Interact with the map
The Maps SDK for Flutter map view natively supports common gestures like pinch and double-tap for zooming. The table below outlines the available gestures and their default behaviors on the map.
| Gesture | Description |
|---|---|
| Tap | Tap the screen with one finger. This gesture does not have a predefined map action. |
| Double Tap | To zoom the map in by a fixed amount, tap the screen twice with one finger. |
| Long Press | Press and hold one finger to the screen. This gesture does not have a predefined map action. |
| Pan | To move the map, press and hold one finger to the screen, and move it in any direction. The map will keep moving with a little momentum after the finger was lifted. |
| 2 Finger Pan / Shove | To tilt the map, press and hold two fingers to the screen, and move them vertically. No behavior is predefined for other directions. |
| 2 Finger Tap | To align map towards north, tap the screen with two fingers. |
| Pinch | To zoom in or out continuously, press and hold two fingers to the screen, and increase or decrease the distance between them. To rotate the map continuously, press and hold two fingers to the screen, and change the angle between them either by rotating them both or by moving one of them. |
The SDK provides support in GemMapController, for informing whenever the user performs and action that could be detected. Usually, you will want to add a specific behavior to your application after a gesture was detected, like performing a selection after a tap on map.
- Tap:
registerTouchCallback - Double Tap (one finger taps the same area in quick succession):
registerDoubleTouchCallback - Two Taps (two fingers tap the screen simultaneously):
registerTwoTouchesCallback - Long Press:
registerLongPressCallback - Pan:
registerMoveCallbackobtains the two points between which the movement occurred. - Shove:
registerShoveCallbackobtains the angle, and gesture specific points - Rotate:
registerMapAngleUpdateCallback - Fling:
registerSwipeCallback - Pinch:
registerPinchCallback
The user can also listen for composite gestures:
- Tap followed by a pan:
registerTouchMoveCallback - Pinch followed by a swipe:
registerPinchSwipeCallback - Tap followed by a pinch:
registerTouchPinchCallback - Two double touches:
registerTwoDoubleTouchesCallback
Keep in mind that only one listener can be active at a time for a specific gesture. If multiple listeners are registered, only the most recently set listener will be invoked when the gesture is detected.
Use registerOnMapViewMoveStateChanged to retrieve the corresponding RectangleGeographicArea currently visible whenever the map starts or stops moving.
mapController.registerMapViewMoveStateChangedCallback((hasStarted, rect) {
if (hasStarted) {
print('Gesture started at: ${rect.topLeft.toString()} , ${rect.bottomRight.toString()}');
} else {
print('Gesture ended at: ${rect.topLeft.toString()} , ${rect.bottomRight.toString()}');
}
});
This callback is triggered when the camera is moved programmatically using methods like centerOnRoutes, followPosition, or centerOnArea, but not when the user performs a panning gesture. For detecting user behaviour, use registerMoveCallback.
The callback function is defined as void Function(bool isCameraMoving, RectangleGeographicArea area), where the isCameraMoving parameter is true when the camera is moving and false when it is stationary.
Enable and disable gestures
Touch gestures can be disabled or enabled by calling enableTouchGestures method like so:
mapController.preferences.enableTouchGestures([TouchGestures.onTouch, TouchGestures.onMove], false);
The desired gestures in the TouchGestures enum list can be enabled or disabled by setting the enabled parameter to true or false, respectively. By default, all gestures are enabled.
The TouchGestures enum supports the following gesture types:
- Basic Touch: onTouch, onLongDown, onDoubleTouch, onTwoPointersTouch, onTwoPointersDoubleTouch
- Movement: onMove, onTouchMove, onSwipe
- Pinch and Rotation: onPinchSwipe, onPinch, onRotate, onShove
- Combined Gestures: onTouchPinch, onTouchRotate, onTouchShove, onRotatingSwipe
- Other: internalProcessing
For checking if a gesture is enables the isTouchGestureEnabled method can be used:
bool isTouchEnabled = mapController.preferences.isTouchGestureEnabled(TouchGestures.onTouch);
Implement gesture listeners
Let's see an example of how gesture listeners can be registered. The GemMapController provides specific listeners for each gesture. As soon as you register a listener, it will receive all related events for that gesture via the dedicated callback.
// previous code
// attach the _onMapCreated callback to GemMap
GemMap(
onMapCreated: _onMapCreated,
appAuthorization: projectApiToken,
),
void _onMapCreated(GemMapController mapController) async {
mapController = mapController;
mapController.registerMapAngleUpdateCallback((angle) {
print("Gesture: onMapAngleUpdate $angle");
});
mapController.registerTouchCallback((point) {
print("Gesture: onTouch $point");
});
mapController.registerMoveCallback((point1, point2) {
print('Gesture: onMove from (${point1.x} ${point1.y}) to (${point2.x} ${point2.y})');
});
mapController.registerOnLongPressCallback((point) {
print('Gesture: onLongPress $point');
});
mapController.registerMapViewMoveStateChangedCallback((hasStarted, rect) {
if (hasStarted) {
print('Gesture started at: ${rect.topLeft.toString()} , ${rect.bottomRight.toString()}');
} else {
print('Gesture ended at: ${rect.topLeft.toString()} , ${rect.bottomRight.toString()}');
}
});
}
Executing resource-intensive tasks within map-related callbacks can degrade performance.
Implement map render listeners
The registerViewportResizedCallback method allows you to monitor when the map's viewport dimensions change. This can occur when the user resizes the application window or changes the orientation of the device. In this callback, you receive a Rectangle<int> object representing the new viewport size.
mapController.registerViewportResizedCallback((Rectangle<int> rect) {
print("Viewport resized to: ${rect.width}x${rect.height}");
});
Use cases include:
- Adjusting overlays or UI elements to fit the new viewport size.
- Triggering animations or updates based on the map's dimensions.
The registerViewRenderedCallback method is triggered after the map completes a rendering cycle. This listener provides a MapViewRenderInfo object containing details about the rendering process.
mapController.registerViewRenderedCallback((MapViewRenderInfo renderInfo) {
print("View rendered: ${renderInfo.status}");
});
Map selection functionality
After detecting a gesture, such as a tap, usually some specific action like selecting a landmark or a route is performed on GemMap. This selection is made using a map cursor, which is invisible by default. To showcase its functionality, the cursor can be made visible using the MapViewPreferences setting:
void _onMapCreated(GemMapController mapController) {
// Save mapController for further usage.
mapController = mapController;
// Enable cursor (default is true)
mapController.preferences.enableCursor = true;
// Enable cursor to render on screen
mapController.preferences.enableCursorRender = true;
}
Doing this inside maps's onMapCreated callback will result in a crosshair like icon in center of screen.
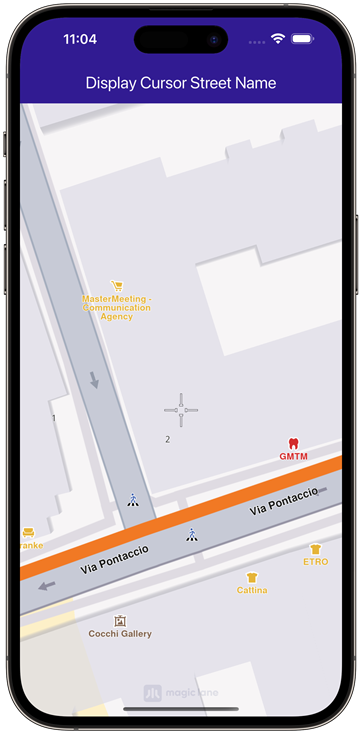 |
|---|
| Displaying a cursor |
Landmark selection
To get the selected landmarks, you can use the following code (possibly placed in the onMapCreated callback):
mapController.registerTouchCallback((pos) async {
// Set the cursor position.
await mapController.setCursorScreenPosition(pos);
// Get the landmarks at the cursor position.
final landmarks = mapController.cursorSelectionLandmarks();
for(final landmark in landmarks) {
// handle landmark
}
});
At higher zoom levels, landmarks provided by the cursorSelectionLandmarks method may lack some details for optimization purposes. Use SearchService.searchLandmarkDetails to retrieve full landmark details if needed.
To unregister the callback:
mapController.registerTouchCallback(null);
The selected landmarks are returned by the cursorSelectionLandmarks function, which is called after updating the cursor's position. This step is essential because the SDK only detects landmarks that are positioned directly under the cursor.
The cursor screen position is also used for determining the default screen position for centering (unless other values are specified). Modifying the screen position might change the behavior of centering in unexpected ways. Reset the cursor position to the center of the screen using the resetMapSelection method from the GemMapController (needs to be awaited).
Street selection
The following code can be used inside _onMapCreated callback in order to return selected streets under the cursor:
// Register touch callback to set cursor to tapped position
mapController.registerTouchCallback((point) async {
await mapController.setCursorScreenPosition(point);
final streets = mapController.cursorSelectionStreets();
String currentStreetName = streets.isEmpty ? "Unnamed street" : streets.first.name;
});
Setting the cursor screen position is an asynchronous operation and each function call needs to be awaited. Otherwise, the result list may be empty.
Street name can then be displayed on screen. This is the result:
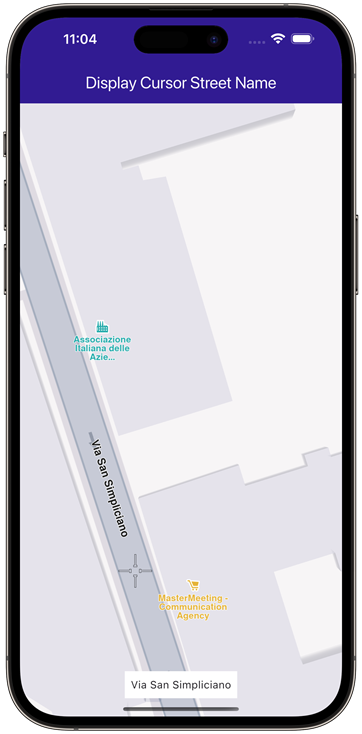 |
|---|
| Displaying a cursor selected street name |
The visibility of the cursor has no impact whatsoever on the selection logic.
Getting the current cursor screen position is done by calling cursorScreenPosition getter of GemMapController. Resetting the cursor position to its default location (the center of the screen) is done by resetMapSelection (needs to be awaited).
List of selection types
To summarize, there are multiple methods used to select different types of elements on the map. You can see all those in the following table.
| Entity | Select method | Result type | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landmark | cursorSelectionLandmarks | List<Landmark> | |
| Marker | cursorSelectionMarkers | List<MarkerMatch> | Returns MarkerMatch, not a Marker |
| OverlayItem | cursorSelectionOverlayItems | List<OverlayItem> | |
| Street | cursorSelectionStreets | List<Landmark> | Streets are handled as landmarks |
| Route | cursorSelectionRoutes | List<Route> | |
| Path | cursorSelectionPath | Path? | Null is returned if no path is found |
| MapSceneObject | cursorSelectionMapSceneObject | MapSceneObject? | Null is returned if no map scene object is found |
| TrafficEvent | cursorSelectionTrafficEvents | List<TrafficEvent> |
As you can see, when selecting markers a list of MarkerMatch elements is returned. The match specifies information about the matched marker (the marker collection in which the marker resides, the index of the marker in the collection, the matched part index, the matched index of the point in the part).
You can also register callbacks that are called when the cursor is placed over elements on the GemMapController class:
registerCursorSelectionUpdatedLandmarksCallbackfor landmarksregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedMarkersCallbackfor markersregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedOverlayItemsCallbackfor overlay itemsregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedRoutesCallbackfor routesregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedPathCallbackfor pathsregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedTrafficEventsCallbackfor traffic eventsregisterCursorSelectionUpdatedMapSceneObjectCallbackfor map scene objects
These callbacks are triggered whenever the selection changes — for example, when new elements are selected, the selection switches to different elements, or the selection is cleared (in which case the callback is invoked with null or an empty list).
To unregister a callback, simply call the corresponding method with null as the argument.
Capture the map view as an image
In certain situations, it may be necessary to save the map as an image — for example, to generate previews that are too expensive to redraw in real time.
In this case, the captureImage method can be used. It returns a Future<Uint8List?> representing the image as a JPEG.
final Uint8List? image = await mapController.captureImage();
if (image == null){
print("Could not capure image");
}
There are subtle differences between platforms:
- iOS: The captured image excludes on-screen elements such as the cursor.
- Android: The captured image includes all on-screen elements, including the cursor.
Capturing the map view as an image may not work correctly when the rendering rule is set to RenderRule.noRender or RenderRule.onDemand.
To ensure that any ongoing map animations or loading have completed, wait for the callback provided to registerViewRenderedCallback to be triggered with dataTransitionStatus set to ViewDataTransitionStatus.complete before capturing the image.
Make sure to implement a timeout, as the registerViewRenderedCallback is only triggered when the map is rendering — and will not be called if everything is already loaded.