Human Voices ¶
|
|
|||
Setup ¶
Prerequisites ¶
Build and Run ¶
Go to the
human_voices
directory within the Flutter examples directory. This is the directory name for this example project.
|
|
|||
Note - the
gem_kit
directory containing the Maps SDK for Flutter
should be in the
plugins
directory of the example, e.g.
example_pathname/plugins/gem_kit
- see the environment setup guide above.
Run:
flutter
pub
get
Configure the native parts:
First, verify that the
ANDROID_SDK_ROOT
environment variable
is set to the root path of your android SDK.
In
android/build.gradle
add the
maven
block as shown,
within the
allprojects
block, for both debug and release builds:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
maven {
url "${rootDir}/../plugins/gem_kit/android/build"
}
}
}
in
android/app/build.gradle
within the
android
block, in the
defaultConfig
block,
the android SDK version
minSdk
must be set as shown below.
Additionally, for release builds, in
android/app/build.gradle
,
within the
android
block, add the
buildTypes
block as shown:
Replace
example_pathname
with the actual project pathname
android {
defaultConfig {
applicationId "com.magiclane.gem_kit.examples.example_pathname"
minSdk 21
targetSdk flutter.targetSdk
versionCode flutterVersionCode.toInteger()
versionName flutterVersionName
}
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled false
shrinkResources false
// TODO: Add your own signing config for the release build.
// Signing with the debug keys for now, so `flutter run --release` works.
signingConfig signingConfigs.debug
}
}
}
Then run the project:
flutter run --debugorflutter run --release
App entry and initialization ¶
const projectApiToken = String.fromEnvironment('GEM_TOKEN');
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
This code initializes the projectApiToken with the required authorization token and launches the app.
How It Works ¶
This example integrates several components to simulate navigation with voice instructions. Here’s a breakdown of the key functionalities:
-
Calculate routes based on user-defined landmarks and route preferences.
-
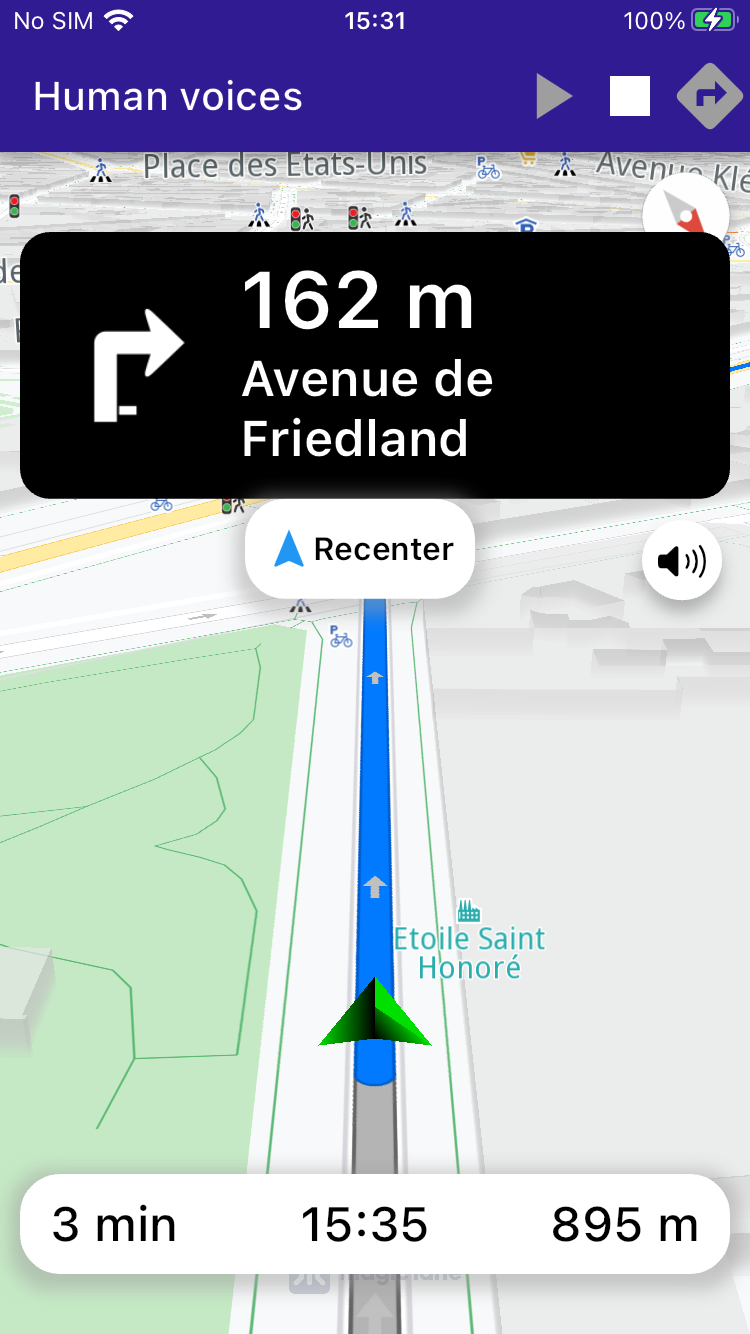
Simulate navigation along a calculated route with real-time text-to-speech (TTS) instructions.
-
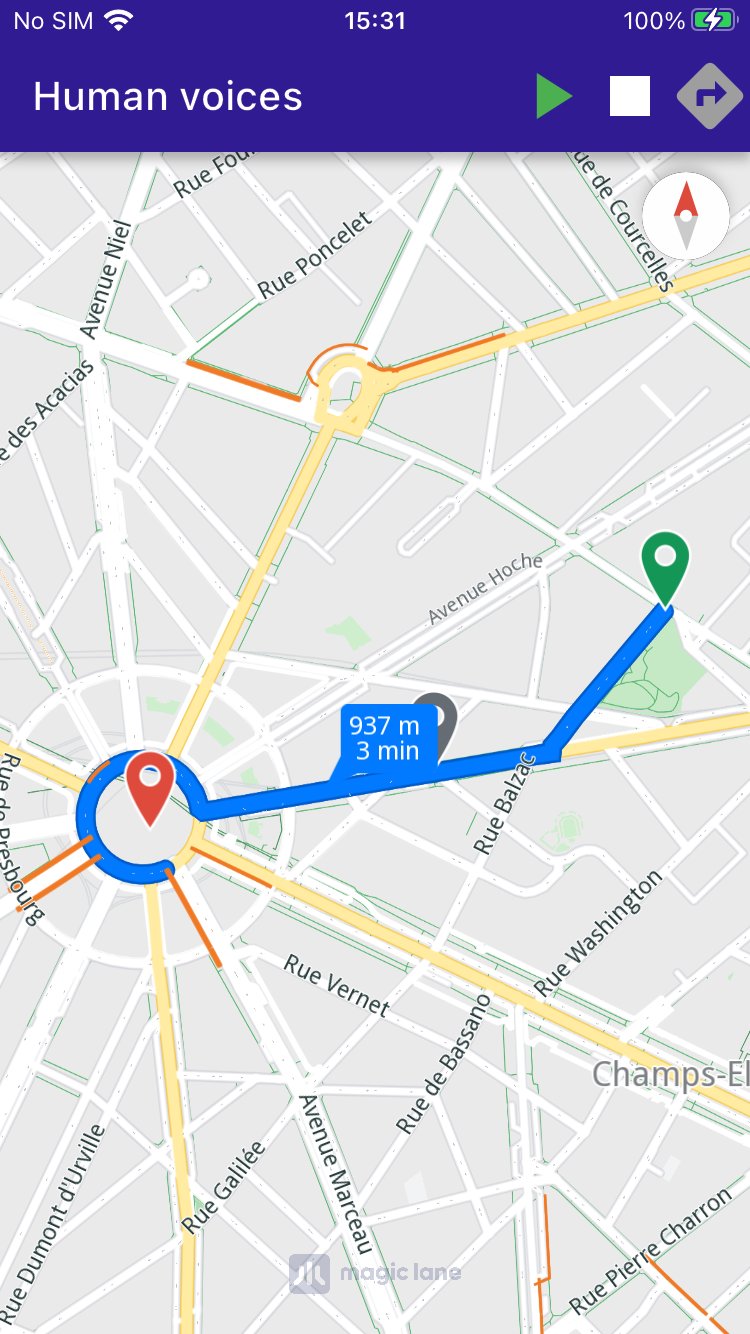
Display and center routes on the map, with the camera following the simulated position.
|
|
|||
Route Calculation ¶
The user can trigger route calculation, which involves defining landmarks and preferences, then using
RoutingService.calculateRoute
to compute the route.
:lineno-start: 1 void _onBuildRouteButtonPressed(BuildContext context) { _showSnackBar(context, message: 'The route is calculating.'); // Define landmarks. final departureLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 48.87586, longitude: 2.30311); final intermediaryPointLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 48.87422, longitude: 2.29952); final destinationLandmark = Landmark.withLatLng(latitude: 48.87361, longitude: 2.29513); // Define the route preferences. final routePreferences = RoutePreferences(); // Calculate the route. _routingHandler = RoutingService.calculateRoute( [departureLandmark, intermediaryPointLandmark, destinationLandmark], routePreferences, (err, routes) { _routingHandler = null; ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).clearSnackBars(); if (err == GemError.success) { final routesMap = _mapController.preferences.routes; for (final route in routes!) { routesMap.add(route, route == routes.first, label: route.getMapLabel()); } _mapController.centerOnRoutes(routes: routes); setState(() => _areRoutesBuilt = true); } }); }
UI Components ¶
The example includes custom UI components, such as NavigationInstructionPanel and NavigationBottomPanel , to display navigation instructions and other relevant details during the simulation.