Public Transit Routing
In this guide you will learn how to render an interactive map, compute and render a public transit route on the map, and fly to the route.
Setup
- Get your Magic Lane API key token: if you do not have a token, see the Getting Started guide
- Download the Maps & Navigation SDK for Android archive file
- Download the PublicTransitRoutingOnMap project archive file or clone the project with Git
- See the Configure Android Example guide
Run the example
In Android Studio, from the File menu, select Sync Project with Gradle Files
An android device should be connected via USB cable.
Press SHIFT+F10 to compile, install and run the example on the android device.
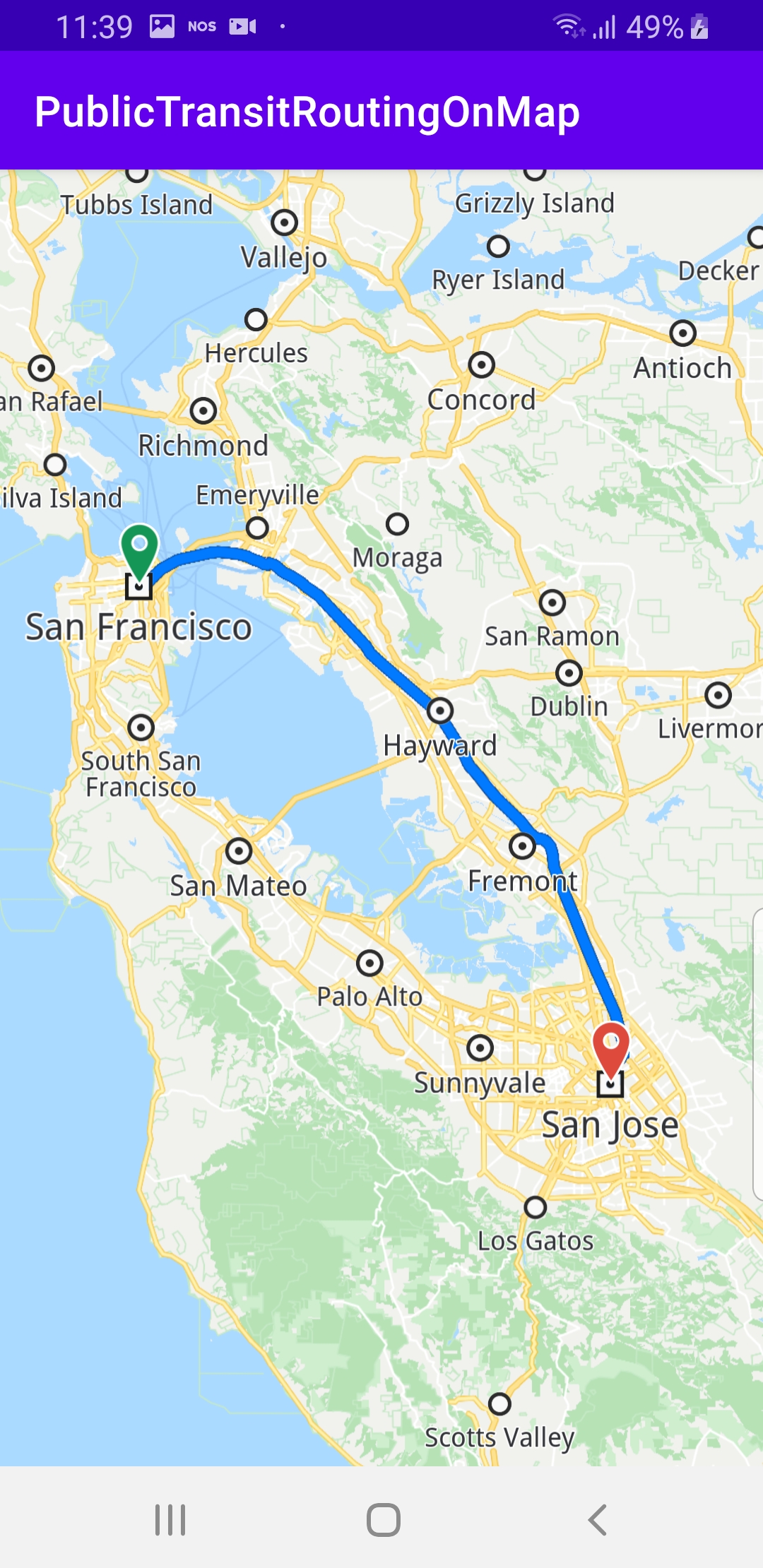
This example computes and draws a public transit route on the map and flies to it. Displays an interactive map which is fully 3D, supporting pan, pinch-zoom, rotate and tilt.
How it works
You can open the MainActivity.kt file to see how the route is computed and rendered on the map.
// Kotlin code
private fun calculateRoute() {
val waypoints = arrayListOf(
Landmark("San Francisco", Coordinates(37.77903, -122.41991)),
Landmark("San Jose", Coordinates(37.33619, -121.89058))
)
when (val gemError = SdkError.fromInt(reason)) {
SdkError.NoError -> {
SdkCall.execute {
// Get the main route from the ones that were found.
val mainRoute: Route? = if (routes.size > 0) {
routes[0]
} else {
null
}
// Add routes to the map.
addRoutes(routes)
if (mainRoute != null) {
flyToRoute(mainRoute)
}
}
}
}
}
routingService.preferences.setTransportMode(ERouteTransportMode.Public)
routingService.calculateRoute(waypoints)
}
private fun addRoutes(routes: ArrayList<Route>) {
for (routeIndex in 0 until routes.size) {
val route = routes[routeIndex]
// Add the route to the map so it can be displayed.
mapView?.preferences()?.routes()?.add(route, routeIndex == 0)
}
}
private fun flyToRoute(route: Route) {
val animation = Animation()
animation.setType(EAnimation.Fly)
// Center the map on a specific route using the provided animation.
mapView?.centerOnRoute(route, Rect(), animation)
}
In the calculateRoute() function, 2 Landmark instances are defined, one for the departure, and one for the destination coordinates of the route endpoints. A route must have at least 2 Landmark instances(waypoints), but optionally can have more, for any optional additional waypoints along the route.
Next, public transport mode is selected in the routing service: routingService.preferences.setTransportMode(ERouteTransportMode.Public)
Next, the routing service computes the route, and calls the routingService.onCompleted callback with the resulting routes, as there could be more than one: routingService.calculateRoute(waypoints)
Then, addRoutes(routes) adds the routes to the map so they are rendered.
If there is at least one route, flyToRoute(mainRoute) calls the centerOnRoute() API function to fly to the selected route, such that its bounding box fits in the viewport.
Android Examples
Maps SDK for Android Examples can be downloaded or cloned with Git