|
In this guide you will learn how to compute a route based on the accessibility given by the physical characteristics of a truck, such as height, weight, length, width and number of axles, and then render the route on the map.
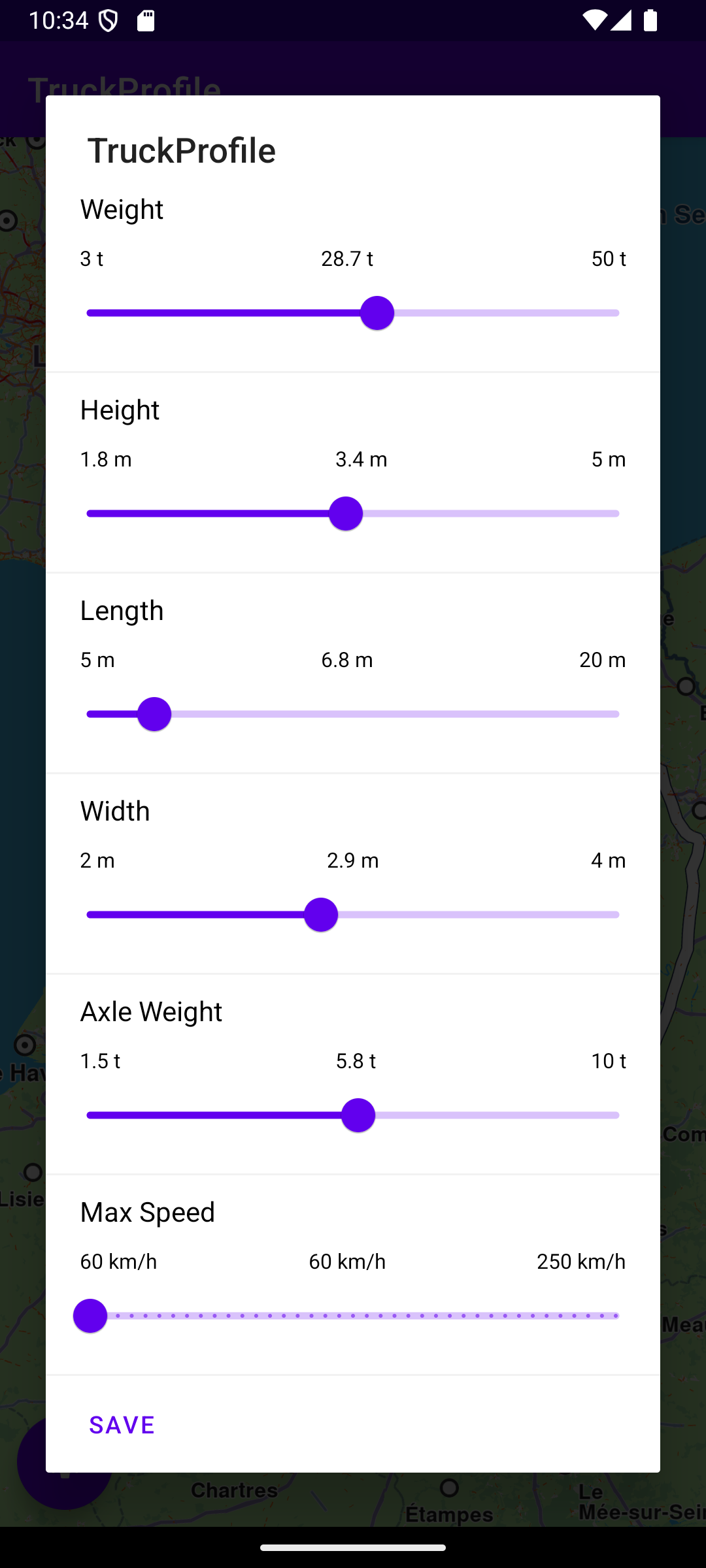
Truck profile settings panel
Routing
A routing service is instantiated to compute and render the truck route.
The onStarted and onCompleted routing callbacks are overridden and implemented, to show, and then hide, respectively, the routing computation progress bar, which is useful for very slow devices, where the route computation may take long enough to be noticeable by the user.
The line adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(0, routesList.size) updates the views for all items from the beginning of the routesList up to its current size, because their content may have changed.
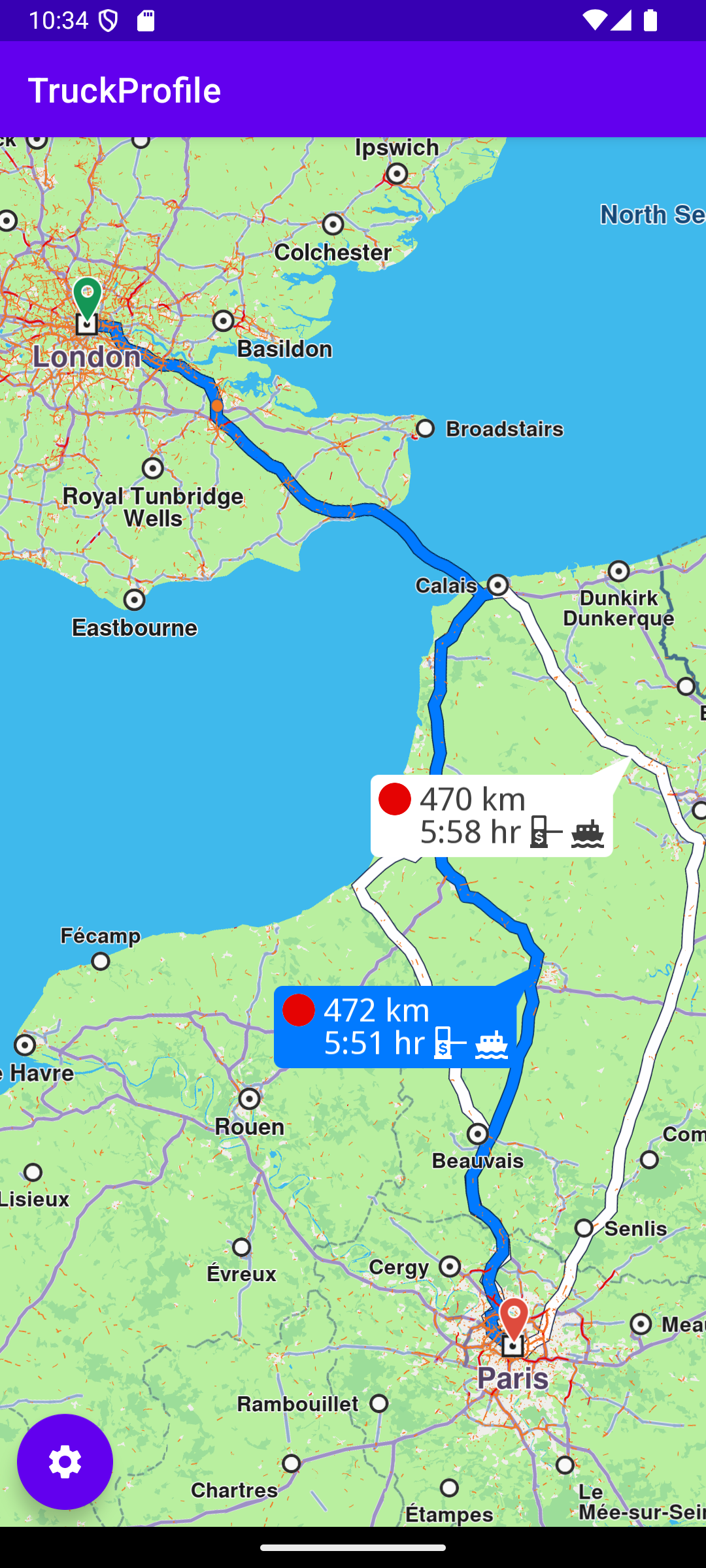
When the route calculation is completed, if there is no error, the resulting routes (as there could be more than one alternate route in the resulting set between the specified departure and destination points) are drawn on the map:
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.presentRoutes()
Then the settings button is set to visible settingsButtons.visibility = View.VISIBLE, so that the user can introduce the physical characteristics of the truck.
Upon saving these, the route is computed again, in case it has to change to accommodate the updated characteristics of the truck, such as its dimensions and weight.
private val routingService = RoutingService(
onStarted = {
progressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE
},
onCompleted = { routes, errorCode, _ ->
progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
when (errorCode)
{
GemError.NoError ->
{
routesList = routes
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(0, routesList.size)
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.presentRoutes(
routes = routes,
displayBubble = true
)
}
settingsButtons.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
GemError.Cancel ->
{
showDialog("The routing action was canceled.")
}
else ->
{
showDialog("Routing service error: ${GemError.getMessage(errorCode)}")
}
}
}
)
Map Implementation
A click listener is set for the settings button, to recompute the route when the user changes the physical parameters of the truck.
it.setOnClickListener { onSettingsButtonClicked() }
When the map is loaded and ready,
onMapDataReady@{}
the routing service instantiated and shown above is used to calculate the route between a list of 2 predefined waypoints where the first is the departure point and the second is the destination point:
routingService.calculateRoute(waypoints)
Each waypoint is a Landmark containing a name, a latitude, in degrees, and a longitude, in degrees:
Landmark("Paris", 48.8566932, 2.3514616)
The list of waypoints from which a route is calculated must have at least 2 elements, for the departure and destination, respectively, but can have more elements, for additional waypoints along the route. In this example there are 2 waypoints in the list.
Also, a default TruckProfile is instantiated with some default values for it's fields preferencesTruckProfile = TruckProfile(...)
A touch listener is defined gemSurfaceView.mapView?.onTouch = xy -> and gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionRoutes is used to see if the user touched one or more routes on the map. If so, the first touched route (at index 0) is selected and set as the main route, which causes it to be drawn in dark blue on the map.
Then the camera centers on the bounding box containing all routes between the departure and destination points.
centerOnRoutes(routesList)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface_view)
progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progress_bar)
settingsButtons = findViewById<FloatingActionButton?>(R.id.settings_button).also {
it.setOnClickListener {
onSettingsButtonClicked()
}
}
SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = onMapDataReady@{ isReady ->
if (!isReady) return@onMapDataReady
SdkCall.execute {
waypoints = arrayListOf(
Landmark("London", 51.5073204, -0.1276475),
Landmark("Paris", 48.8566932, 2.3514616)
)
routingService.calculateRoute(waypoints)
preferencesTruckProfile = TruckProfile(
(3 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Weight.unit).toInt(),
(1.8 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Height.unit).toInt(),
(5 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Length.unit).toInt(),
(2 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Width.unit).toInt(),
(1.5 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.AxleWeight.unit).toInt(),
(60 * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.MaxSpeed.unit).toDouble()
)
}
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.onTouch = { xy ->
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorScreenPosition = xy
val routes = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionRoutes
if (!routes.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val route = routes[0]
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.apply {
preferences?.routes?.mainRoute = route
centerOnRoutes(routesList)
}
}
}
}
}
...
}
Settings Change
The inner class TruckProfileSettingsAdapter represents the custom RecyclerView adapter for the truck profile settings.
private val adapter = TruckProfileSettingsAdapter(getInitialDataSet())
The getInitialDataSet() function sets the default initial values in the form with the truck dimensions and other attributes required for identifying a corresponding route between the given departure and destination which is navigable by the specified truck.
private fun getInitialDataSet(): List<TruckProfileSettingsModel>
{
return mutableListOf<TruckProfileSettingsModel>().also {
it.add(
TruckProfileSettingsModel(
"Weight",
ESeekBarValuesType.DoubleType,
"3 t",
"3.0 t",
"50 t",
0,
0,
0,
3.0f,
3.0f,
50.0f,
"t"
)
)
...
}
}
The onSettingsButtonClicked() function is called by the listener defined in the onCreate() function above, when the user clicks the industrial wheel settings button to modify the truck profile attributes.
This function uses the adapter variable to display the truck attribute values and enable the user to modify them, so they can then be used to find a route appropriate for the truck.
A save button is defined, which closes the dialog and calls the onSaveButtonClicked() function to calculate the route using the updated truck parameter values.
private fun onSettingsButtonClicked()
{
val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(this)
val convertView = layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.truck_profile_settings_view, null)
val listView =
convertView.findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.truck_profile_settings_list).apply {
layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this@MainActivity)
addItemDecoration(
DividerItemDecoration(
applicationContext,
(layoutManager as LinearLayoutManager).orientation
)
)
}
listView.adapter = adapter
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(0, ETruckProfileSettings.entries.size)
builder.setTitle(getString(R.string.app_name))
builder.setView(convertView)
builder.setNeutralButton(getString(R.string.save)) { dialog, _ ->
onSaveButtonClicked()
dialog.dismiss()
}
val dialog = builder.create()
dialog.show()
}
The onSaveButtonClicked() function sets the truck profile attributes in the preferences and then calculates the route using
calculateRoute(waypoints)
private fun onSaveButtonClicked()
{
EspressoIdlingResource.increment()
val dataSet = adapter.dataSet
val width =
(dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.Width.ordinal].currentDoubleValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Width.unit).toInt()
val height =
(dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.Height.ordinal].currentDoubleValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Height.unit).toInt()
val length =
(dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.Length.ordinal].currentDoubleValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Length.unit).toInt()
val weight =
(dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.Weight.ordinal].currentDoubleValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.Weight.unit).toInt()
val axleWeight =
(dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.AxleWeight.ordinal].currentDoubleValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.AxleWeight.unit).toInt()
val maxSpeed =
dataSet[ETruckProfileSettings.MaxSpeed.ordinal].currentIntValue * ETruckProfileUnitConverters.MaxSpeed.unit.toDouble()
SdkCall.execute {
routingService.apply {
preferences.alternativesSchema = ERouteAlternativesSchema.Never
preferences.transportMode = ERouteTransportMode.Lorry
preferencesTruckProfile = TruckProfile(
massKg = weight,
heightCm = height,
lengthCm = length,
widthCm = width,
axleLoadKg = axleWeight,
maxSpeedMs = maxSpeed
)
preferences.truckProfile = preferencesTruckProfile
calculateRoute(waypoints)
}
}
}