Routing On Map
In this guide you will learn how to render an interactive map, compute and render a route on the map and fly to the route.
Routing Service
Inside MainActivity.kt retain a RoutingService instance.
Normally in Android's MVVM, services are retained in the Repository layer, injected via dependency injection, and ultimately consumed by ViewModels but for the scope of this example we will use it inside an activity.
The routing service has onStarted and onCompleted callbacks which will update the UI.
Calculating route
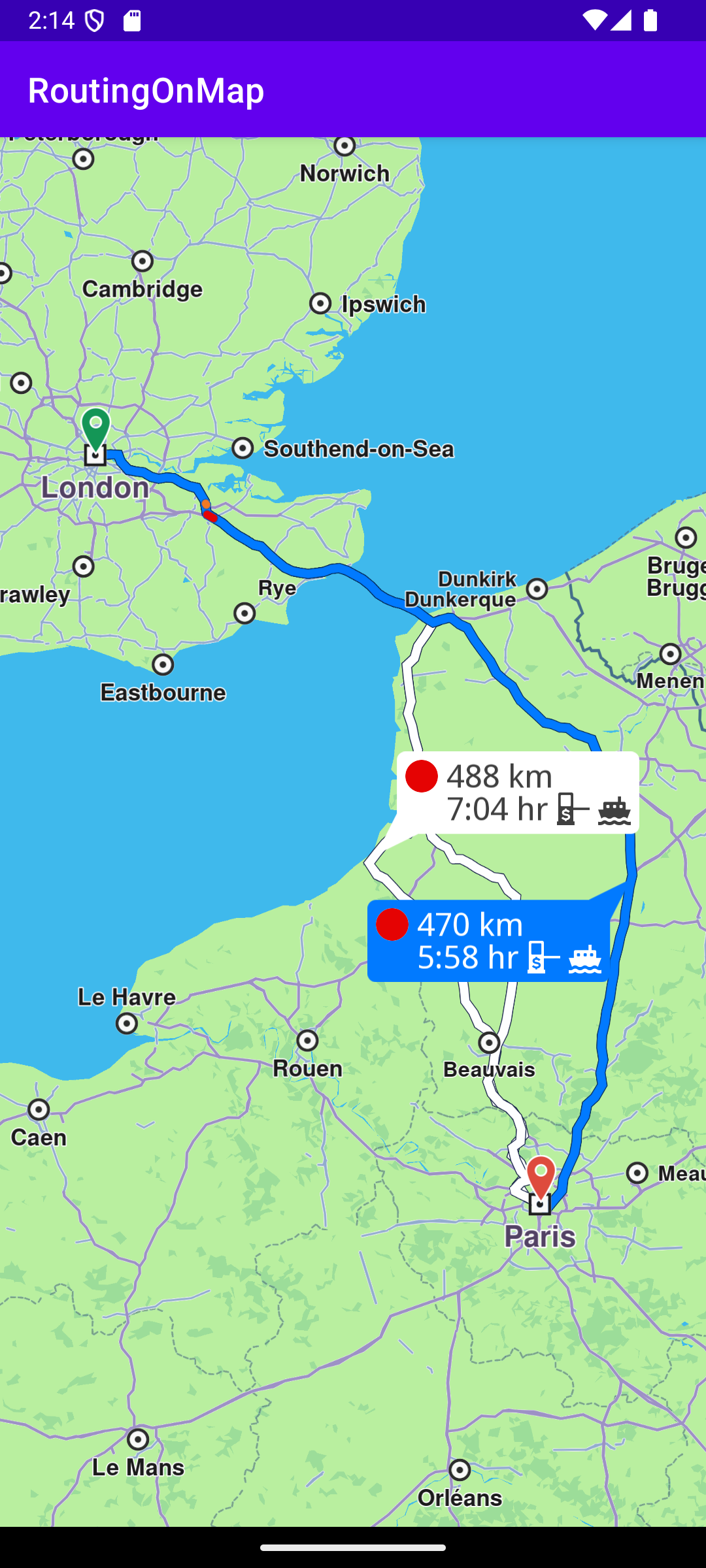
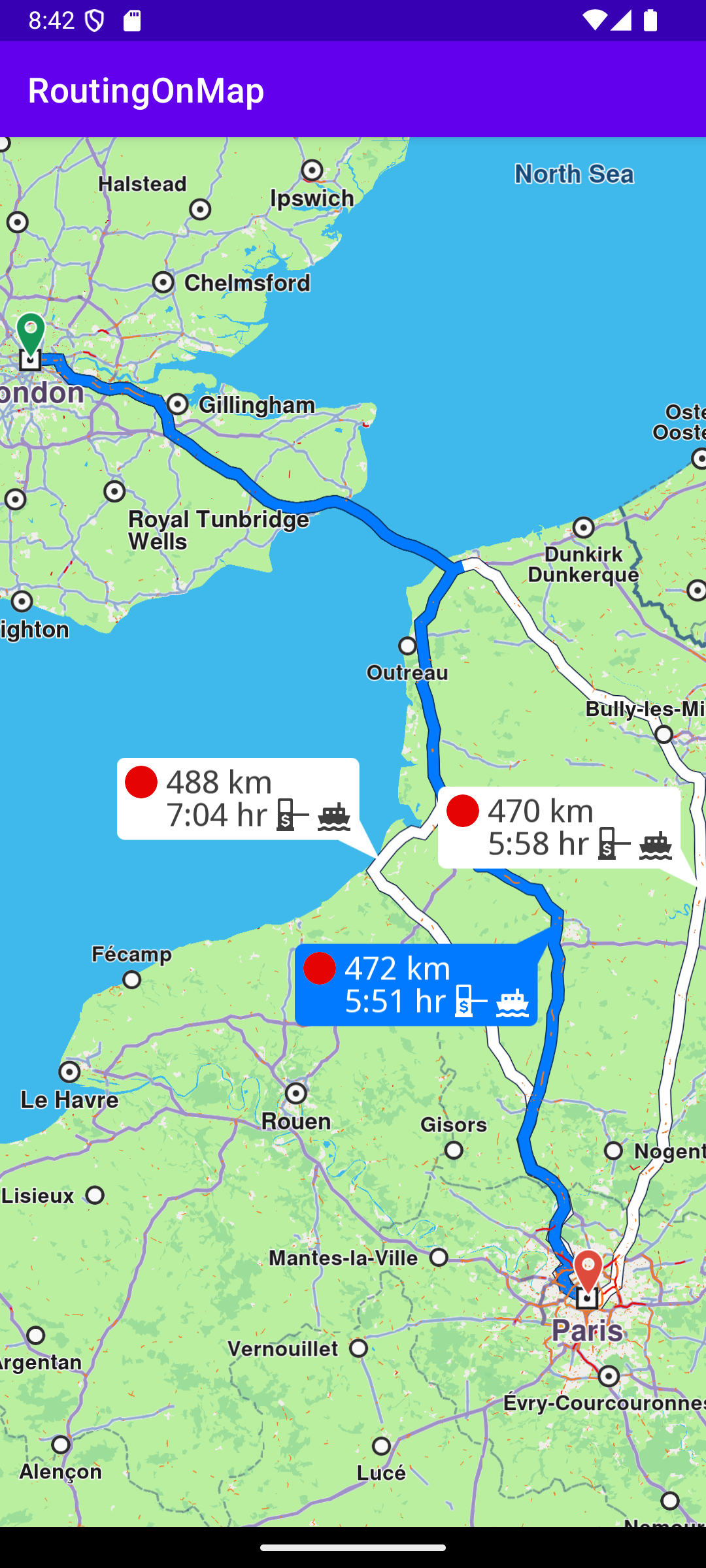
In the calculateRoute() function 2 Landmark instances are defined, one for the departure, and one for the destination coordinates of the route endpoints. A route must have at least 2 Landmark instances(waypoints), but optionally can have more, for any optional additional waypoints along the route.
The starting, or departure point of the route is the first waypoint in a list of 2 or more Landmarks (2 in this case), each containing a name, latitude (in degrees) and longitude (in degrees). The destination point is the last waypoint in the list.
In this example, the route departure point is London, and the destination is Paris, as specified by the Coordinates in the 2 Landmark instances.
The list of waypoints is passed to the routingService to calculate the route.
When the map is ready, that is, instantiated and loaded, the calculateRoute() function shown above is called. When the route calculation completes, the routing service callback is triggered and the resulting route(s) are rendered on the map.