Recorder
The Recorder module is a comprehensive tool designed for managing sensor data recording.
The Recorder supports a wide range of configurable parameters through the RecorderConfiguration, allowing developers to tailor recording behavior to specific application needs. Features include:
- Customizable storage options: Define log directories, manage disk space, and specify the duration of recordings.
- Data type selection: Specify which data types (e.g., video, audio, or sensor data) to record.
- Video and audio options: Set video resolution, enable/disable audio recording, and manage chunk durations. It's possible to record only sensor data, sensor data + video, sensor data + audio or sensor data + video + audio.
The Recorder provides comprehensive methods to control the recording lifecycle:
- Start, stop, pause, and resume recordings.
- Automatic restarts for continuous recording with chunked durations.
The Recorder supports various transportation modes (e.g., car, pedestrian, bike), enabling detailed analysis and classification of recordings based on context.
To prevent overwhelming the device's storage, the Recorder allows for setting disk space limits and automatically manages logs based on specified retention thresholds.
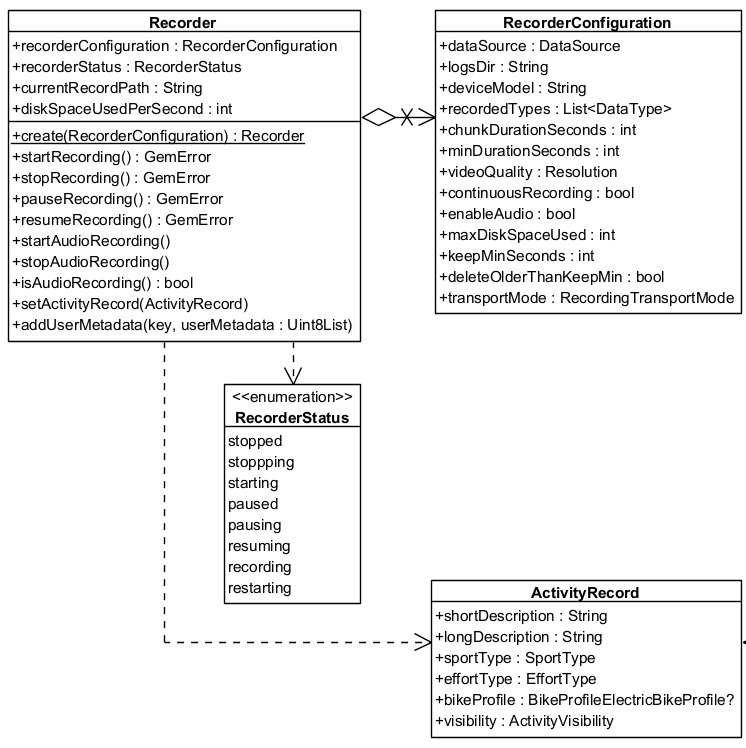
In the following class diagram you can see the main classes used by the Recorder and the relationships between them:
Initialize the Recorder
The Recorder cannot be directly instantiated. Instead, the create method is used to obtain a configured Recorder instance.
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
dataSource: dataSource,
logsDir: tracksPath,
recordedTypes: [DataType.position],
);
Recorder recorder = Recorder.create(recorderConfiguration);
If the dataSource, logsDir and recordedTypes parameters are not populated with valid data, the startRecording method will return GemError.invalidInput and no data will be recorded.
Configure the RecorderConfiguration
| Recorder configuration attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| dataSource | The source providing the data to be recorded. |
| logsDir | The directory used to keep the logs |
| deviceModel | The device model. Deprecated, use hardwareSpecifications instead. |
| hardwareSpecifications | Extensive details about the device as a hashmap. |
| recordedTypes | The data types that are recorded |
| minDurationSeconds | The minimum duration for the recording to be saved |
| videoQuality | The video quality |
| chunkDurationSeconds | The chunk duration time in seconds |
| continuousRecording | Whether the recording should continue automatically when chunk time achieved |
| enableAudio | This flag will be used to determine if audio is needed to be recorded or not |
| maxDiskSpaceUsed | When reached, it will stop the recording |
| keepMinSeconds | Will not delete any record if this threshold is not reached |
| deleteOlderThanKeepMin | Older logs that exceeds minimum kept seconds threshold should be deleted |
| transportMode | The transport mode |
If the log duration is shorter than minDurationSeconds the stopRecording method of Recorder will not save the recording and will return GemError.recordedLogTooShort.
The GemError.recordedLogTooShort error may also occur if an insufficient number of positions were emitted, even when the duration between startRecording and stopRecording exceeds minDurationSeconds. To test the recording functionality, you can create a custom external DataSource and push custom positions. Refer to the custom positioning guide for more details. The external DataSource created needs to be provided to the RecorderConfiguration object.
The GemError.general result might be returned if the application has been sent to background without making the required configuration. See the record while app is in background section below.
Be aware that if minChunkDuration is set too high, it may cause GemError.noDiskSpace since the SDK will determine how much space is required for the entire chunk.
The path_provider package can be used to obtain a valid path to save recordings. The following snippet shows how to obtain a valid folder path in a platform independent way:
Future<String> getTracksPath() async {
// Requires the path_provider package
final rootDir = await path_provider.getApplicationDocumentsDirectory();
final tracksPath = path.joinAll([rootDir.path, "Data", "Tracks"]);
return tracksPath;
}
Recording lifecycle
-
Starting the Recorder:
- Call the
startRecordingmethod to initiate recording. The recorder transitions to therecordingstate.
- Call the
-
Pausing and Resuming:
- Use
pauseRecordingandresumeRecordingto manage interruptions.
- Use
-
Chunked Recordings:
- If a chunk duration is set in the configuration, the recording automatically stops when the duration is reached. A new recording will begin seamlessly if continuous recording is enabled, ensuring uninterrupted data capture.
-
Stopping the Recorder:
- The
stopRecordingmethod halts recording, and the system ensures logs meet the configured minimum duration before saving them as .gm files insidelogsDir.
- The
How to use the Recorder
The following sections will present some use cases for the recorder, demonstrating its functionality in different scenarios.
String tracksPath = await _getTracksPath();
DataSource? dataSource = DataSource.createLiveDataSource();
if (dataSource == null){
showSnackbar("The datasource could not be created");
return;
}
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
dataSource: dataSource,
logsDir: tracksPath,
recordedTypes: [DataType.position],
);
// Create recorder based on configuration
final recorder = Recorder.create(recorderConfiguration);
GemError errorStart = await recorder.startRecording();
if (errorStart != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error starting recording: $errorStart");
}
// Other code
GemError errorStop = await recorder.stopRecording();
if (errorStop != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error stopping recording: $errorStop");
}
The Recorder will only save data explicitly defined in the recordedTypes list, any other data will be ignored.
The startRecording and stopRecording methods must be awaited to ensure proper execution. Otherwise it may lead to unexpected behavior.
Don't forget to request permission for location usage before starting a recorder.
Record audio
The recorder also supports audio recording. To enable this functionality, set the enableAudio parameter in the RecorderConfiguration to true and invoke the startAudioRecording method from the Recorder class. To stop the audio recording, use the stopAudioRecording method. The following code snippet illustrates this process:
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
dataSource: dataSource,
logsDir: tracksPath,
recordedTypes: [DataType.position],
enableAudio: true
);
// Create recorder based on configuration
Recorder recorder = Recorder.create(recorderConfiguration);
GemError errorStart = await recorder.startRecording();
if (errorStart != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error starting recording: $errorStart");
}
// At any moment enable audio recording
recorder.startAudioRecording();
// Other code
// At any moment stop audio recording
recorder.stopAudioRecording();
GemError errorStop = await recorder.stopRecording();
if (errorStop != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error stopping recording: $errorStop");
}
The audio recording will result in a log file of type .mp4. This file also contains the binary data of a .gm file, but it is accessible by system players.
Don't forget to request permission for microphone usage if you set the enableAudio parameter to true.
Record video
The recorder also supports video recording. To enable this functionality, add DataType.camera to the recordedTypes and set the videoQuality parameter in the RecorderConfiguration to your desired resolution, we recommend using Resolution.hd720p. The video recording starts at the call of the startRecording method and stops at the stopRecording method. The following code snippet illustrates this process:
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
dataSource: dataSource,
logsDir: tracksPath,
videoQuality: Resolution.hd720p,
recordedTypes: [DataType.position, DataType.camera],
);
// Create recorder based on configuration
Recorder recorder = Recorder.create(recorderConfiguration);
GemError errorStart = await recorder.startRecording();
if (errorStart != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error starting recording: $errorStart");
}
// Other code
GemError errorStop = await recorder.stopRecording();
if (errorStop != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error stopping recording: $errorStop");
}
The audio recording will result in a log file of type .mp4. This file also contains the binary data of a .gm file, but it is accessible by system players.
Don't forget to request permission for camera usage if you add the DataType.camera parameter to recordedTypes.
Record multimedia
To record a combination of audio, video and sensors you can do that by setting up the RecorderConfiguration with all the desired functionalities. The following code snippet illustrates this process:
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
dataSource: dataSource,
logsDir: tracksPath,
videoQuality: Resolution.hd720p,
recordedTypes: [DataType.position, DataType.camera],
enableAudio: true
);
// Create recorder based on configuration
Recorder recorder = Recorder.create(recorderConfiguration);
GemError errorStart = await recorder.startRecording();
if (errorStart != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error starting recording: $errorStart");
}
// At any moment enable audio recording
recorder.startAudioRecording();
// Other code
// At any moment stop audio recording
recorder.stopAudioRecording();
GemError errorStop = await recorder.stopRecording();
if (errorStop != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error stopping recording: $errorStop");
}
The audio recording will result in a log file of type .mp4. This file also contains the binary data of a .gm file, but it is accessible by system players.
Don't forget to request permission for camera and microphone usage if you set the enableAudio parameter to true and add the DataType.camera parameter to recordedTypes.
Recorder Bookmarks and Metadata
The SDK utilizes the proprietary .gm file format for recordings, offering several advantages over standard file types:
- Supports multiple data types, including acceleration, rotation, and more.
- Allows embedding custom user data in binary format.
- Enables automatic storage management by the SDK to optimize space usage.
Recordings are saved as .gm or .mp4 files by the Recorder. The RecorderBookmarks class provides functionality for managing recordings, including exporting .gm or .mp4 files to other formats such as .gpx, as well as importing external formats and converting them to .gm for seamless SDK integration.
Additionally, the LogMetadata class serves as an object-oriented representation of a .gm or .mp4 file, offering features such as retrieving start and end timestamps, coordinates, and path details at varying levels of precision.
The RecorderBookmarks class for enhanced log management:
- Export and Import Logs: Convert logs to/from different formats such as GPX, NMEA, and KML.
- Log Metadata: Retrieve details like start and end timestamps, transport mode and size.
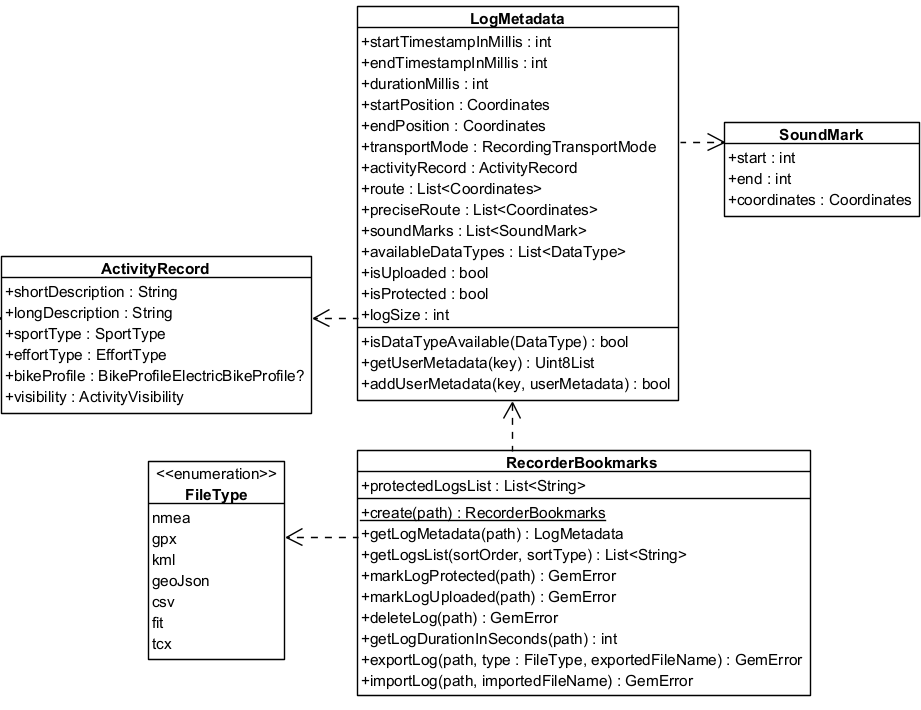
In the following class diagram you can see the main classes used by the RecorderBookmarks and the relationships between them:
Export logs
// Create recorderBookmarks
// It loads all .gm and .mp4 files at logsDir
RecorderBookmarks? bookmarks = RecorderBookmarks.create(tracksPath);
if(bookmarks == null) return;
// Get list of logs
List<String> logList = bookmarks.getLogsList();
// Export last recording as a GPX file with a given name
// Assumes the logList is not empty
GemError exportLogError = bookmarks.exportLog(
logList.last,
FileType.gpx,
exportedFileName: "My_File_Name",
);
if (exportLogError != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error exporting log: $exportLogError");
}
The resulting file will be My_File_Name.gpx. If the name of the exported file is not specified, then the log name will be used.
Exporting a .gm file to other formats may result in data loss, depending on the data types supported by each format.
The exported file will be in the same directory as the original log file.
Import logs
Importing logs involves loading a standard file format (such as gpx, nmea or kml) into a .gm file, enabling it to be processed further.
GemError importError = bookmarks.importLog("path/to/file", importedFileName: "My_File_Name");
if (importError != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error importing log: $importError");
}
Access metadata
Each log contains metadata accessible through the LogMetadata class.
RecorderBookmarks? bookmarks = RecorderBookmarks.create(logsDir);
if(bookmarks != null) {
LogMetadata logMetadata = bookmarks.getLogMetadata(logList.last);
}
The metadata within a LogMetadata object contains:
- startPosition / endPosition: Geographic coordinates for the log's beginning and end.
- getUserMetadata / addUserMetadata: Store and retrieve additional data using a key-value approach.
- preciseRoute: A comprehensive list of all recorded coordinates, capturing the highest level of detail possible.
- route: A list of route coordinates spaced at least 20 meters apart, with a three-second recording delay between each coordinate.
- transportMode:
RecordingTransportModeof recording. - startTimestampInMillis / endTimestampInMillis: Timestamp of the first/last sensor data.
- durationMillis: Log duration.
- isProtected: Check if a log file is protected. Protected logs will not be automatically deleted after
keepMinSecondsspecified inRecorderConfiguration. - logSize: Get the log size in bytes.
- isDataTypeAvailable: Verify if a data type is produced by the log file.
- soundMarks: A list of recorded soundmarks.
- activityRecord: The recorded activity details.
- logMetrics: Basic metrics about the recorded log.
To visualize the recorded route, a Path object can be constructed using the route coordinates from the LogMetadata. This path can then be displayed on a map. For more details, refer to the documentation on the path entity and display paths.
Custom user metadata
Users can add custom metadata to a log either during recording or after it has been completed. This is done using the addUserMetadata method, available in both the Recorder and LogMetadata classes.
The method requires a String key and the associated data as a Uint8List.
To retrieve previously added metadata, use the getUserMetadata method of the LogMetadata class.
LogMetadata logMetadata = recorderBookmarks!.getLogMetadata(logPath);
// Save image encoded in Uint8List
Uint8List imageSample = ...;
logMetadata.addUserMetadata("ImgData", imageSample);
// Save text by encoding to Uint8List
String text = 'Hello world!';
final encodedText = utf8.encode(text);
// Get image
Uint8List imageData = logMetadata.getUserMetadata("ImgData");
// Get text
Uint8List encodedTextGot = logMetadata.getUserMetadata("textData");
String textData = utf8.decode(encodedTextGot);
Record while app is in background
The recording might fail with error code GemError.general when calling stopRecording if the app is sent to the background during the recording.
Set positionActivity to true on the PositionActivity associated to the data source before instantiating the Recorder:
DataSource dataSource = DataSource.createLiveDataSource()!;
PositionSensorConfiguration sensorConfiguration = dataSource.getConfiguration(DataType.position);
sensorConfiguration.allowsBackgroundLocationUpdates = true;
dataSource.setConfiguration(type: DataType.position, config: sensorConfiguration);
RecorderConfiguration recorderConfiguration = RecorderConfiguration(
recordedTypes: [DataType.position],
logsDir: logsDir,
deviceModel: "",
minDurationSeconds: 5,
dataSource: dataSource,
);
Recorder _recorder = Recorder.create(
recorderConfiguration
);
For iOS:
Make sure you add the NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription and UIBackgroundModes keys into the Info.plist file, within the <dict> block:
<key>NSLocationAlwaysAndWhenInUseUsageDescription</key>
<string>Location is needed for map localization and navigation.</string>
and
<key>UIBackgroundModes</key>
<array>
<string>fetch</string>
<string>location</string>
</array>
For Android:
In the app's manifest file add the ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION permission.
ActivityRecord
The ActivityRecord class captures details about a recorded activity, including descriptions, sport type, effort level, and visibility settings. It ensures comprehensive metadata for recorded sessions.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
shortDescription | A brief summary of the activity. |
longDescription | A detailed explanation of the activity. |
sportType | The type of sport involved in the activity. |
effortType | The intensity of effort (e.g., easy, moderate, hard). |
bikeProfile | Bike profile details (if applicable). |
visibility | Defines who can view the activity. |
LogMetrics
The LogMetrics object provides essential statistics about a recorded log. These metrics are useful for analyzing movement, elevation, and speed data.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
distanceMeters | Total distance covered during the log, measured in meters. |
elevationGainMeters | Total elevation gained over the course of the log, measured in meters. |
avgSpeedMps | Average speed throughout the log, measured in meters per second. |
Setting the activity record
GemError errorStart = await recorder.startRecording();
if (errorStart != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error starting recording: $errorStart");
}
// Other code
recorder.setActivityRecord(ActivityRecord(
shortDescription: "Morning Run",
longDescription: "A 5km run through the park.",
sportType: SportType.run,
effortType: EffortType.moderate,
visibility: ActivityVisibility.everyone,
));
// Other code
GemError errorStop = await recorder.stopRecording();
if (errorStop != GemError.success) {
showSnackbar("Error stopping recording: $errorStop");
}
Call this method while recording, calling it after stopping will not affect the existing recordings.
Getting the activity record
final bookmarks = RecorderBookmarks.create(tracksPath);
if (bookmarks == null){
showSnackbar("Bookmarks could not be created");
return;
}
final logList = bookmarks.getLogsList();
LogMetadata metadata = bookmarks.getLogMetadata(logList.last);
ActivityRecord activityRecord = metadata.activityRecord;