Navigate Route
In this guide, you will learn how to compute a route between a departure point and a destination point, render the route on an interactive map, and then navigate along the route.
How it works
This example demonstrates the following features:
- Compute routes between a departure and destination.
- Display routes on a map and allow for multiple route alternatives.
- Begin turn-by-turn navigation along the selected route with real-time positioning.
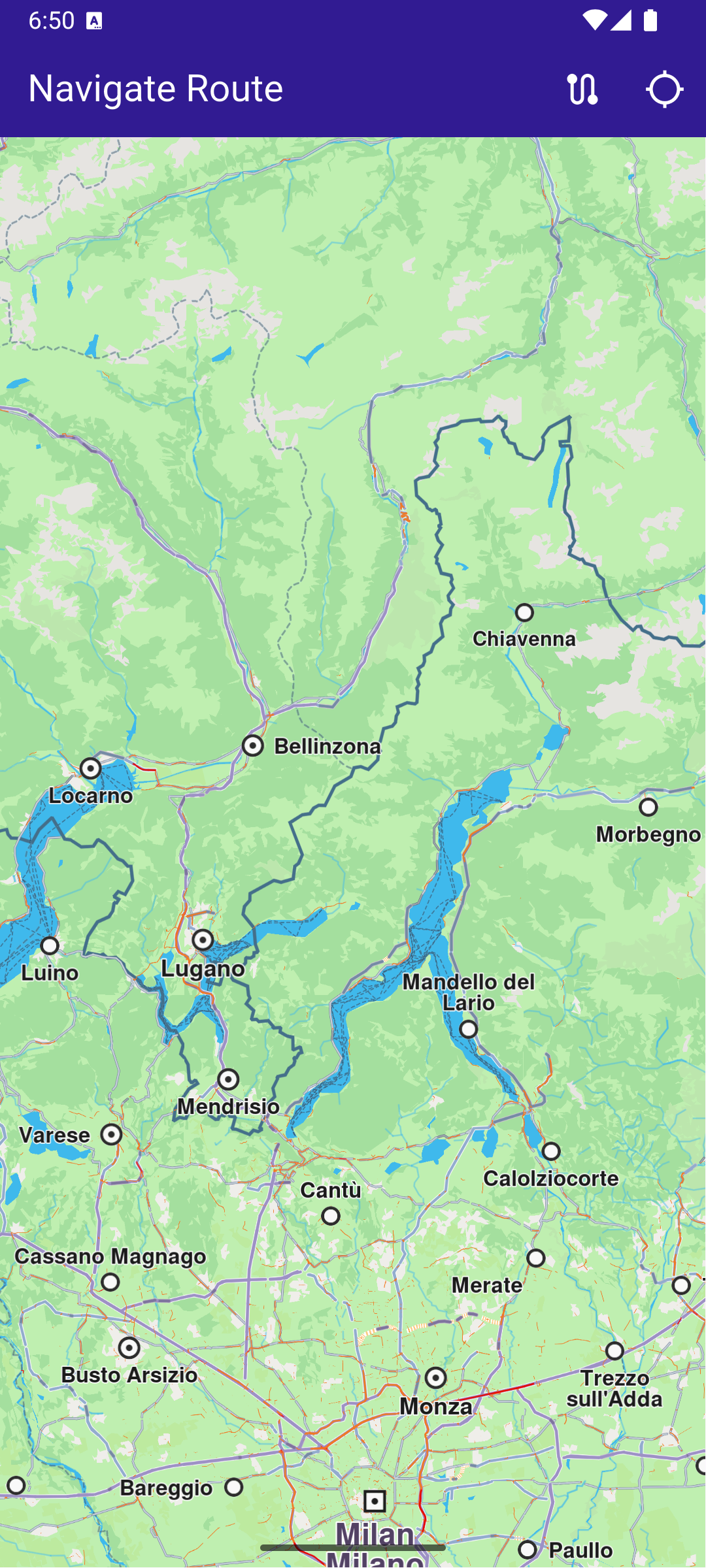
Map Initialization
This callback function is called when the interactive map is initialized and ready to use.
Building the Route
When the route button in the upper right corner is pressed, a route is computed from the current position to a preset location in Europe.
A route must have at least two waypoints, one for the departure, and one for the destination. Optionally, zero or more intermediate waypoints may be specified through which the route will pass, in order from departure to destination.
Each waypoint is a Landmark and has latitude and longitude coordinates. In this case, the current location is obtained and set in the departure landmark waypoint:
final departureLandmark = Landmark.withCoordinates(_currentLocation!);
and the destination is set to preset coordinates:
final destinationLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 52.51614, longitude: 13.37748);
then the route is calculated:
RoutingService.calculateRoute()
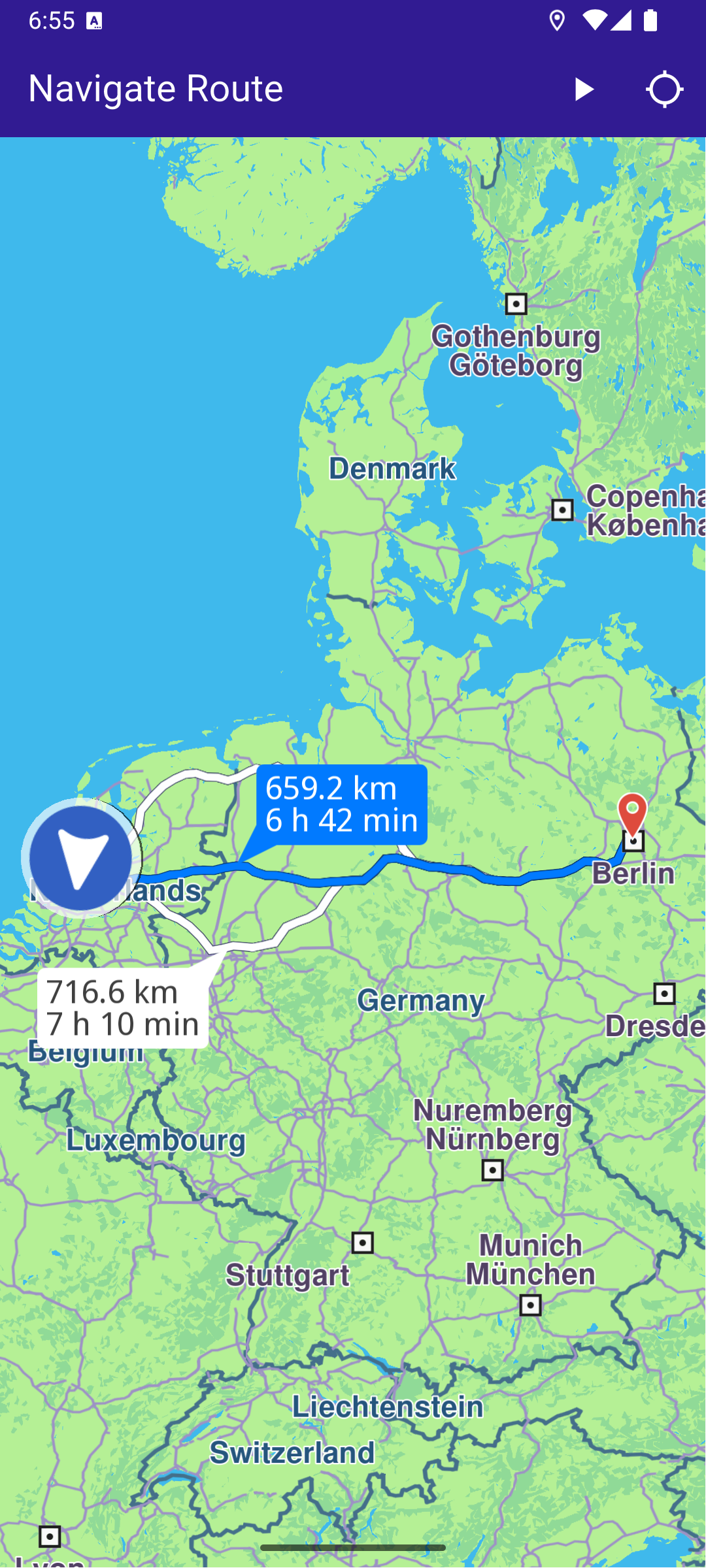
If there are no errors, the list of resulting routes (as there may be a few alternatives) is added to the map:
routesMap.add()
The first resulting route is auto-selected as the main route, and then the map is centered on the resulting routes, such that they fit in the viewport:
_mapController.centerOnRoutes(routes);
Starting Navigation
Once a route is computed, tapping the play button in the upper right starts navigation on the selected route.
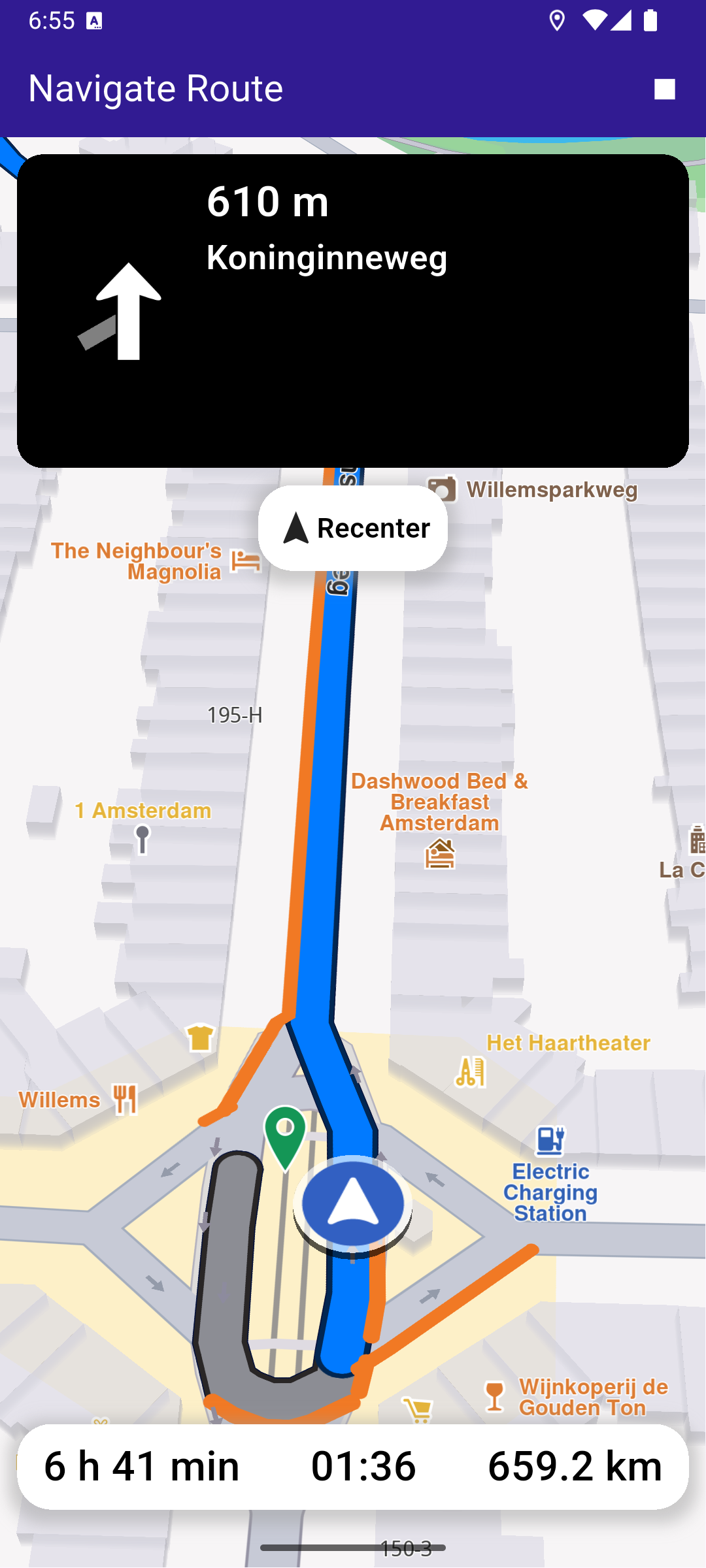
Following the Position
Follow position means the camera tracks the position of the phone/device, indicated by an arrow moving along the route on the map.
_mapController.startFollowingPosition();
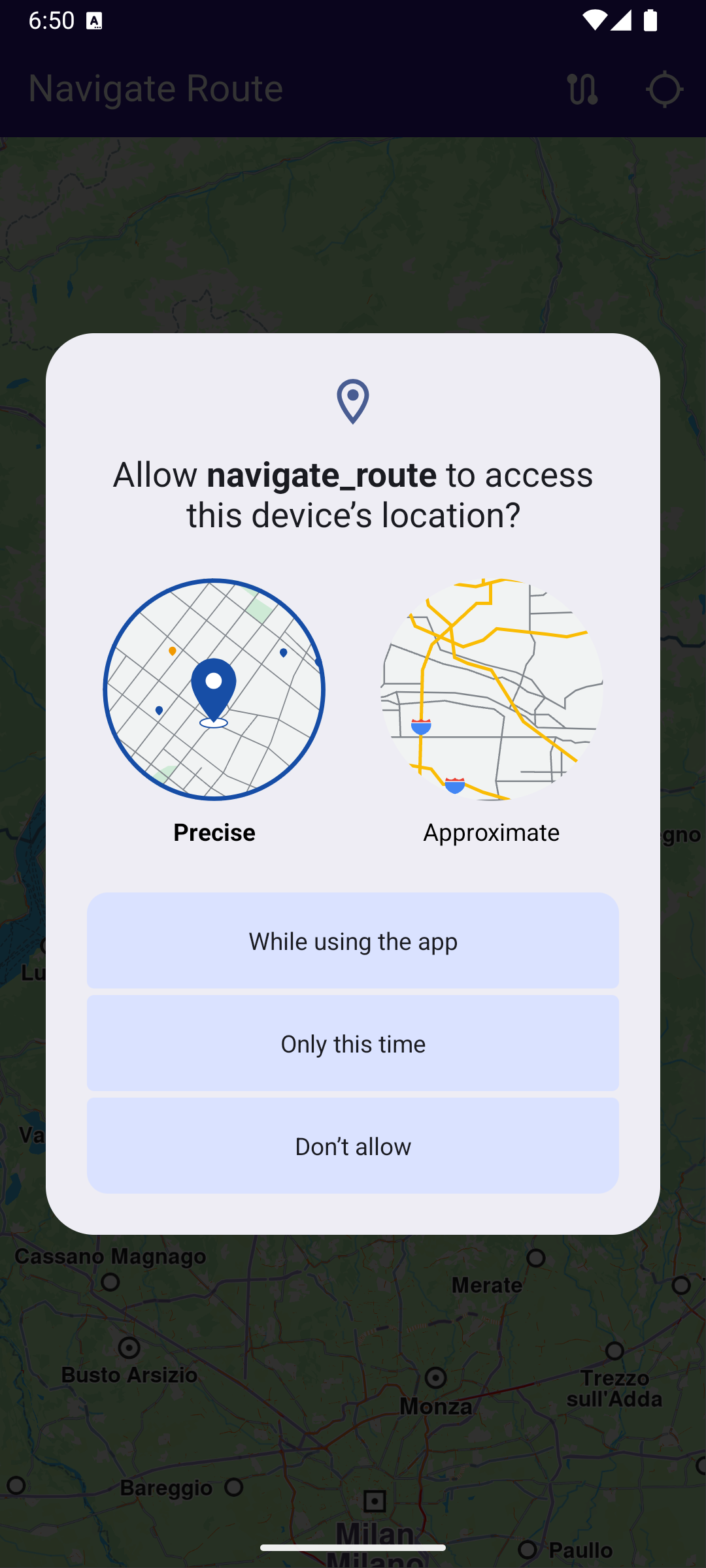
Note that if location (GPS sensor) permission was not previously granted, the app will ask for location permission from the user, as this is required for navigation.
_locationPermissionStatus = await Permission.locationWhenInUse.request();
Once permission is granted by the user, it is possible to set the location (GPS sensor) as the data source for the phone/device position on the map:
PositionService.setLiveDataSource();
If the user pans the map away from the route, clicking the Re-center button starts following position again.
Top Navigation Instruction Panel
Bottom Navigation Panel
- Android
- iOS
Add the following code to the android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml file, within the <manifest> block:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION" />This example uses the Permission Handler package. Be sure to follow the setup guide.
Add the following to ios/Runner/Info.plist inside the <dict>:
<key>NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription</key>
<string>Location is needed for map localization and navigation</string>This example uses the Permission Handler package. Follow the official setup instructions. Add this to your ios/Podfile:
post_install do |installer|
installer.pods_project.targets.each do |target|
flutter_additional_ios_build_settings(target)
target.build_configurations.each do |config|
config.build_settings['GCC_PREPROCESSOR_DEFINITIONS'] ||= [
'$(inherited)',
'PERMISSION_LOCATION=1',
]
end
end
end