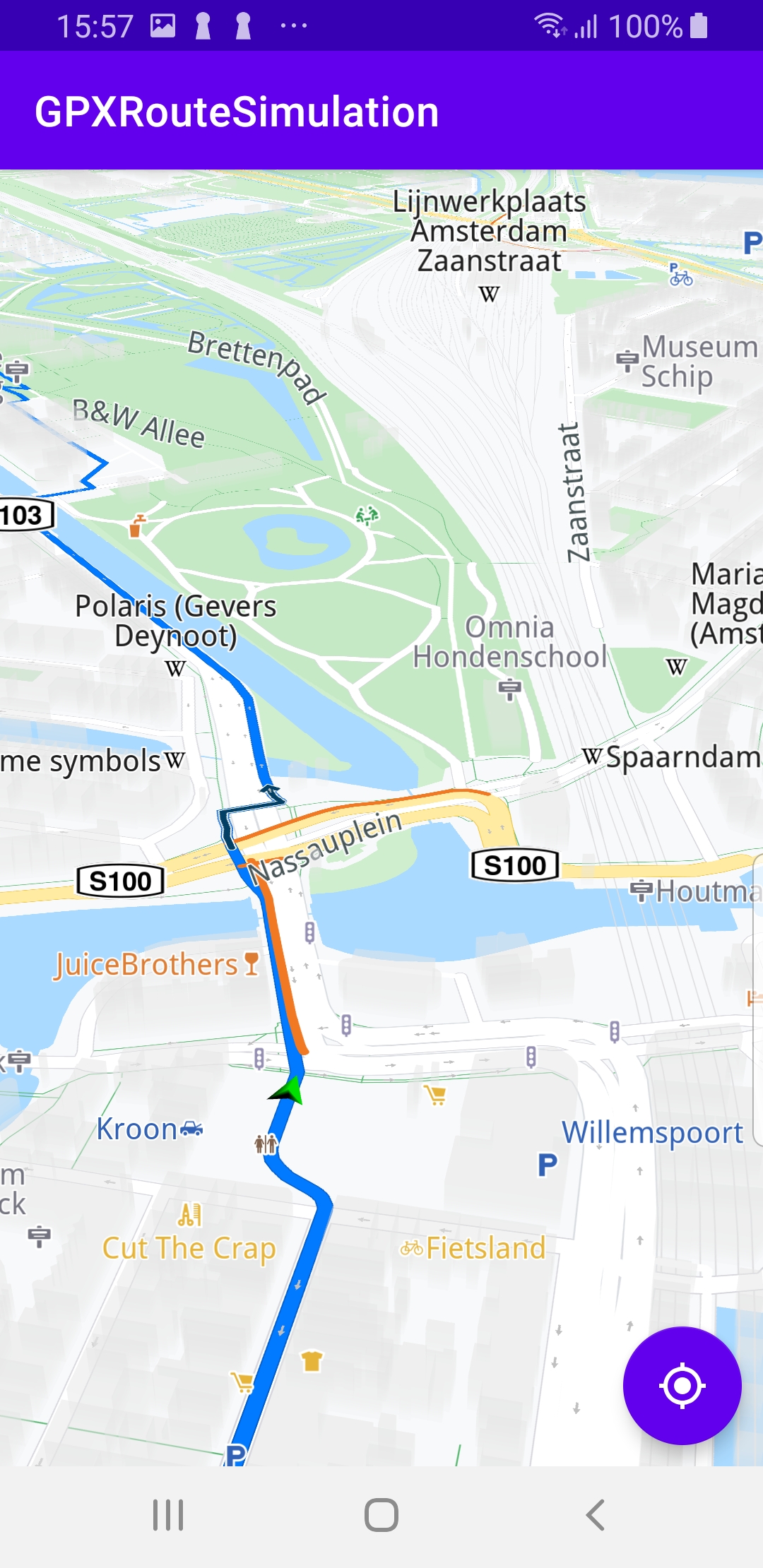
A GPX route is loaded and rendered on the map. Navigation along the GPX route is simulated. If a pan occurs, a button appears in the lower right corner of the screen. Pressing this button resumes following/tracking the green navigation simulation arrow along the route.
How it works
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how the GPX route is imported and rendered on the map.
In the class MainActivity:AppCompatActivity(), an instance of
val routingService = RoutingService() is created.
The override fun onCreate() calls the calculateRouteFromGPX() function after the map is loaded.
private fun calculateRouteFromGPX() = SdkCall.execute {
val gpxAssetsFilename = "gpx/test_route.gpx"
// Opens GPX input stream.
val input = applicationContext.resources.assets.open(gpxAssetsFilename)
// Produce a Path based on the data in the buffer.
val track = Path.produceWithGpx(input/*.readBytes()*/) ?: return@execute
// Set the transport mode to bike and calculate the route.
routingService.calculateRoute(track, ERouteTransportMode.Bicycle)
}
This function defines the name of the GPX route file name as "gpx/test_route.gpx" which is found in the assets/ directory of this example.
Next, the file is opened, and a route is generated from the GPX data.
track = Path.produceWithGpx(input)
The routing service is used to calculate the route for bicycles.
routingService.calculateRoute(track, ERouteTransportMode.Bicycle)
Inside the val routingService = RoutingService(), the simulation is started automatically when the route computation is completed, using the first (index 0) route routes[0] in the resulting route list:
GemError.NoError -> {
val route = routes[0]
SdkCall.execute {
navigationService.startSimulationWithRoute(
route,
navigationListener,
routingProgressListener
)
}
}
The purpose of the val navigationListener: NavigationListener is to detect when a user-driven pan of the map occurred.
private val navigationListener: NavigationListener
= NavigationListener.create(
onNavigationStarted = {
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.let { mapView ->
mapView.preferences?.enableCursor = false
navRoute?.let { route ->
mapView.presentRoute(route)
}
enableGPSButton()
mapView.followPosition()
}
}
}
)
In that case, the camera no longer follows/tracks the green navigation simulation arrow, and a “GPS” button becomes visible in the lower right corner of the screen.
When the user presses this button, the button disappears and the camera resumes following/tracking the green navigation simulation arrow.
Android Examples
Maps SDK for Android Examples can be downloaded or cloned with Git