|
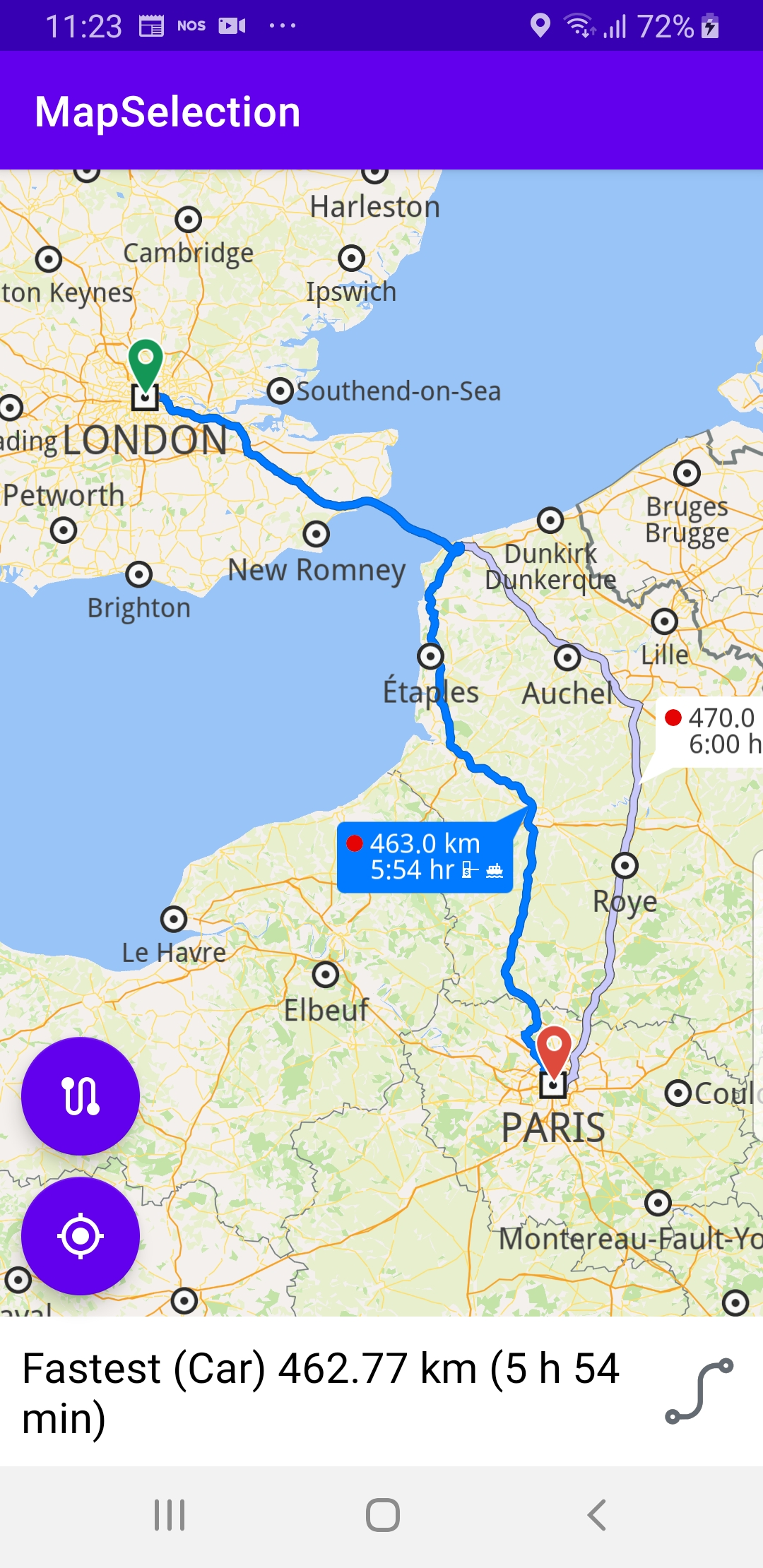
In the calculateRoute() function, 2 Landmark instances are defined, one for the departure, and one for the destination coordinates of the route endpoints. A route must have at least 2 Landmark instances(waypoints), but optionally can have more, for any optional additional waypoints along the route.
The starting, or departure point of the route is the first waypoint in a list of 2 or more Landmarks (2 in this case), each containing a name, latitude (in degrees) and longitude (in degrees). The destination point is the last waypoint in the list.
In this example, the route departure point is London, and the destination is Paris, as specified by the Coordinates in the 2 Landmark instances.
The list of waypoints is passed to the routingService to calculate the route.
private fun calculateRoute() = SdkCall.execute {
val waypoints = arrayListOf(
Landmark("London", 51.5073204, -0.1276475),
Landmark("Paris", 48.8566932, 2.3514616)
)
routingService.calculateRoute(waypoints)
}
A RoutingService is instantiated to compute a route and render it on the map. The onStarted and onCompleted callbacks are implemented, to detect when the route computation is started and when it is completed.
When the route computation is completed, and there is no error, the list of resulting routes is rendered on the map using presentRoutes().
The displayBubble flag is set to true to show the distance in km, and the time in hours, next to each route.
private val routingService = RoutingService(
onStarted = {
progressBar.visibility = View.VISIBLE
},
onCompleted = { routes, errorCode, _ ->
progressBar.visibility = View.GONE
when (errorCode)
{
GemError.NoError ->
{
routesList = routes
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.presentRoutes(routes, displayBubble = true)
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.preferences?.routes?.mainRoute?.let { selectRoute(it) }
}
flyToRoutesButton.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
GemError.Cancel ->
{
}
else ->
{
showDialog("Routing service error: ${GemError.getMessage(errorCode)}")
}
}
EspressoIdlingResource.decrement()
}
)
The onCreate() function calls the calculateRoute() function shown above, once the map is ready( instantiated and loaded ). It also uses findViewById() to get pointers/handles to each of the various graphical elements, such as the button in the lower left used for flying to the calculated routes, or the other button used for flying to the position of the device, also referred to as GPS position which appears in the lower left of the viewport.
The fly to GPS position button, which looks like a target, accessed by followCursorButton, is shown only if the camera is not already following the position of the device, indicated by a green arrow on the map.
The center on routes button, with a stylized s-shaped serpentine road section drawn on it, accessed by flyToRoutesButton, is used to fly back to the currently selected precalculated route, after panning away from it for example; this button is shown after the route is calculated and rendered.
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
progressBar = findViewById(R.id.progress_bar)
gemSurfaceView = findViewById(R.id.gem_surface)
overlayContainer = findViewById(R.id.overlay_container)
name = findViewById(R.id.name)
description = findViewById(R.id.description)
image = findViewById(R.id.image)
followCursorButton = findViewById(R.id.follow_cursor)
flyToRoutesButton = findViewById<FloatingActionButton?>(R.id.fly_to_route).also {
it.setOnClickListener {
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.let { mapView ->
mapView.deactivateAllHighlights()
mapView.preferences?.routes?.mainRoute?.let { mainRoute ->
selectRoute(mainRoute)
}
}
}
}
}
imageSize = resources.getDimension(R.dimen.image_size).toInt()
EspressoIdlingResource.increment()
SdkSettings.onMapDataReady = onMapDataReady@{ isReady ->
if (!isReady) return@onMapDataReady
calculateRoute()
SdkCall.execute {
val hasLocationPermission =
PermissionsHelper.hasPermission(this, Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION)
if (hasLocationPermission)
{
Util.postOnMain { enableGPSButton() }
} else
{
requestPermissions(this)
}
}
...
}
...
}
The requestPermissions() function asks the user for internet and location permissions. The onRequestPermissionsResult() function is overridden, to receive the results of the permission requests.
private fun requestPermissions(activity: Activity): Boolean
{
val permissions = arrayListOf(
Manifest.permission.INTERNET,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION,
Manifest.permission.ACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION
)
return PermissionsHelper.requestPermissions(
REQUEST_PERMISSIONS, activity, permissions.toTypedArray()
)
}
The onTouch listener is defined for the mapView to get the cursorScreenPosition. Once the x, y position of the user touch event has been set in the mapView, the code verifies what map element was selected.
val myPosition = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionSceneObject
First, check if it is a scene object, such as a 3D car or plane, etc, simulated in the scene. If so, myPosition.coordinates gets the coordinates of the scene object (it), and uses the gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates function to move the camera with a flying animation (Animation(EAnimation.Linear)) to the selected object.
val landmarks = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionLandmarks
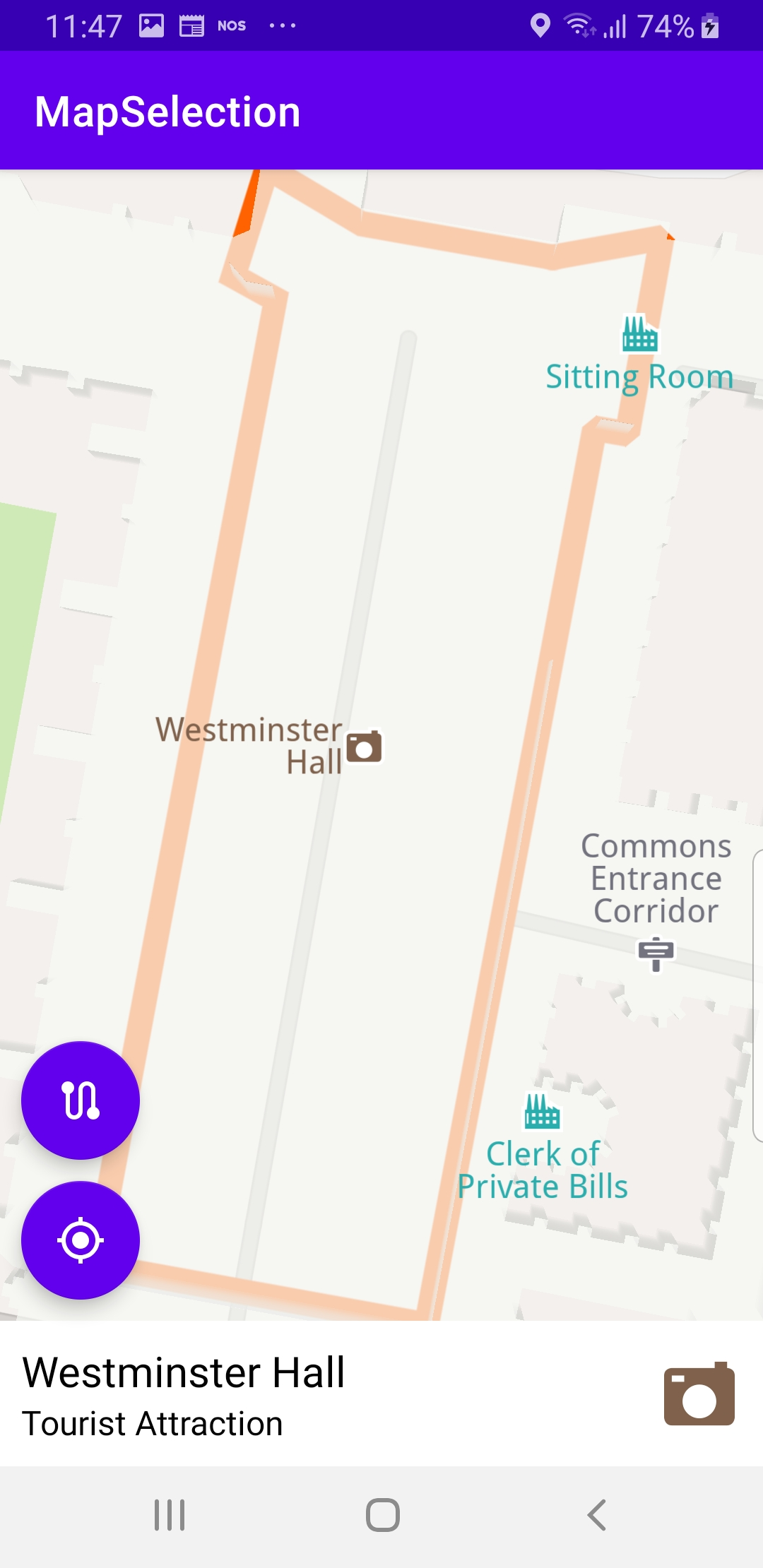
Next, check if the selected object is a landmark.
val contour = landmark.getContourGeographicArea()
If landmarks is not null, check if it is a geographic area, (contour is also not null) and in that case, use the gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnArea() function to move the camera with a flying animation to the selected region, such that the bounding box of the selected region fits snugly in the viewport.
If contour is null, then this is a simple landmark, so just get its coordinates and move the camera to the landmark with a flying animation: landmark.coordinates?.let { gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates()}
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.onTouch = { xy ->
SdkCall.execute {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorScreenPosition = xy
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.deactivateAllHighlights()
val centerXy =
Xy(gemSurfaceView.measuredWidth / 2, gemSurfaceView.measuredHeight / 2)
val myPosition = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionSceneObject
if (myPosition != null && isSameMapScene(
myPosition,
MapSceneObject.getDefPositionTracker().first!!
)
)
{
showOverlayContainer(
getString(R.string.my_position),
"",
ContextCompat.getDrawable(this, R.drawable.ic_current_location_arrow)
?.toBitmap(imageSize, imageSize)
)
myPosition.coordinates?.let {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates(
it,
-1,
centerXy,
Animation(EAnimation.Linear),
Double.MAX_VALUE,
0.0
)
}
return@execute
}
val landmarks = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionLandmarks
if (!landmarks.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val landmark = landmarks[0]
landmark.run {
showOverlayContainer(
name.toString(),
description.toString(),
image?.asBitmap(imageSize, imageSize)
)
}
val contour = landmark.getContourGeographicArea()
if (contour != null && !contour.isEmpty())
{
contour.let {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnArea(
it,
-1,
centerXy,
Animation(EAnimation.Linear),
)
val displaySettings = HighlightRenderSettings(
EHighlightOptions.ShowContour,
Rgba(255, 98, 0, 255),
Rgba(255, 98, 0, 255),
0.75
)
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.activateHighlightLandmarks(
landmark,
displaySettings
)
}
} else
{
landmark.coordinates?.let {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates(
it,
-1,
centerXy,
Animation(EAnimation.Linear),
Double.MAX_VALUE,
0.0
)
}
}
return@execute
}
val trafficEvents = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionTrafficEvents
if (!trafficEvents.isNullOrEmpty())
{
hideOverlayContainer()
openWebActivity(trafficEvents[0].previewUrl.toString())
return@execute
}
val overlays = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionOverlayItems
if (!overlays.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val overlay = overlays[0]
if (overlay.overlayInfo?.uid == ECommonOverlayId.Safety.value)
{
hideOverlayContainer()
openWebActivity(overlay.getPreviewUrl(Size()).toString())
} else
{
overlay.run {
showOverlayContainer(
name.toString(),
overlayInfo?.name.toString(),
image?.asBitmap(imageSize, imageSize)
)
}
overlay.coordinates?.let {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates(
it,
-1,
centerXy,
Animation(EAnimation.Linear),
Double.MAX_VALUE,
0.0
)
}
}
return@execute
}
val routes = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionRoutes
if (!routes.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val route = routes[0]
selectRoute(route)
return@execute
}
}
}
Also check if the selected object is a traffic event
val trafficEvents = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionTrafficEvents
and if so, get the string description of the first one(openWebActivity(trafficEvents[0].previewUrl.toString())) at index 0, in case there are more than one.
val trafficEvents = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionTrafficEvents
if (!trafficEvents.isNullOrEmpty())
{
hideOverlayContainer()
openWebActivity(trafficEvents[0].previewUrl.toString())
return@execute
}
Check if the selected object is an overlay(val overlays = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionOverlayItems) and in the usual case fly to it's coordinates overlay.coordinates?.let { gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates() }.
val overlays = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionOverlayItems
if (!overlays.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val overlay = overlays[0]
if (overlay.overlayInfo?.uid == ECommonOverlayId.Safety.value)
{
hideOverlayContainer()
openWebActivity(overlay.getPreviewUrl(Size()).toString())
}
else
{
overlay.run {
showOverlayContainer(
name.toString(),
overlayInfo?.name.toString(),
image?.asBitmap(imageSize, imageSize)
)
}
overlay.coordinates?.let {
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnCoordinates(
it,
-1,
centerXy,
Animation(EAnimation.Linear),
Double.MAX_VALUE,
0.0
)
}
}
return@execute
}
Finally, get the visible routes at the touch event point
val routes = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionRoutes
and if there is any route under the cursor, get a list of routes with the cursorSelectionRoutes function.
If the resulting list of routes is not empty, then the first route in this list, at index 0, is set as the main route, and selectRoute() is called on this route to center it with an animated motion.
...
val routes = gemSurfaceView.mapView?.cursorSelectionRoutes
if (!routes.isNullOrEmpty())
{
val route = routes[0]
selectRoute(route)
return@execute
}
}
}
}
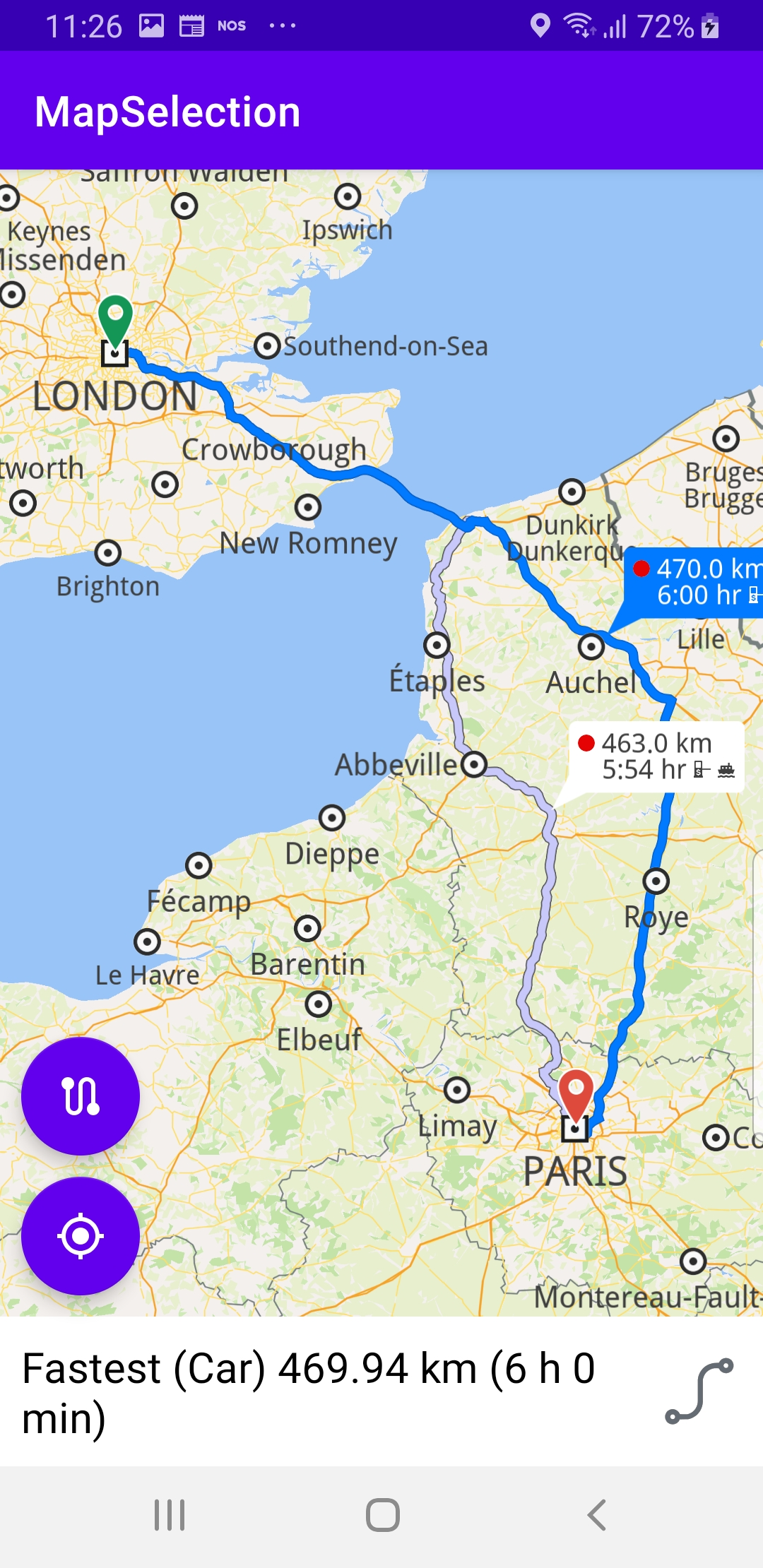
The selectRoute() function uses centerOnRoutes() to fly the camera with an animated motion to the set of computed routes, if there are more than one in the result, such that their bounding box fits in the viewport, so that all alternate routes are visible.
If a route is selected by the user then that route is set as the mainRoute in order to highlight that particular route.
Note that centering on a particular route with an animated camera motion can also be done like this:
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnRoute(route)
private fun selectRoute(route: Route)
{
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.apply {
route.apply {
showOverlayContainer(
summary.toString(),
"",
ContextCompat.getDrawable(
this@MainActivity,
if (isDarkThemeOn()) R.drawable.ic_baseline_route_24_night else R.drawable.ic_baseline_route_24
)?.toBitmap(imageSize, imageSize)
)
}
preferences?.routes?.mainRoute = route
}
gemSurfaceView.mapView?.centerOnRoutes(routesList)
}
The showOverlayContainer() function is used to show for example the outline of the selected building, or park, or the border of the selected country, etc.
private fun showOverlayContainer(name: String, description: String, image: Bitmap?) =
Util.postOnMain {
if (!overlayContainer.isVisible)
{
overlayContainer.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
this.name.text = name
if (description.isNotEmpty())
{
this.description.apply {
text = description
visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
} else
{
this.description.visibility = View.GONE
}
this.image.setImageBitmap(image)
}
The onCreate() function also checks if internet access is available and if not, shows a dialog that internet connection is required (because it is used to download map data).
SdkSettings.onApiTokenRejected = {
showDialog("TOKEN REJECTED")
}
if (!Util.isInternetConnected(this))
{
showDialog("You must be connected to the internet!")
}